![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True or false. Most of the dietary iron intake is absorbed by the gut.
|
False. Only 5-10% of dietary intake is absorbed, most of the iron is recycled within the body.
|
|
|
What are the storage forms of iron within the cells?
|
Ferritin (in most cells and readily mobilized) and hemosiderin (higher iron concentration but slow release).
|
|
|
What are the 3 main places the body stores iron?
|
In the liver, bone marrow, and spleen. It can also be stored in other tissues.
|
|
|
What is the role of transferrin?
|
It is the transport protein for iron in the blood.
|
|
|
Where does most of the iron used by the body come from?
|
The destruction of Red Blood Cells. Destruction of old erythrocytes by tissue macrophages generates ~20-25 mg/day. Absorption is only about 1-2 mg/day.
|
|
|
Where is iron transported to for haemoglobin synthesis?
|
The bone marrow.
|
|
|
True or false. Macrophages can act as a storage site for iron.
|
True.
|
|
|
True or false. Infection, inflammation, and malignancy promote the release of iron from macrophages.
|
False. Infection, inflammation, and malignancy interfere with the release of iron from macrophages and may cause a drop in red cell production despite the presence of adequate iron reserves.
|
|
|
What is the main function of Hepcidin?
|
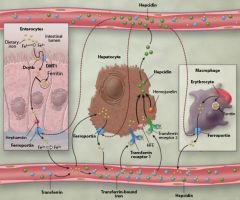
It is the main regulator of iron metabolism. It controls the flow of iron out of the intestinal cells into the blood by binding to ferroportin (transporter) and inhibiting iron release.
|
|
|
What is the main cause of iron deficiency?
|
Blood loss. In men it is usually a GI bleed, in women it is menstruation.
|
|
|
True or false. Approximately 70% iron is found in hemoglobin, 10% in myoglobin, enzymes and proteins, and 20% in storage pool.
|
True
|
|
|
Why is iron needed in hematopoiesis?
|
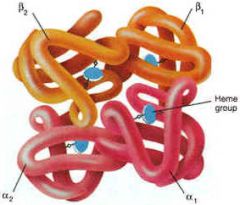
It is what makes up the heme group in haemoglobin which is required for O2 transport.
|
|
|
What organelle is responsible for heme synthesis?
|
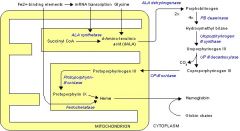
Mitochondria.
|
|
|
Where is iron absorption mostly occurring?
|
Duodenum
|
|
|
True or false. Iron is in the same state in the lumen of the gut as it is within the enterocyte.
|
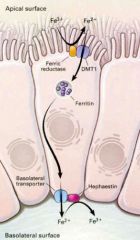
False. Iron must be converted from Fe3+ (ferric) to Fe2+ (ferrous) by ferric reductase found on the brush border of enterocytes.
|
|
|
What protein must Vitamin B12 bind to in order to be absorbed?
|
Intrinsic factor. This complex is formed within the duodenum.
|
|
|
Where is intrinsic factor produced?
|
In the parietal cells of the stomach.
|
|
|
Where is Vitamin B12 absorbed within the gut?
|
In the distal ileum.
|
|
|
How is vitamin B12 transported within the blood and to the bone marrow?
|
Via plasma-binding protein transcobalamin II (TCII). Note: another protein TCI is produced by granulocytes and macrophages and also binds vitamin B12 but does not enable it to be transferred readily to marrow so in myeloproliferative diseases with high granulocytes, B12 deficiency may present.
|
|
|
Does Vitamin B12 play a role in protein synthesis or DNA synthesis for hematopoiesis?
|
DNA synthesis
|
|
|
Where is folate absorbed?
|
In the duodenum and jejunum.
|
|
|
In what form is folate absorbed?
|
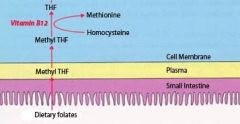
During absorption, folate is converted to methyl THF (methyltetrahydrofolate). Once inside the enterocyte they are converted to folate polyglutamates.
|
|
|
What importance does folate have in hematopoiesis?
|
It is involved in DNA synthesis.
|
|
|
What role does vitamin B12 play in the folate metabolism pathway?
|
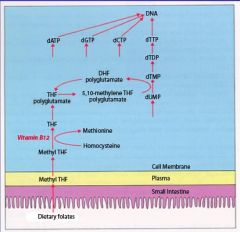
Vitamin B12 is an important cofactor in the conversion of methyl THF to THF which is an important step in the production of thymidine monophosphate
|
|
|
Do folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies only affect hematopoiesis?
|
No. Because DNA synthesis is required for all cells, all cell lines could be affected resulting in a pancytopenia.
|

