![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
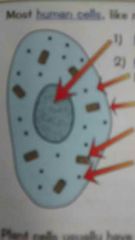
Label the cell and explain what the parts do. |

|
|
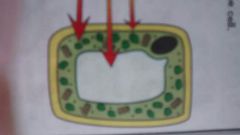
Label and explain the new parts. |

|
|
|
How are palisade leaf cells adapted? |
-adapted for photosynthesis -lots of chloroplasts packed at the top of the cell -tall shape so big surface area down the side for absorbing CO2 -thin shape so you can pack loads together at the top of the leaf -lots of them grouped together is called the palisade layer |
|
|
How are guard cells adapted? |
-special kidney shape which opens and closes stomata (pores) in a leaf -when plant has lots of water the guard cells fill with it and go plump and turgid, which makes the stomata open so gasses can be exchanged for photosynthesis -when there's little water cells loose water and become flaccid making the stomata close and stopping too much water vapour from escaping -thin outer walls and thick inner walls to make opening and closing work -sensitive to light and close at night to save water -adapted for gas exchange and controlling water loss |
|
|
How are red blood cells adapted? |
-concave shape gives a big surface area for absorbing oxygen and helps them pass smoothly through capillaries -packed with haemoglobin (pigment that absorbs oxygen) -in nucleus |
|
|
How are sperm and egg cells specialised? |
-egg cell: contains food reserves: membrane changes structure to stop any more sperm getting in -sperm: long tail and streamlined head to help it swim: lots of mitochondria to provide energy needed: enzymes in head to digest through cell membrane |
|
|
What is diffusion? |
The passive movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. |
|
|
What 3 things affect diffusion? |
Distance- shorter distance faster rate of diffusion Concentration difference/gradient- the bigger the difference the faster the rate Surface area- bigger area faster rate |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
The movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration. |
|
|
What is a partially permeable membrane? |
A membrane with very small holes in it so only small molecules like water can pass through them. |
|
|
How is osmosis used by cells? |
-tissue fluid (water with oxygen, glucose and other things dissolved in it) surrounds the cells in the body. It is squeezed out of the blood capillaries to supply the cells with what they need. -the tissue fluid and fluid inside the cell have different concentrations meaning the water will move into and out of the cell via osmosis |
|
|
What is the equation for photosynthesis? |
Carbon dioxide + water ---(sunlight+ chlorophyll)---> glucose + oxygen |
|
|
What 4 things are needed for photosynthesis to happen? |
Light Chlorophyll -absorbs energy and uses it to combine CO2 and water to make glucose Carbon dioxide Water -reaches the cells via leaf veins |
|
|
What is a limiting factor? |
Something which limits the rate of photosynthesis. |
|
|
Describe and explain a graph about how light affects the rate of photosynthesis. |

As light level increases the rate of photosynthesis does too until after a certain point where a different factor is limiting it. |
|
|
Describe and explain a graph showing how CO2 level affects photosynthesis. |

As CO2 level increases the rate of photosynthesis does too until after a certain point where a different factor is limiting it. |
|
|
Describe and explain a graph showing how temperature affects photosynthesis. |

The rate of photosynthesis increases with temperature until a certain point where the enzymes needed for photosynthesis begin to get denatured. |
|
|
What 6 things do plants use glucose for? |
Respiration- to release energy which enables them to convert the rest of the glucose into useful substances Making fruits- glucose along with fructose is turned into sucrose for storing in fruits Making cell walls- glucose is converted into cellulose for making cell walls Making proteins- glucose is combined with nitrates to make amino acids Stored in seeds- glucose turned to lipids (fats and oils) Stored as starch- glucose turned into starch and stored in roots, leaves and stems, ready for use when photosynthesis isn't happening (I.e. winter) starch is insoluble which makes it better for storing, as it doesn't bloat the storage cells by osmosis like glucose would. |
|
|
How is glucose used in respiration? |
Respiration- to release energy which enables them to convert the rest of the glucose into useful substances |
|
|
How is glucose used to make fruits? |
Making fruits- glucose along with fructose is turned into sucrose for storing in fruits. Fruits deliberately taste nice so animals will spread their seeds in their poo. |
|
|
How is glucose used to make cell walls? |
Making cell walls- glucose is converted into cellulose for making cell walls, especially in rapid growing plants. |
|
|
How is glucose used to make proteins? |
Making proteins- glucose is combined with nitrates to make amino acids, which are then made into proteins. |
|
|
How is glucose stored in seeds? |
Stored in seeds- glucose turned to lipids (fats and oils) and stored in seeds. Seeds also store starch. |
|
|
How is glucose stored as starch? |
Stored as starch- glucose turned into starch and stored in roots, leaves and stems, ready for use when photosynthesis isn't happening (i.e. winter) starch is insoluble which makes it better for storing, as it doesn't bloat the storage cells by osmosis like glucose would. |
|
|
Where do plants get nitrates, how do they use them, and what happens if they don't have them? |
1) from the soil by absorbing them through their roots 2) needed to make amino acids which are then made into protiens 3) stunted growth |
|
|
Where do plants get magnesium, how do they use it, and what happens if they don't have it? |
1) by absorbing it from the soil 2) used to make chlorophyll 3) leaves turn yellow (no chlorophyll to make leaves green) |
|
|
What are 2 other minerals needed by plants? |
Potassium and phosphates, which are used for making DNA and cell membranes, and helping the enzymes involved in photosynthesis and respiration work properly. |
|
|
What is monoculture and how can it cause deficiencies? |
- where one type of crop is grown in the same field year after year. - the plants all need the same minerals so the soil becomes deficient in minerals that that crop uses a lot of. This causes poor growth and a reduced yield. Fertiliser needs to be added to replenish the depleted minerals. |
|
|
What are 4 ways that energy is lost in each tropic level of a food chain/pyramid of biomass? |
- plants use a small percent of light energy from the sun to make food during photosynthesis. This energy is stored in the plant's cells and gradually makes its way up the food chain. - respiration supplies the power for all life processes, including movement. - most of the energy is lost as heat. - some of the material which makes up animals and plants is inedible (i.e bones) and so doesn't pass on to the next food chain level. - material and energy are also lost from the food chain in excretion. |
|
|
What are two ways you can improve the efficiency of food production? |
Reduce the number of stages in the food chain (because energy is lost on each level) Restrict the energy loss by farm animals (kept close together indoors so they're warm and can't move about) |
|
|
What are two cons for reducing the number of stages in the food chain? |
-people need a varied diet -some land is unsuitable for growing crops |
|
|
What are 5 cons and 2 pros to factory farming? |
1) seen as cruel 2) crowded conditions mean diseases spread more easily 3) to prevent diseases animals are given antibiotics, which can enter humans when they're eaten. This allows microbes that infect humans to develop immunity to those antibiotics. 4) environment where animals are kept needs to be carefully controlled often through the use of fossil fuels. 5) animals are often fed fish which is unnatural for them. 1) cheaper. 2) gives farmers a better standard of living. |
|
|
Describe the carbon cycle. |

|
|
|
What are enzymes and why are they used? |
A biological catalyst. -normally to increase the rate of a reaction you would increase the temperature, however this also increases the reactions you don't want, so your body uses enzymes. |
|
|
What is a catalyst? |
A substance which increases the speed of a reaction without being changed or used up in the reaction. |
|
|
What are enzymes made of? |
Chains of amino acids that called protiens and folded into unique shapes. |
|
|
Why do enzymes need to be particular shapes? |
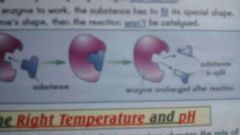
Every enzyme has a unique shape that fits onto the substance involved in a reaction. They usually only catalyse one reaction. This is because for an enzyme to work the substance has to fit it's shape to catalyse the reaction. |
|
|
Why do enzymes need a specific temperature? |
- at first a higher temperature increases the rate of reaction, however if it gets too hot, some of the bonds holding the enzyme together break which destroys its special shape. This is called being denatured. - enzymes in the human body normally work best at 37 degrees (body temperature). |
|
|
Why do enzymes need a specific pH? |
If the pH is too high or low it interferes with the bonds holding the enzyme together. Most enzymes work best at a pH of 7 (neutral). Pepsin (breaks down protiens in the stomach) works best at pH 2. |
|
|
Which 3 main chemical reactions are controlled by enzymes? |
Respiration Protein synthesis - synthesise molecules like amino acids and catalyse protein synthesis by joining together amino acids. Photosynthesis |
|
|
What is respiration? |
The process of releasing energy from glucose, which goes on in every cell. It is catalysed by enzymes. |
|
|
What is aerobic respiration and it's word equation? |
- respiration using oxygen. - most efficient way to release energy from glucose - happens in the mitochondria - glucose + oxygen ----> carbon dioxide + water + energy |
|
|
Name 4 ways the energy released from aerobic respiration is used. |
1) to build larger molecules from smaller ones (i.e. protiens from amino acids) 2) in animals to allow muscles to contract and relax (movement) 3) in mammals and birds to keep their body temperature steady (because they are warm blooded) 4) in plants to build sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids, which are then built up into protiens. |
|
|
What does the digestive enzyme amylase do, where is it made and where does it work? |

Converts starch into simple sugars. - salivary gland, pancreas and small intestine - mouth and small intestine |
|
|
What does the digestive enzyme protease do, where is it made and where does it work? |

- converts protiens into amino acids - stomach (called pepsin there), pancreas and small intestine - stomach and small intestine
|
|
|
What does the digestive enzyme lipase do, where is it made and where does it work? |

- converts fats into glycerol and fatty acids - pancreas and small intestine - small intestine |
|
|
What does bile do and where is it produced? |
- neutralises stomach acid to create optimum pH conditions for the enzymes in the small intestine and emulsifies fat to give them a much bigger surface area for the enzyme lipase to work on, thus speeding up digestion. - produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder before being released into the small intestine. |
|
|
What does stomach acid do? |
Stomach acid (hydrochloric acid) kills bacteria in food, denatures protiens (making digestion easier) and activates stomach enzymes. |
|
|
Name and explain 2 ways enzymes are used in industry. |
Biological detergents - mainly proteases and lipase - because the enzymes attack animal and plant matter they're ideal for removing stains like food or blood. To change foods - proteases pre-digest some baby foods - carbohydrases can be used to turn starch syrup into sugar syrup - glucose syrup can be turned into fructose syrup using an isomerase enzyme. Fructose is a sweetener so you can use less of it. |
|
|
What are 4 pros of using enzymes in industry? |
1) specific so only catalyse the reaction you want. 2) using lower temperatures and pressures means lower cost and saves energy. 3) enzymes can be continually reused for a long time. 4) biodegradable and therefore cause less pollution. |
|
|
What are 3 cons of using enzymes in industry? |
1) some people can develop allergies to them. 2) can be denatured and are susceptible to poisons and changes in pH - conditions have to be carefully controlled. 3) contamination of the enzyme with other substances can affect the reaction. |
|
|
What is homeostasis? |
The maintenance of a constant internal environment. |
|
|
Name 6 things that need to be controlled inside the body (and are part of homeostasis). |
1) body temperature 2) water content 3) ion content 4) blood sugar level 5) removing carbon dioxide 6) removing urea (a waste product made from excess amino acids). |
|
|
How is body temperature monitored? |
- there is a thermoregulatory centre in the brain which acts as a thermostat - it contains receptors that are sensitive to the temperature of the blood flowing through the brain - the thermoregulatory centre also receives impulses from the skin giving information about skin temperature |
|
|
What happens when you're too hot? |
Hairs lie flat. Sweat is produced by sweat glands and evaporates from the skin, which removes heat. Blood vessels supplying the skin dilate so more blood flows close to the surface of the skin. This makes it easier for heat to be transferred from the blood to the environment. |
|
|
What happens when you're too cold? |
Hairs stand up and trap an insulating layer of air. No sweat is produced. Blood vessels supplying skin capillaries constrict to close off the skins blood supply. You shiver (your muscles automatically contract) which needs respiration which releases energy as heat. |
|
|
What three main things do kidneys do? |
1) removal of urea form the blood 2) adjustment of ions in the blood 3) adjustment of water content of the blood |
|
|
What is urea? |
- proteins can't be stored by the body so any excess amino acids are converted into fats and carbohydrates which can be stored. This process occurs in the liver and urea is a waste product from the reactions. - urea is poisonous - it is released into the bloodstream by the liver and the kidneys filter it out and it is excreted from the body in urine. |
|
|
How are ions taken into and out of the body? |
- ions such as sodium are taken into the body in food and absorbed into the blood - if ion content is wrong then too much or little water is drawn into cells in osmosis - excess ions are removed by the kidneys or lost in sweat |
|
|
How is water taken into and out of the body? |
- taken in as food and drink - taken out in urine, sweat and in the air that we breathe |
|

|
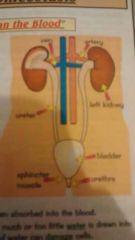
Vein Artery Ureter Left Kidney Sphincter muscle Bladder Urethra |
|
|
How are blood sugar levels controlled? |
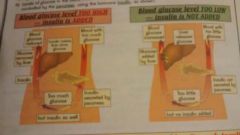
Monitored and controlled by the pancreas using the hormone insulin. - if glucose level is too high insulin is added. - if glucose level is too low insulin is not added. . - food containing carbohydrate puts glucose into the blood from the gut - normal metabolism (reactions) removes glucose from blood - exercise also removes glucose from blood |
|
|
What is type one diabetes? |
A genetic disorder where the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin. This means their blood sugar levels could rise to a level that can kill them. |
|
|
What are 2 ways that diabetes can be controlled? |
1) avoid foods rich in simple carbohydrates and exercise after eating to use up extra glucose. This is impractical 2) inject insulin into the blood at mealtimes. This makes the liver remove the glucose as soon as it enters the blood from the gut. This is very effective but they need to eat sensibly or their blood sugar levels could drop dangerously. |
|
|
How was insulin discovered? |
In the 1920s by Banting and Best, who ran experiments on dogs to eventually isolate the hormone insulin. |
|
|
Where did insulin originally come from and where does it now? |
At first it was extracted from the pancreas's of pigs and cows. Diabetics used glass syringes that had to be boiled before use. In the 1980s human insulin made by genetic engineering became available. This didn't cause any adverse reactions in humans like animal insulin sometimes did. |
|
|
What are two transplants that could be offered to diabetics? |
1) pancreas transplant - body can reject the tissue, which means you will have to take costly immunosuppressive drugs that can have serious side effects. 2) only transplant the cells which produce insulin - still at an experimental stage and there are still problems with rejection. (3) modern research into artificial pancreases and stem cell research may eventually eliminate organ rejection.) |

