![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Five functional cell types are identified in the pars distalis on the basis of =
|
immunocytochemical reactions: ***
(*** know all 5) Nm them = |
SOMATOTROPES
LACTOTROPES THYROTROPES GONADOTROPES CORTICOTROPES |
|
|
Nm the aka
& initials & 3rd slide name Hormones produced SOMATOTROPES |
GH cells)
- acidophilic - Somatotropin or growth hormone; acts on growth of long bones via somatomedins (insulin like growth factor 1) synthesized in liver; numerous secretory granules; |
Stimulated by Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH); inhibited by somatostatin.
|
|
|
LACTOTROPES
|
MAMMOTROPES (PRL cells)-
|
acidophilic
Prolactin PRH PIH )- acidophilic - Prolactin, promotes milk secretion; increases mammary gland in size during pregnancy and lactation; PRH and PIH (prolactin releasing and inhibiting hormones). |
|
|
THYROTROPES
|
TSH cells
basophilic |
- Thyrotropin
- TSH, stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis, storage and liberation; small granules, TRH - thyrotropin-releasing hormone. |
|
|
GONADOTROPES
|
(FSH and LH cell)
basophilic |
(FSH and LH cell) - basophilic, FSH
(follicle stimulating H) and LH (luteinizing hormone); FSH promotes ovarian follicle development. and estrogen secretion in women and stimulates spermatogenesis in men. LH promotes ovarian follicle maturation and progesterone secretion in women and Leydig cell stimulation and androgen secretion in men; GnRH - gonadotropin releasing H; FRH-follicle releasing H and LRH – lutein releasing H. |
|
|
CORTICOTROPES
|
(ACTH cells)
basophilic |
Corticotropin (ACTH),
CRH |
|
|
SOMATOTROPES
|
- acidophilic - Somatotropin or growth hormone; acts on growth of long bones via somatomedins (insulin like growth factor 1) synthesized in liver; numerous secretory granules; Stimulated by Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH); inhibited by somatostatin.
|
|
|
|
LACTOTROPES
|
or MAMMOTROPES (PRL cells)- acidophilic - Prolactin, promotes milk secretion; increases mammary gland in size during pregnancy and lactation; PRH and PIH (prolactin releasing and inhibiting hormones).
|
|
|
|
THYROTROPES
|
basophilic - Thyrotropin - TSH, stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis, storage and liberation; small granules, TRH - thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
|
|
|
|
GONADOTROPES
|
) - basophilic, FSH (follicle stimulating H) and LH (luteinizing hormone); FSH promotes ovarian follicle development. and estrogen secretion in women and stimulates spermatogenesis in men. LH promotes ovarian follicle maturation and progesterone secretion in women and Leydig cell stimulation and androgen secretion in men; GnRH - gonadotropin releasing H; FRH-follicle releasing H and LRH – lutein releasing H.
|
|
|
|
CORTICOTROPES
|
- basophilic - Corticotropin (ACTH), stimulates secretion of adrenal cortex hormones, large granules, CRH - corticotropin-releasing hormone.
|
|
|
|
CONTROL OF PARS DISTALIS:
Main mechanism use = |
peptide hormones =
produced in = |
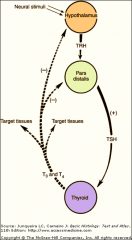
aggregates of neurosecretory cells and stored in median eminence.
|
|
|
CONTROL OF PARS DISTALIS:
. Hypothalamic releasing/inhibiting hormones the brain affect the function of = |
hypophysis --and other organs.
|
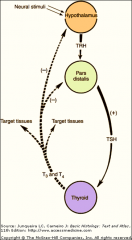
|
|
|
CONTROL OF PARS DISTALIS:
Direct effect of hormones from stimulated |
endocrine cells
on the release of peptides from the _______________ and the ___________ Feedback mechanism. |
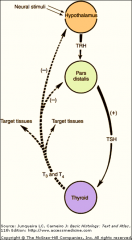
median eminence
pars distalis. |
|
|
PARS TUBERALIS
|
FSH
LH ACTH |
funnel-shaped region surrounding the infundibulum of neurohypophysis. Most of the cells secrete gonadotropins (FSH and LH) or ACTH and are arranged in cords alongside the blood vessels.
|
|
|
PARS INTERMEDIA:
|
The pars intermedia, which develops from the dorsal portion of Rathke's pouch is, in humans, a rudimentary region made up of cords and follicles of weakly basophilic cells that contain small secretory granules. α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α -MSH) is probably produced in the intermediate zone, and probably also by basophils of the pars distalis.
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
consists of three histologic components |
1. Pituicytes
2. Unmyelinated axons 3. Fenestrated capillaries |
|
|
|
1. Pituicytes
2. Unmyelinated axons 3. Fenestrated capillaries come from = |
Neurohypophysis
|
|
|
|
1. Pituicytes
|
resembling astrocytes, provide support to the axons.
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
resembling astrocytes, provide support to the axons. |
1. Pituicytes
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
2. Unmyelinated axons |
derived from neuroendocrine cells of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei, make up the infundibulum and form the hypothalamohypophysial tract.
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
derived from neuroendocrine cells of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei, make up the infundibulum and form the hypothalamohypophysial tract. |
2. Unmyelinated axons
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
2. Unmyelinated axons |
Axons, with bulging intermittent segments and terminals (called =)
secretory products (the neurophysin-hormone complex), are found in the pars nervosa (neural lobe). Both the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei contain neurons synthesizing ADH and oxytocin. |
Herring bodies
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
3. Fenestrated capillaries are derived from the |
inferior hypophysial artery.
|
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis
derived from the inferior hypophysial artery. |
Fenestrated capillaries
|
|
|
|
Pituicytes
cytoplasmic processes of pituicytes |
1. surround the axons derived from the neuroendocrine cells.
2. extend between the axon terminals and the basal lamina surrounding fenestrated capillaries 3. retract to enable the release into the blood of secretory granules stored in the axon terminals. Axons in the neurohypophysis derive from the supraoptic nuclei and the paraventricular nuclei. |
|

