![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the process of the fusion of two gametes |
fertilization |
|
|
what is the process for animal fertilization |
gametes are haploid, then once fertilization happens, a diploid zygote is formed |
|
|
what are the steps of cleavage division |
2, 4, 8, etc cells each time it divides (zygote doesnt change size but individual gets cells get smaller and smaller as there are more of them) |
|
|
what is a solid mass of cells resulting from cleavage division |
morula |
|
|
what is the fluid filled cavity that forms within the embryo after the morula is formed |
blastocoel (at this point the embryo is called a blastula and is a hollow ball of cells) |
|
|
what is the process in which specific layers are formed |
gastrulation |
|
|
when the zygote is finally a gastrula, what are the three layers of embryonic tissue called |
germ layers (endoderm; ectoderm; mesoderm) |
|
|
what tissue layer becomes the archenteron and digestive tract |
endoderm (inner lining of gut, lining of respiratory system; organs such as pancreas and liver) |
|
|
what tissue layer becomes the outer layer of the adult and the nervous system |
ectoderm (epidermis and associated structures (hair, nails, horns); brain and nervous system) |
|
|
what tissue layer becomes the muscle, bone, and the circulatory system |
mesoderm (notochord; muscle; mesenchyme; bone and cartilage; circulatory system) |
|
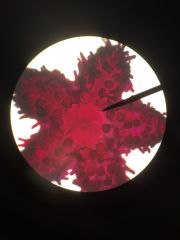
Clade? Phylum? Class? Common name? Proto or Deutero |
Clade Animals Phylum Echinodermata Class Asteroidea Name Sea star or starfish Deuterostomes (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
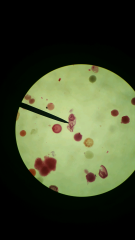
Clade Phylum Class Name object at the pointer Proto or Deutero |
Clade Animals Phylum Echinodermata Class Asteroidea Name Asterias eggs Pointer on Planktonic larvae Deuterostomes (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
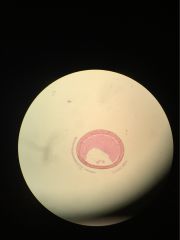
Clade Phylum subphylum class name proto or deutero |
clade animals phylum chordata subphylum vertebrata class amphibia name frog blastula deuterostome (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
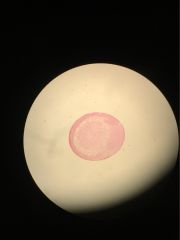
Clade Phylum subphylum class name proto or deutero |
clade animals phylum chordata subphylum vertebrata class amphibia name frog gastrula deuterostome (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
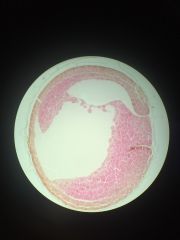
Clade Phylum subphylum class name proto or deutero |
clade animals phylum chordata subphylum vertebrata class amphibia name frog yolk plug (late gastrula) deuterostome (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
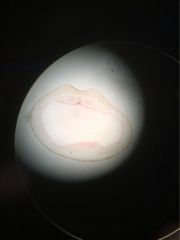
Clade Phylum subphylum class name proto or deutero |
clade animals phylum chordata subphylum vertebrata class amphibia name neurula groove deurterostome (blastopore becomes anus) |
|
|
what are the four main tissue types in animals |
epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, nervous tissue |
|
|
-cells that form a layer or sheet over external or internal surfaces -typically tightly fitted together with one surface exposed to the lumen and the other attached to the underlying tissues |
epithelial tissue |
|
|
what are the layerings of epithelial tissue what are the shapes of epithelial tissue |
layerings: simple, stratified, pseudostratified shapes: cuboidal, squamous, columnar |
|
|
-elongated, spindle-shaped cells that are contractile -three types of this tissue |
muscle tissue -skeletal( peripheral nuclie), smooth(central nuclei), cardiac(central nuclei)(pointed ends) |
|
|
-helps provide framework for the body -most have few cells and large amounts of extracellular matrix |
connective tissue |
|
|
-neurons and glial cells -info to the spinal cord and brain; integration; response via brain and spinal cord to organ/tissue -parts of a neuron? |
nervous tissue -dendrites, cell body, axon |
|
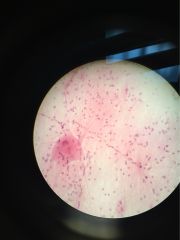
tissue type name |
Nervous tissue motor neuron |
|

tissue type name |
muscle tissue skeletal muscle |
|
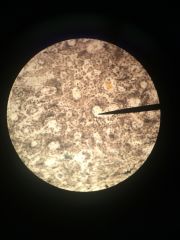
tissue type name |
connective tissue compact bone |
|
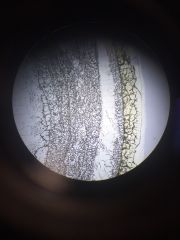
tissue type name |
connective tissue hyaline cartilage |
|
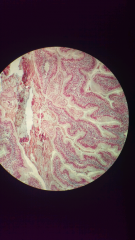
tissue type name |
epithelial tissue Rana pipiens small intestines (simple columnar epithelial) |

