![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Breast tissue locations
|
Subcutaneous tissue/superficial fascia
|
|
|
The breast is a modified ______
|
sweat gland
|
|
|
Breast composed of
-15-20 ___ |
-Lobules
|
|
|
Lobes contain ____ draining them, ending in a branched glandular pattern
|
Ducts
|
|
|
The majority of fat in breast tissue found in:
|
Axillary tail
|
|
|
Septa in breast formed by
|
Suspensory ligaments
|
|
|
Areola contains _____ glands
|
Montgomery
|
|
|
Montgomery glands are a ____ type of gland
|
Sebaceous
|
|
|
Montgomery glands secrete
|
Oily substance for lubrication during suckling
|
|
|
The nipple serves as
|
An opening for the ducts
|
|
|
All breast cancer arises from:
|
Glandular tissue (duct or gland itself)
|
|
|
Location of most cancers in the breast
|
upper outer quadrant because this is where most tissue is located
|
|
|
Upper outer quadrant drains to which lymph nodes?
|
Axillary
|
|
|
Layout (arrangement) of the breast
|
Radially arrayed
|
|
|
Breast lobules are supported by:
|
Suspensory ligaments
|
|
|
Milk is only produced with:
|
Prolactin
|
|
|
Metastasis occurs most commonly to
|
Axillary nodes
|
|
|
Peau d'orange
|
Tumor expanding against suspensory ligaments, causing dimpling of skin looking like orange
|
|
|
Most common type of breast cancer
|
Ductocarcinoma
|
|
|
Leathery skin of breast caused by
|
Cancer interfering with lymph drainage, build up of fluid occurs
|
|
|
Cancer is harder to detect in:
|
larger breasts
|
|
|
Breast tissue is _____ dependent
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
Each lobule has one _____
|
one duct
|
|
|
Breast exams should evaluate
- - |
Axillary tail
All axillary nodes |
|
|
Duct system goes away after:
|
Menopause
|
|
|
2 sources of blood to the breast
-Primary - |
-Internal thoracic off subclavian
-Lateral thoracic |
|
|
Venous drainage of breast to
|
Axillary vein
|
|
|
Innervation of breast
|
T2-T6
|
|
|
____ will be the reverse of arterial supply
|
Lymphatic
|
|
|
Lymphatic channels drain
|
Radially
|
|
|
Lymph nodes of breast superior to inferior
|
-Apical
-Central -Lateral -Medial |
|
|
Bad signs in breasts (4; ONED)
|
1. Peau d'orange
2. New nipple inversion 3. Upper limb edema 4. Dimpling |
|
|
Why are cancers associated with enlarged lymph towards the axilla
|
Primary drainage is to the axillary nodes
|
|
|
Upper limb lymph drainage
|
Lateral nodes
|
|
|
All nodes are draining toward ___-node
|
apical
|
|
|
Swollen lymph above clavicle
|
Lung cancer
|
|
|
peau d'orange found:
|
Wherever the lymph drainage is coming from
|
|
|
Enclosed in the thoracic wall is the:
|
Thoracic cavity
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity has 2 divisions
|
1. Pleural cavity
2. Mediastinum |
|
|
Sternal notch
|
Junction of manubrium and clavicle
|
|
|
Sternal notch around ____ vertebral level
|
T2
|
|
|
Sternal angle around ____ vertebral level
|
T5
|
|
|
Dome of diaphragm around ____ vertebral level
|
T9
|
|
|
___ fills the inferior thoracic aperature
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Axillary lines
- - - |
-Anterior
-Mediclavicular -Median/Midsternal |
|
|
Thoracic outlet location
|
Between 1st rib and manubrium
|
|
|
The only bony attachment of the upper extremity is:
|
Sternoclavicular joint
|
|
|
The sternal angle is important because
|
this is where the 2nd rib attaches to the sternum
|
|
|
What forms the costal arch?
|
Cartilage of ribs 8-10
|
|
|
Intercostal spaces are found:
|
Under their their named rib
|
|
|
____ of a rib articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra
|
Tubercle
|
|
|
Ribs/vertebra relationship
|
Rib named for transverse process it articulates with
|
|
|
What's located in the costal groove
|
Intercostal V. A. N.
|
|
|
Why is the intercostal n. susceptible to damage?
|
It is not as protected by the costal groove as the a. and v.
|
|
|
Posterior ribs on X ray are ______ (direction)
|
Horizontal/perpendicular to vertebrae
|
|
|
Anterior ribs are ______
|
Pointed anteriorly/ inferiorly
|
|
|
Articulation of the 7th rib to the sternum is at:
|
Body/xiphoid junction
|
|
|
Vertebral body level of sternal angle
|
T4/T5
|
|
|
Superior limits of what organ are found at the line of the sternal angle
|
Heart
|
|
|
Below sternal angle:
Above sternal angle: |
Heart
Aorta, branches, etc |
|
|
What separates the internal intercostals and innermost intercostals?
|
Intercostal v. a. n.
|
|
|
Innermost intercostals in relation to transversus thoracis
|
Innermost - lateral
Transversus - medial |
|
|
Muscles that are a common cause of faux chest pain
|
Transversus thoracis
|
|
|
Most quiet inspiration done via _____ muscle
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Levator costarum
-Longus crosses ___ spaces -Brevis |
2
1 |
|
|
inspiratory muscles
|
External, innermost intercostals
Subcostal Levator costarum Serratus posterior superior |
|
|
Expiratory muscles
|
Internal intercostal
Transversus thoracis Serratus posterior inferior |
|
|
Key to inspiration is:
|
Increasing intrathoracic volume
|
|
|
Most respiration occurs by depressing ____ to gain intrathoracic volume
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Any muscle attached to the rib can be used to:
|
Inspire
|
|
|
Usual job of intercostal muscles
|
Keep a stiff intercostal space allowing rigid thoracic wall that can expand as a unit
|
|
|
Internal thoracic a. arises from
|
Subclavian
|
|
|
Branches of internal thoracic
(5 total, 2 main) |
Pericardiophrenic
Anterior intercostal Anterior perforating branch (Musculophrenic) (Superior epigastric) |
|
|
Skin near sternum supplied by what artery
|
Anterior perforating branches
|
|
|
Intercostal spaces supplied by what a.
|
Anterior intercostal
|
|
|
A. traveling with the phrenic n. supplying the diaphragm
|
Pericardiophrenic
|
|
|
2 terminal branches of the internal thoracic a.
|
Musculophrenic
Superior epigastric |
|
|
Musculophrenic a. course & branches
|
Along costal arch, has anterior intercostal branches for ribs 7-10
|
|
|
Superior epigastric course
|
Enters the abdomen next to xiphoid process
|
|
|
Intercostal arteries arise from
(4) |
1. Intercostal a of costocervical trunk
2. Superior thoracic a. 3. Aorta 4. Internal thoracic |
|
|
Internal thoracic a. braches from:
Lateral thoracic branches from: |
Subclavian
Axilarry |
|
|
Anterior intercostal a. come from ____
|
Internal thoracic a.
|
|
|
Posterior intercostal a. come from
|
Posterior intercostal a.
|
|
|
Thoracoepigastric v. communicates between ___ & ___ veins
|
Lateral thoracic
Superficial epigastric |
|
|
Intercostal veins drain to
|
Superior intercostal v.
Azygos Hemiazygos Accessory hemiazygos |
|
|
Epigastric vein communicates with
|
Internal thoracic v.
|
|
|
Intercostal n. are VPR of
|
T1-T11
|
|
|
Subcostal n. is VPR of
|
T12
|
|
|
Parietal pleura is next to:
|
Chest wall
|
|
|
Visceral pleur in contact with
|
Viscera (lung)
|
|
|
What holds the plural cavity open
|
Vacuum
|
|
|
Best place for thoracocentesis is done where?
|
Costodiaphragmatic recess
|
|
|
Costodiaphragmatic recess found near what rib level
|
Rib 8, posteriorly
|
|
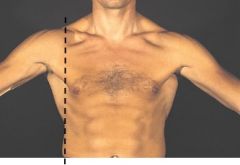
Which line is this?
|
Axillary
|
|
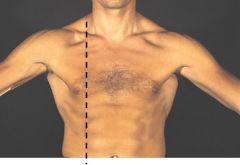
Which line is this?
|
Midclavicular
|
|
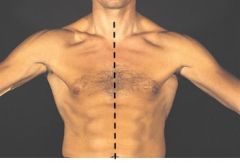
Which line is this?
|
Median/midclavicular
|

