![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
RNA |
Grupo nucleic acid in nucleic acid present in all living cells its principal role is to act as a messenger caring instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins |
|
|
|
ATP |
A compound consisting of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups present in all living tissue the breakage of one of these phosphates linkage( to form adenosine diphosphate, ADP) provides energy for all physiological processes such as a muscular contraction |
|
|
|
Anabolic |
Reaction build larger compounds from smaller compounds |
|
|
|
Catabolic |
Process breaks larger compounds into smaller compounds |
|
|
|
Catabolism and anabolism equals what? |
Metabolism |
|
|
|
Exergonic |
A reaction that a reaction that gives off energy |
|
|
|
Endergonic |
A reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings |
|
|
|
ADP |
H |
|
|
|
ATPase |
The enzyme that catalyzes ATP ->ADP + Pi + energy |
|
|
|
Rate-limiting enzyme |
An enzyme that catalyzes the slowest step in a series of chemical reactions |
|
|
|
Chart of the energy systems |

|

|
|
|
Phosphocreatine system |
This system will always apply energy in the beginning stages of all types of exercise. ATP is produced in the phosphocreatine system anaerobically without oxygen present |
|
|
|
Anaerobic |
Without oxygen |
|
|
|
Aerobic |
With oxygen |
|
|
|
Myokinase reaction |
Can generate ATP anaerobically for short-term which generates ATP from two ADP. This reaction results in the production of one ATP and one adenosine monophosphate ( amp) . AMP is important to the control of metabolism it's a potential stimulator of glycolysis |
|
|
|
Creatine kinase reaction |
Phosphocreatine is combined with ATP in the presence of an enzyme creatine kinase to form a new ATP |
|
|
|
Glycolysis |
The breakdown of glucose by enzymes releasing energy and pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
Fast glycolysis |
Breaks down glucose to pyruvate and eventually to lactic acid anaerobiclly with the net production of two atp's |
|
|
|
Slow glycolysis |
Is the path the pyruvate takes if sufficient oxygen is present for a aerobic metabolism. Less power is generated but pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl- coenzyme A (acA [acettylCoA])fed through the oxidative Kreb's cycle more ATP produced and fatigue is delayed |
|
|
|
Which rate-limiting enzyme controls the glycolytic system |
Phosphofructokinase pfk |
|
|
|
Where is the Krebs cycle located |
Takes place in the mitochondria which is the site of aerobic ATP production |
|
|
|
How many atp's are produced by 1 molecule of glucose |
38 atp's |
|
|
|
Lactic acid |
. Is formed as a result of fast glycolysis is immediately buffered and changed to lactate.Lottie is a useful metabolic compound that can be transported to the liver and change into glucose in a process called glucose Genesis then use by the body as fuel during exercise Lottie is a useful metabolic compound that can be transported to the liver and change into glucose in a process called glucose Genesis then use by the body as fuel during exercise |
|
|
|
Percentage of lactate waste versus use |
75 - 8% is disposed of through oxidation and the other is converted to glucose or glycogen in the process called gluco Genesis |
|
|
|
Lactate threshold |
Anaerobic exercise a higher lactic threshold be most advantageous |
|
|
|
Kreb's cycle |
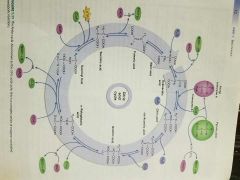
|
|
|
|
ETS system |
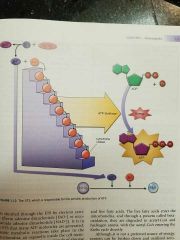
|
|
|
|
Summary of catabolic process breakdown of food |
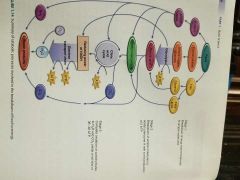
|
|
|
|
Epoc excess post-exercise oxygen consumption |
Oxygen debt the amount of oxygen required to restore your body to its normal resting level of metabolic function called homeostasis |
|
|
|
Myocardium |
The heart muscle |
|
|
|
Intercalated discs |
Fibers of The myocardium are multinucleated and interconnected and to end by intercalated discs |
|
|
|
Interventricular septum |
The solid muscular wall that separates the left and the right ventricle |
|
|
|
Systole |
The contraction phase in which the Atria or ventricles expel the blood into their Chambers |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Relaxing phase in which the chambers fill with blood |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle |
One complete revolution of systole and diastole is referred to as the cardiac cycle |
|
|
|
Diastasis |
Very little blood flow into the ventricle and is referred to as diastasis |
|
|
|
End-diastolic volume |
Blood volume in The ventricle at the end of the diastole |
|

