![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
amino
|
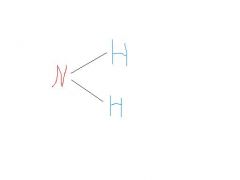
polar, water soluble, weak base can accept H
|
|
|
carbonyl
|
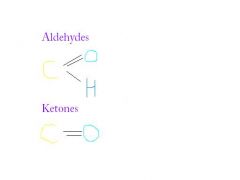
polar and water soluble, in sugars, if at end: aldehyde (formaldehyde), if internal: ketone (acetone)
|
|
|
carboxyl
|
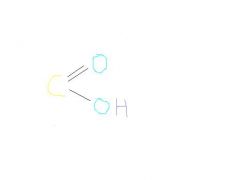
polar and water soluble,donates protons, acidic, organic acids (acidic acid)
|
|
|
Hydroxyl
|
OH
Polar, water soluble, compounds with OH are alcohols |
|
|
Phosphate
|
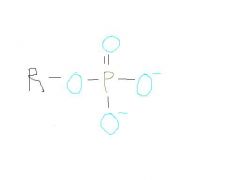
polar and water soluble, loses protons, therefore acid, can lose two protons (neg charged), very biologically important in energy storage
|
|
|
Sulfhydryl
|
SH
Help stabilize the structure of pprotein S-S links |
|
|
hydrophyilic
|
ionic or polar
|
|
|
hydrophobic
|
nonionic, nonpolar
|
|
|
why do ionic or polar solutes dissolve in water?
|
electronegitivity
|
|
|
cohesion vs. adhesion
|
co- water molecules stick to eachother
ad- water molecules stick to other molecules |
|
|
acid-base reaction
|
require a proton donor (becomes acid) and acceptor (becomes base)
|
|
|
pH=...
|
pH= -log(10)(H+)
logartithmic scale so each pH unit is 10x different. 7 is neutral, 5 acidic, 9 basic |

