![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
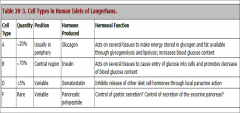
.immunocytochemical methods, four types of cells
|
.cells—A, B, D, and F
—have been recognized in the islets |
|
|
|
.Each islet of Langerhans is formed by two components:
|
.Anastomosing cords
A vascular component, insuloacinar portal system |
|
|
|
Venules leaving the islets of Langerhans supply blood to adjacent =
|
pancreatic acini
This portal system enables the local action of insular hormones on the = |
exocrine pancreas.
|
|
|
Anastomosing cords of endocrine =
4ct |
cells
A (α cells = B (β cells) = D (δ cells) = F cell = cells-each secreting a single hormone. |
A (α cells = Glucagon
B (β cells) = Insulin D (δ cells) = Somatostatin F cell = Pancreatic Polypeptide |
|
|
insuloacinar portal system =
3ct |
an afferent arteriole
rise to a capillary network lined by fenestrated endothelial cells. |
|
|
|
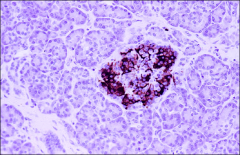
.Islet - insulin
|
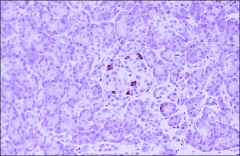
Islet - somatostatin
|
|
|
Type I diabetes
|
loss of endocrine cells in the pancreatic islets
autoimmune response |
|
|
|
Type II diabetes
resistance of target cells to the effect of insulin |
resistance of target cells to the effect of insulin
|
|
|
|
Rare
insulin-secreting tumor |
tumors of the islets
excessive secretion insulin-secreting tumor produces hyperinsulinism, with hypoglycemic symptoms. |
|
|
|
thyroid gland produces
|
1. Iodine-containing hormones
tri-iodothyronine (T3) thyroxine (tetra-iodothyronine T4). 2. The polypeptide hormone calcitonin. |
Thyroxine
|
|
|
1. Thyroxine = aka
|
T4
Chem Nm = |
tetra-iodothyronine
|
|
|
T4 aka =
|
Thyroxine
Chem Nm = |
tetra-iodothyronine
|
|
|
tri-iodothyronine = aka
|
T3
Chem Nm = |
liothyronine
|
|
|
T3 = aka
|
triiodothyronine
Chem Nm = |
liothyronine
|
|
|
1. Thyroxine (T4)
and triiodothyronine (T3), are important for = 4ct |
-growth
-cell differentiation -the control of oxygen consumption -basal metabolic rate in the body |
|
|
|
Thyroid hormones affect the metabolism of =
3ct |
proteins
lipids carbohydrates |
|
|
|
Calcitonin regulates =
|
blood calcium levels in conjunction with parathyroid hormone.
|
|
|
|
_______ regulates blood calcium levels in conjunction with parathyroid hormone.
|
Calcitonin
|
|
|
|
Calcitonin lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting the rate of =
|
decalcification of bone by =
and by stimulating = |
osteoclastic resorption
osteoblastic activity |
|
|
Thyroid gland enveloped by a _________ capsule
|
fibrous
fibrous capsule from which fine collagenous septa extend into the gland, dividing it into = |
lobules
|
|
|
The ____ convey a rich blood supply together with lymphatics and nerves.
|
septa
Each lobe of the thyroid gland consists of numerous ___ |
follicles
|
|
|
_______ is the structural and functional unit of the gland.
|
thyroid follicle
|
|
|
|
Thyroid follicle consists of a single layer of $
|
cuboidal
the follicular epithelium, bounded by a basement membrane and enclosing a central lumen containing a colloid substance rich in = |
thyroglobulin......
...an iodinated glycoprotein, yielding a periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive reaction. |
|
|
The follicular epithelium also contains about 10% of scattered =
|
parafollicular cells, also called =
|
C cells.
|
|
|
C cells. = aka
|
parafollicular cells,
|
|
|
|
C cells, derived from
|
neural crest
|
|
|
|
C cells, contain small cytoplasmic granules representing the stored hormone =
|
calcitonin
|
|
|
|
When inactive, thyroid epithelial cells are $ =
|
simple flat or cuboidal cells
|
|
|
|
when actively synthesizing or secreting thyroid hormone thyroid epithelial cells are $ =
|
are tall and columnar.
+ |
morphological appearance of thyroid follicles varies according to the region of the gland and its functional activity.
|
|
|
In the same gland, larger follicles that are full of colloid and have a cuboidal or squamous epithelium, are found alongside follicles that are lined by columnar epithelium.
|
The gland is considered hypoactive when the average composition of these follicles is =
|
squamous
|
|
|
In contrast to other endocrine organs, which have a limited storage capacity, the production of thyroid hormones depends on the follicular storage of the prohormone =
|
thyroglobulin
in the colloid characteristic feature of the thyroid follicular epithelium is its ability to concentrate = |
iodide
|
|
|
thyroid follicular epithelium is its ability to concentrate iodide from the blood and synthesize the hormones =
2ct |
thyroxine
tri-iodothyronine |
|
|
|
synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones involve two phases =
|
exocrine phase
endocrine phase Both phases are regulated by = |
TSH
|
|
|
A (α cells) =
|
Glucagon
what does it do/ctrl = |
Acts on multi-tissues to make energy stored in glycogen & fat available thru glycogenolysis & lipolysis -- increasing blood glucose content.
|
|
|
Glucagon
made by what cell = |
A (α cells)
what does it do/ctrl = |
Acts on multi-tissues to make energy stored in glycogen & fat available thru glycogenolysis & lipolysis -- increasing blood glucose content.
|
|
|
Acts on multi-tissues to make energy stored in glycogen & fat available thru glycogenolysis & lipolysis -- increasing blood glucose content.
|
Glucagon
made by what cell = |
A (α cells)
|
|
|
Insulin
made by what cell = |
B (β cells)
|
|
|
|
B (β cells) =
|
Insulin
|
|
|
|
D (δ cells) =
|
Somatostatin
what does it do/ctrl = |
Inhibits release of other islet cell hormones thru local paracrine action
|
|
|
Somatostatin
made by what cell = |
D (δ cells)
what does it do/ctrl = |
Inhibits release of other islet cell hormones thru local paracrine action
|
|
|
Inhibits release of other islet cell hormones thru local paracrine action
|
Somatostatin
made by what cell = |
D (δ cells)
|
|
|
F cell =
|
Pancreatic Polypeptide
what does it do/ctrl = |
PP function is to self-regulate pancreatic secretion activities (endocrine and exocrine);
Has effects on hepatic glycogen levels and gastrointestinal secretions. Its secretion is increased after a protein meal, fasting, exercise, acute hypoglycemia is decreased by somatostatin and intravenous glucose. Inhibits release of other islet cell hormones thru local paracrine action |
|
|
Pancreatic Polypeptide
made by what cell = |
F cell
what does it do/ctrl = |
|
|
|
PP function is to self-regulate pancreatic secretion activities (endocrine and exocrine);
Has effects on hepatic glycogen levels and gastrointestinal secretions. Its secretion is increased after a protein meal, fasting, exercise, acute hypoglycemia is decreased by somatostatin and intravenous glucose. Inhibits release of other islet cell hormones thru local paracrine action |
Pancreatic Polypeptide
made by what cell = |
F cell
|
|
|
thyroglobulin...... is =
|
...an iodinated glycoprotein,
yielding a = |
periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive reaction.
|
|
|
..an iodinated glycoprotein, =
|
thyroglobulin
|
|
|
|
C cells
are found in the = |
Thyroid in =
|
septa of the thyroid gland
|
|
|
follicular epithelium also contains about 10% of scattered =
|
C cells
|
|
|
|
follicular epithelium ie =
|
follicular cells
are found in the = |
septa of the thyroid gland
|

