![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbohydrate |
Molecules with carbonyl (C=O) and several hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups, along with several to many carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds.
Form ring structures in aqueous solution by transferring a hydrogen from C-5 to the oxygen C-1. These can then form glycosidic linkages. |
|
|
Glycosidic Iinkage |
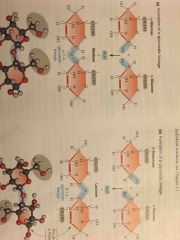
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Starch |
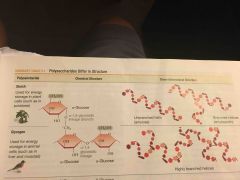
Alpha 1,4 glucose monomers amylose and amylopectin (branched due to alpha C-1 and C-6 linkages), where amylopectin branches every 30 monomers. |
|
|
Glycogen |
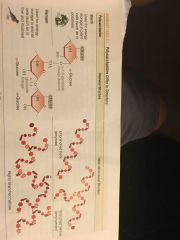
Same as starch accept Alpha 1,6 linkages every 10 glucose subunits |
|
|
Cellulose |
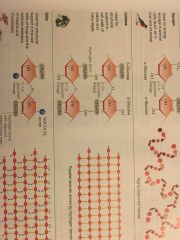
Found in plants cell wall. Polymer made of beta-glucose 1,4 linkages which form a chain. Hydrogen bonds occur between the chains, reinforcing the structure. |

