![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is an organism? |
a living thing |
|
|
|
what is an organism's niche? |
the role they have within their ecosystem |
|
|
|
what is a community? |
made up of populations of different organisms that live in the same habitat |
|
|
|
what is an ecosystem? |
all the living organisms in a particular environment together with non-living components such as soil, air and water |
|
|
|
what is a habitat? |
where a particular organism lives an ecosystem |
|
|
|
what is a population? |
a group made up of individuals of the same species in a habitat |
|
|
|
what are decomposers? |
organisms that break things down to use it up |
|
|
|
what are biotic factors? |
living factors |
|
|
|
what are abiotic factors? |
non-living factors |
|
|
|
what is interdependence? |
organisms can't survive without other organisms — predators need prey |
|
|
|
what are some examples of biotic factors? |
plants, animals, fungi, bacteria |
|
|
|
what are some examples of abiotic factors? |
water, sunlight, soil pH, air, temperature, pollution |
|
|
|
what is desalination? |
removing the salt from something |
|
|
|
what do biotic factors cause? |
competition and predation in ecosystems |
|
|
|
what is precipitation? |
water coming from the sky: — rain — snow — hail — fog |
|
|
|
what is percolation? |
water seeping into the ground |
|
|
|
what is the order of the water cycle? |
water falls from the sky (precipitation) runs off mountains some water is absorbed through plants or seeps into the ground (percolation), the rest of the water accumulates in lakes and oceans water evaporates from lakes/oceans or leaves plants by transpiration to form water vapor in the air the water vapor condenses and cools, before it falls as precipitation again |

|
|
|
what is potable water? |
drinkable water |
|
|
|
why is water filtered? |
to remove large objects |
|
|
|
why is water treated with chemicals such as chlorine? |
to destroy pathogens |
|
|
|
nitrates are used to make.. |
proteins |
|
|
|
what is distillation? |
evaporating water from salt water and condensing the water vapor |
|
|
|
what is reverse osmosis? |
pushing salt water through a membrane to remove salt |
|
|
|
respiration equation? |
glucose + oxygen > carbon dioxide + water |
|
|
|
photosynthesis equation? |
carbon dioxide + water > oxygen + glucose |
|
|
|
complete combustion equation? |
carbon containing fuel + oxygen > carbon dioxide + water (+ other gases) |
|
|
|
what is decomposition? |
the break down of organic matter into smaller molecules, and elements |
|
|
|
what do detritivores do in the carbon cycle? |
consume the carbon through digestion — carbon is released in respiration
— carbon is stored as biomass — carbon is decomposed when the detritivore dies |
|
|
|
what do decomposers do in the carbon cycle? |
they breakdown the matter using enzymes, the carbon is then taking in by diffusion — carbon is released during respiration — carbon is stored as biomass |
|
|
|
why is decay important? |
— the decay process releases substances that plants need to grow — it ensures the soil contains mineral ions that plants need i.e nitrates to make proteins — decomposers remove dead bodies – stops them piling up |
|
|
|
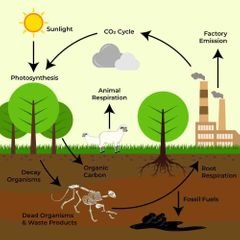
what is the order of the carbon cycle? |
carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis animals feed on plants, passing the carbon compounds along the food chain. most carbon they consume is exhaled as carbon dioxide during respiration. the animals and plants eventually die. dead organisms are eaten by decomposers and carbon in their bodies is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. in some conditions decomposition is blocked. the plant and animal material may then be available as fossil fuel in the future for combustion |
|
|
|
what do decomposers do in the nitrogen cycle? |
produce ammonium (NH4+) during the decomposition process |
|
|
|
what does nitrifying bacteria do in the nitrogen cycle? |
converts ammonium (NH4+) to nitrates (NO3-) which are used for making amino acids & proteins |
|
|
|
what does nitrogen fixing bacteria do in the nitrogen cycle? |
converts unreactive nitrogen (N2) into ammonium (NH4+) or nitrates (NO3-) |
|
|
|
what does denitrifying bacteria do in the nitrogen cycle? |
converts nitrates (NO3-) into unreactive nitrogen (N2) |
|
|
|
what do plants do in the nitrogen cycle? |
converts nitrates (NO3-) into amino acids to make proteins |
|
|
|
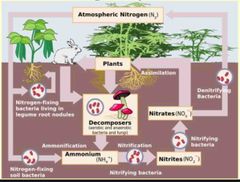
what is the order of the nitrogen cycle? |
decomposers - convert dead and waste > ammonium (NH4+) nitrifying bacteria - converts ammonium (NH4+) > nitrates (NO3-) plants - convert nitrates (NO3-) > amino acids denitrifying bacteria - converts nitrates (NO3-) > unreactive nitrogen (N2) nitrogen fixing bacteria - converts unreactive nitrogen (N2) > ammonium (NH4+) |
|
|
|
why do farmers use crop rotation? |
farmers make use of the relationship between bacteria nitrogen to keep their soil fertile planting a sequence of crops in different years such as wheat followed by potatoes is called crop rotation farmers keep the roots of their crops after harvesting and dig them back into the soil this maintains the nitrogen fixing bacteria in the soil nitrogen fixing bacteria found in the roots of some plants such as peas is an example of mutualism |
|
|
|
what is mutualism? |
two organisms have a beneficial relationship — sunflower & bee ^ sunflower can reproduce, been gets nutrition |
|
|
|
what is parasitism? |
one organism benefits, other is harmed — dog & parasite ^ dog gets harmed, parasite gets nutrition |
|
|
|
what are the four resources animals compete for? |
food water mates shelter |
|
|
|
what is interspecific competition? |
members of different species fight for competition |
|
|
|
which resource does not cause interspecific competition? |
members of different species will not compete for mates. |
|
|
|
what do plants compete for? |
light water minerals space |
|
|
|
why might a size of a population vary? |
disease migration predation intraspecific competition |
|
|
|
how can adaptations be classified? |
yearly, daily OR behavioral, structural or functional |
|
|
|
what is biodiversity? |
having a balanced range of different species in an ecosystem |
|
|
|
what are positives/negatives of fish farming? |
positives: — reduces fishing of natural “stocks” minimises biomass loss. smaller space to “fish”
negatives: — increased risk of pathogen spread — escape of non-indigenous species. — predator attraction & harm. |
|
|
|
what is eutrophication? |
fertilizer run off algal blooms plant death decomposition & bacterial respiration hypoxia / anoxia > fish death |
|
|
|
what is meant by non-indigenous? |
an organism introduced to an ecosystem it doesn’t normally live in |
|
|
|
why must organisms be adapted to their environment? |
so they are able to win the competition for resources and survive and reproduce |
|
|
|
what do plants need to survive? |
water sunlight minerals from soil space warmth |
|
|
|
what is meant by abundance? |
the quantity of something in an area |
|
|
|
how to calculate scale factor? |
total area / size of quadrant |
|
|
|
what is a belt transect used for? |
used to investigate how changing abiotic factors affect the distribution of a population |
|
|
|
what are some issues & ethics with sampling? |
more mobile organisms must be sampled in other ways no organisms should be negatively impacted by the method of sampling. |
|
|
|
how can quadrants be used for sampling? |
quadrants can be used by finding the size of the field and seeing how many quadrants can fit in then, you pick random quadrants and count how many organisms are there repeat & find average times average by number of quadrants in field |
|
|
|
estimated population size calculation |
estimated population = mean per quadrat x total number of quadrants |
|
|
|
what is the method of using a transect? |
peg out a transect take measurements at regular intervals along the transect. place quadrats count organisms measure the abiotic factors |
|
|
|
what is the method of using a quadrat? |
randomly place quadrat. count number of organisms repeat the process a number of times. calculate the mean (average) number of organisms. calculate the area of the field and divide by the quadrat size to get the total number of quadrats multiply this by the mean number of organisms to get the estimated population size |
|
|
|
what are some examples of parasitism? |
head lice living on humans — parasites benefit by sucking blood for nutrients, human is harmed
tapeworm lives inside intestines — benefits by absorbing nutrients, host is harmed
mistletoe on trees — mistletoe benefits by taking nutrients an water, tree is harmed by lack of growth
fleas live on mammals — flea benefits by taking blood for nutrients, host is harmed |
|
|
|
how are head lice adapted as parasites? |
head lice have sharp claws and mouthparts to grip onto the hair and pierce the skin |
|
|
|
how are parasites adapted as parasites? |
tapeworms have flattened bodies to increase surface area for absorption and suckers to attach to small intestine wall |
|
|
|
what are some examples of mutualism? |
flower & insect — the flower is pollinated and the insect collects nectar for food
cleaner fish and shark — the cleaner fish gets food and the shark has bacteria and parasites removed
coral and algae — the algae are protected by the coral. the algae photosynthesize and share the food with the coral
ox and oxpecker — the ox is cleaned from parasites and the oxpecker gets food |
|
|
|
what do decomposers secrete to break down organic matter? |
enzymes |
|

