![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some requirements for RBC Production?
|
Iron
Vitamin B12 Folic acid Growth factors |
|
|
Which type of deficiency causes a microcytic, hypochromatic anemia?
|
iron deficiency
|
|
|
↓ Iron
↓ ↓ ???? ↓ Microcytic, hypochromic anemia |
↓ hemoglobin
|
|
|
↓Low erythropoeitin levels
↓ ↓???? ↓ Normocytic, Normochromic Anemia |
↓ Production of RBCs
|
|
|
A deficiency in what can lead to nerve demyelinization and damage?
|
↓ Vitamin B12
|
|
|
↓Folic acid & ↓Vit. B12
↓ ↓???? ↓ MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA |
↓ DNA Synthesis
|
|
|
Reduced DNA synthesis is due to ↓ ____ and ↓ ______
|
Folic Acid
Vit. B12 |
|
|
T/F
There is an increased requirement for iron during pregnancy |
True
|
|
|
T/F
Blood loss can cause iron deficiency |
True
|
|
|
What would you use for iron deficiency anemia?
|
200 mg elemental iron/day for 3-6 months
|
|
|
Why treat iron deficiency anemia with Why 200 mg/day?
|
About 50-100 mg of elemental iron can be incorporated into Hb daily
↓ About 25% of ferrous salt can be absorbed (50mg daily) |
|
|
Oral preparations of irons are also known as _______
|
ferrous salts
|
|
|
Which ferrous salt is least irritating to the stomach?
|
Ferrous gluconate
|
|
|
Which ferrous salt gives the highest absorption of elemental iron?
|
Ferrous Fumarate
(137mg) |
|
|
What are the Parenteral Preparations of Iron?
|
Iron Dextran
***Iron Sucrose*** --> ON EXAM Sodium ferric gluconate complex in sucrose Ferumoxytol |
|
|
Oral iron ineffective
Noncompliance Anemia of chronic kidney disease** What would you use? |
Parenteral Preparations of Iron
|
|
|
Why would you get anemia with
chronic kidney disease? A. Blood loss during hemodialysis B. Reduced erythropoietin C. Reduced availability of stored iron D. Reduced vitamin B12 stores E. Reduced iron absorption F. Multiple blood draws |
A. Blood loss during hemodialysis
B. Reduced erythropoietin C. Reduced availability of stored iron E. Reduced iron absorption F. Multiple blood draws |
|
|
Why would you use parental iron
with anemia from CKD? |
Iron deficiency anemia is common with CKD, especially those on hemodialysis
Many patients do not respond adequately to oral iron |
|
|
How would you decrease Skin discoloration, local inflammation and pain associated with IM iron?
|
Use z-track injection technique
|
|
|
Oral
**GI** irritation, nausea, diarrhea or constipation ** IM** Skin discoloration, local inflammation, pain Adverse effects of? |
Iron
|
|
|
You give a patient iron and later that day they develop arthralgia,backache, myalgia, fever, chills, dizziness, headache, malaise, nausea, and vomiting. What's going on?
|
Delayed hypersensitivity rxn
|
|
|
How would you check and see if a patient will have an acute hypersensitivity rxn to IV or IM iron?
|
Give small test dose before giving the full dose
|
|
|
-Occurs in children
-Due to its corrosive effects on the GI mucosa -GI toxicity followed by multiorgan failure |
Acute Iron Toxicity
|
|
|
Treatment for acute iron toxicity?
|
Induce vomiting
Gastric lavage Deferoxamine (Desferal) Iron chelator Supportive therapy |
|
|
**Stage of Acute Iron Toxicity**
GI irritation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, lassitude, drowsiness, pallor, cyanosis, seizures, shock, coma |
Stage 1
|
|
|
**Stage of Acute Iron Toxicity**
Apparent Recovery |
Stage 2
|
|
|
**Stage of Acute Iron Toxicity**
CNS - lethargy, coma, convulsions Metabolic acidosis Hepatotoxicity - necrosis Renal failure - acute tubular necrosis Susceptibility to bleeding Cardiovascular collapse - intractable hypotension, pulmonary edema |
Stage 3
(Multiorgan Failure) |
|
|
**Stage of Acute Iron Toxicity**
Intestinal obstructions Pyloric stenosis Hepatic cirrhosis Severe gastric scarring |
Stage 4
(Delayed Effects) Intestine is scarred and liver is damaged |
|
|
-Excess iron deposits in the heart, liver, pancreas, pituitary and synovia
-Organ failure & death This describes? |
Chronic Iron Toxicity
(you really need an underlying dz to get this. It's almost impossible to get from dietary excess) |
|
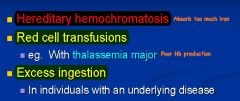
These are causes of?
|
Chronic Iron Toxicity
|
|
|
Tx for Chronic Iron Toxicity?
|
Phlebotomy
Deferoxamine (Desferal) – IM or IV Deferasirox (Exjade) – Oral |
|
|
Deferoxamine
Deferasirox These are? |
Iron Chelators
|
|
|
What is needed in the GI system to adequately absorb Vit. B12?
|
Acid in stomach
IF |
|
|
What type of things will most likely cause a B12 deficiency?
|

|
|
|
Strict Vegans and People on Proton Pump Inhibitors are most likely to develop what?
|
Vit. B12 deficiency
|
|
|
Gastric Abnormalities
Pancreatitis Small Bowel Dz These Can Lead to? |
Vit. B12 deficiency
|
|
|
If you have adequate stores of B12, but you just had a gastrectomy, how long will it be before you have symptoms of a B12 deficiency without treatment?
|
A couple of years
**Lots of it is stored in the Liver** |
|
|
What are the stores of folic acid like in the liver?
|
Pretty shitty... There isn't a lot
|
|
|
What are some things that will cause folic acid deficiency
|

|
|
|
If your intake of folic acid suddenly stops, how long will it be before you develop symptoms of a folic acid deficiency?
|
A few months
You don't really store all that much |
|
|
Both Folate and B12 are needed for _________
|
DNA Synthesis
|
|
|
A deficiency in what will affect the myelin sheaths of neurons?
|
B12
|
|
|
What may happen to
homocysteine levels in a patient with a folic acid deficiency? |
Increase
|
|
|
What type of anemia would you
see with either a vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency? |
Megalolastic
|
|
|
Why are the red blood cells very
large with a B12 deficiency? |
Adequate RNA synthesis, but inadequate DNA synthesis
|
|
|
Which type of deficiency can cause
nerve demyelination and neurological symptoms? |
B12 deficiency
|
|
|
Tx for B12 deficiency?
|
Cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobolamin
-Usually FOR LIFE Oral Folic Acid |
|
|
What may happen if you
treat a vitamin B12 deficiency with large doses of folic acid? |
you will correct the anemia but WILL NOT correct nerve damage
|
|
|
Name the Hematopoietic Growth Factors
|
Epoetin alfa
Darbepoetin Alfa Sargramostim Filgrastim Pegfilgrastim Oprelvekin **No fucking clue how to remember this shit** |
|
|
Analog of erythropoietin with longer half life
This describes? |
Darbepoetin Alfa
|
|
|
**Hematopoietic Growth Factors**
↑RBCS |
Epoetin alfa
Darbepoetin Alfa |
|
|
**Hematopoietic Growth Factors**
↑Neutrophils |
Sargramostim
Filgrastim Pegfilgrastim |
|
|
**Hematopoietic Growth Factors**
↑Platelets |
Oprelvekin
|
|
|
Tx for severe, congenital neutropenia?
|
Filgrastim
Pegfilgrastim |
|
|
Know that the hematopoietic growth factors can treat:
**Thrombocytopenia** **Anemia** **Neutropenia** Associated with AIDS, CKD and Chemotherapy |
that is all
|

