![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trapezius |
O- external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, T1-3 I- upper edge of scapula spine, acromion and lateral 1/3 of clavicle Role- elevates the scapula for shrugging N- accessory nerve (motor), ventral rami of C3+4 (proprioceptive) |
|
|
Latissiumi Dorsi |
O- T6-12 spinous processes, iliac crest and lumbrosacral fascia I- intertubercule groove humerus |
|
|
Levator Scapulae |
O- C1+2 transverse processes, C3+4 posterior tubercles |
|
|
Rhomboid Major or Minor? Then state the role O- C7 and T1 spinous processes |
Minor |
|
|
Rhomboid Major or Minor?Then state the role O- T2-5 spinous processes and intervening ligaments |
Major Elevate and retract the scapula- so up and back shoulder |
|
|
Pec Major- normal + name the two different heads origin |
O- Clavicular Head- medial 1/2 of anterior clavicle. I- lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus N- medial and lateral pectoral |
|
|
Pec minor |
O- Ribs 3-5 |
|
|
O-First rib costochondal junction R- depresses the shoulder/clavicle |
Subclavicus |
|
|
Serratus Anterior |
O- ribs 1-8 anterolateral aspects |
|
|
Deltoid |
O- lateral 1/3 of the anterior border of clavicle, acromion lateral border, and inferior lip of spine of scapula I- deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
|
|
Name the 4 rotator cuff muscles |
Supraspinatous Infra spinatous Teres minor Subscapularis |
|
|
O- almost all anterior aspect of scapula I- lesser tubercle of the humerus |
Subscapularis |
|
|
O- supraspinous fossa |
Supraspinatous N- suprascapular |
|
|
Infraspinatus |
O- upper 2/3 of infraspinous fossa |
|
|
Teres minor |
O- lower 1/3 of infraspinous fossa |
|
|
Which is more inferior teres minor or major? |
Teres major |
|
|
Teres major |
O- lower lateral border of scapula |
|
|
What are the 3 muscles innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve? |
Biceps Brachii Brachialis Coracobrachialis |
|
|
Biceps Brachii (2 heads) |
Origin- long head: supraglenoid tubercle. short head: coracoid process. I- radial tuberosity and deep antebrachial fascia via the aponeurosis N- musculocutaneous |
|
|
Brachialis |
O- humerus anterior surface of the bottom |
|
|
Coracobrachialis |
O- coracoid process |
|
|
Triceps (3 heads) |
O- long: infraglenois tubercle lateral: posterior of shaft of the humerus. medial: medial shaft of humerus I- olecranon of the ulna |
|
|
State the roots of the following nerve, and what it supplies: - Musculcutaneous |
C5,6-7 |
|
|
State the roots of the following nerve, and what it supplies: - Axillary |
C5+6 |
|
|
State the roots of the following nerve, and what it supplies: - Median |
C (5) 6, 7, 8 and T1 |
|
|
State the roots of the following nerve,and what it supplies: - Radial |
C5, 6, 7, 8 and T1 |
|
|
State the roots of the following nerve,and what it supplies: - Ulnar |
C8 and T1
Medial arm and little finger |
|
|
What are the roots of the brachial plexus? |
C5, 6, 7, 8 and T1 |
|
|
What do the roots of the brachial plexus form and describe this arrangement |
Trunks C5+6 superior trunk C7 middle trunk C8+T1 inferior trunk |
|
|
What do the trunks of the brachial plexus form and describe their arrangement |
Divisions Superior A and P Middle A and P Inferior A and P |
|
|
What do the divisions of the brachial plexus form and describe their arrangement |
Cords Lateral- from superior and middle anterior division Posterior- from all 3 posterior divisions Medial- from inferior anterior division |
|
|
What do the divisions of the brachial plexus form and describe their arrangement |
Nerves Musculocutaneous- lateral Axillary- posterior Median- lateral and medial Radial- posterior Ulnar- medial |
|
|
Where does the long thoracic nerve come from in relation to the brachial plexus? |
C5 root Serratus Anterior |
|
|
Where does the thoracodorsal nerve come from in relation to the brachial plexus? What does it supply? |
Posterior cord Latissimus Dorsi |
|
|
Name the 5 lymph node groups of the breast which are in the arm, and draw a diagram to show where they are |
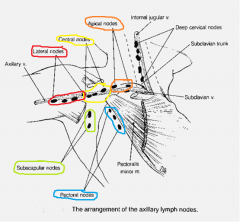
Central Apical Lateral Subscapular Pectoral |
|
|
Describe the relation of the axillary vein and artery |
The axillary vein is antero-lateral to the axillary artery, which is why when inserting a central line you have to be careful not to go to far and hit the artery. Direct medially when putting a central line in |
|
|
Describe/draw the hands nerve supply
|

On the palmar side Thumb to half of ring finger is the median nerve Half of ring finger to little finger is the ulnar nerve On the back Thumb side, not including the tops of the first 3 fingers is the radial nerve Top of the thumb- half of the ring finger is the median nerve Top of the little finger, half of the ring finger and half of the back of the hand is the ulnar nerve |
|
|
Describe (generally) the muscles that each of the following nerves supplies: -Musculocutaneous -Axillary -Median -Radial -Ulnar |
-Musculocutaneous- arm -Axillary- deltoid -Median- flexor- forearm and thenar -Radial- extensor -Ulnar- flexor- hand (-thenar) as well as the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
What causes and what are the consequences of Erbs Palsy
|
When during a difficult birth the baby has to be pulled out and it causes damage to the shoulder and consequently tears C5 root of the plexus
Means that the arm hangs down with fingers cupped and facing backwards |
|
|
What causes and what are the consequences of Klumpke's puress |
During a difficult birth the baby has to be pulled out by its arm and it causes damage to the lower root T1 of the plexus
Means that there are hand problems and basically that the hand is not useable |
|
|
Draw and label the brachial plexus
|
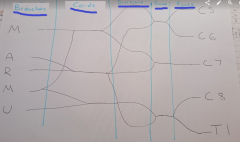
|

