![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell |
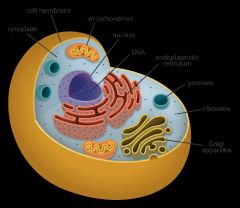
Collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings. Basic unit of all forms of life. |
|
|
Cell theory |
Idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are basic units of structures and function in living things and new cells are produced from existing cells. |
|
|
Nucleous |
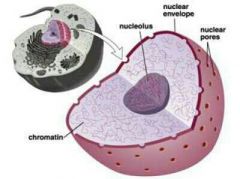
The centre of the atom which contains the cells genetic material (DNA), and controls the cells activities |
|
|
Eukaryote |
Organism whose cells contain nuclei |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Unicellular organism lacking a nucleus |
|
|
Organelle |
Specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Material inside the cell membrane, not including the nucleus |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Thread like structure within the nucleus containing the genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next |
|
|
Chromatin |
Granular material visible within the nucleus : consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Small, dense region within most nuclei in which the assembly of protein begin |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Small particle in the cell on which proteins are assembled, made of RNA and protein |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Internal membrane system in cells in which lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are modified |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
Lyosomes |
Cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates |
|
|
Mitochondrion / mitochondria |
Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convient for the cell to use. |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Internal membrane system in cells in which lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are modified. |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
Lyosomes |
Cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates. |
|
|
Cell membrane |
Thin flexible barrier around a cell. Regulates what enters and leaves a cell. |
|
|
Chloroplasts |
Organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement |
|
|
Centriole |
One of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope |
|
|
Cell wall |
Strong supporting layer around the cell membrane in plants, algae and some bacteria |
|
|
Lipid bilayer |
Double layered sheet that forms the core of nearly all cell membranes |
|
|
Concentration |
The mass of solution in a given volume of solution or mass /volume. |
|
|
Diffusion |
Process by which molecules tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. |
|
|
Equilibrium |
When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a solution |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
Isotonic |
When the concentration of two solutions is the same |
|
|
Hypertonic |
When comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutions. |
|
|
Hypotonic |
When comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutions |

