![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleic Acids 1. What is the element composition? |
Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Hydrogen (H), phosphorus (P), and Oxygen (O). |
|
|
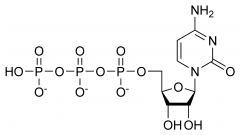
Nucleic Acids 2. Provide examples of the molecular formula and structural formula for a monomer. |
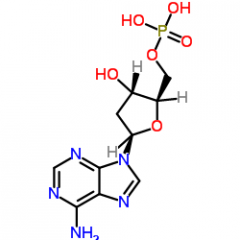
One example of a monomer of nucleic acids (nucleotide) is dAMP or known as C10H14N5O6P. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 3. What functional groups are found in the structural formula? |
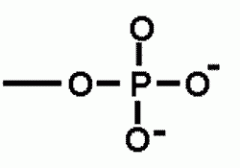
Functional groups that can be found in the structural formula of a nucleic acid are hydroxyl (-OH) and phosphate (-PO4 ). |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 4. What are the monomers and polymers called? |
Monomers are called nucleotides and polymers are called polynucleotides. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 5. Describe the parts of the monomer using pictures and words. |
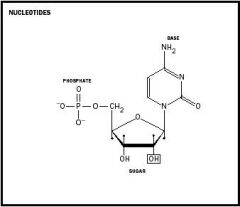
Nucleotides are composed of 3 parts. They include a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base that may be cytosine, thymine, uracil, adenine, or guanine. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 6. What are food sources and examples? |

Some great food sources of nucleic acids include salmon, sardines, nuts, oats, onions, spinach, asparagus. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 7. What is the main function in organisms? |
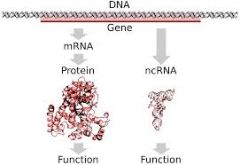
Nucleic acids carry or store genetic information to direct cell activity (DNA) and to make proteins (RNA). |
|
|
Nucleic Acids 8. Recent studies have shown a relationship between the Telomeres of our chromosomes and the rate at which we age. What is the research on these regions of DNA in our cells and what are the suggested treatments for slowing down the aging process? |
Telomeres are the parts of our chromosomes that contain sequences of DNA and gets shorter each time a cell divides until it gets too short and cells can no longer divide/die or become inactive. As a result of becoming shorter or losing base pairs, they protect the DNA strand from becoming shorter, or losing genes. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids (con. 8) |
Recent studies have indicated that as telomeres wear down more, the cells age. There is an enzyme found in the body, telomerase, that is more commonly found with younger cells, that helps telomeres from wearing down to fast and cells aging. However, telomerase appears less with each cell division, causing cells to age. |
|
|
Nucleic Acids (con. 8) |
Currently, scientists have used telomerase (which is made of protein and RNA) to help extend the amount of times cells divide, successfully, and used it to research other diseases/cancer. There currently is no suggested treatment, as there are still ongoing experiments, but use of telomerase is currently appearing more like a possible treatment. |

