![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Why do conditions in the body need to be kept steady even when the external environment changes |
Cells need the right condition in order to function properly and the right conditions for enzyme action |
|
|
|
What is homeostasis |
Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions inside your body to maintain a stable internal environment in response to changes in bothw internal and external conditions |
|
|
|
What do automatic control systems do |
Regulate your internal environment |
|
|
|
Give examples of 2 automatic control systems |
Nervous and hormonal communication systems
E.g. Systems that control * body temperature * blood glucose level *water content |
|
|
|
What 3 main things are all automatic control systems made up of |
* receptors (cells) * coordination centres (e.g. Brain / pancreas / spinal cord) * effectors |
|
|
|
What mechanism do automatic control systems use to keep internal environment stable |
Negative feedback |
|
|
|
Give an example of how automatic control systems use negative feedback |
When the level of something (e.g. Water or temperature) gets to high or low the body uses negative feedback to bring it back to normal |
|
|
|
What 3 main things are all automatic control systems made up of |
* receptors (cells) * coordination centres (e.g. Brain / pancreas / spinal cord) * effectors |
|
|
|
What mechanism do automatic control systems use to keep internal environment stable |
Negative feedback |
|
|
|
Give an example of how automatic control systems use negative feedback |
When the level of something (e.g. Water or temperature) gets to high or low the body uses negative feedback to bring it back to normal |
|
|
|
What are receptors and what do they do |
Receptors are cells that detect stimuli |
|
|
|
Give an example of a stimulus |
Low light |
|
|
|
What does the coordination centre do |
The coordination centre receives and processes information then organises a response |
|
|
|
What do effectors do |
Effectors produce a response which counteracts the change and restores the optimum level |
|
|
|
Describe the response of an automatic control system if the level of something is too low |
Receptors detect a stimuli e.g. (The level is too low)
The coordination centre receives and processes information and organises a response
An effectors produces a response that counteracts the change and restores the optimum level (e.g. The level decreases) |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
Describe the response of an automatic control system if the level of something is too low |
Receptors detect a stimuli e.g. (The level is too low)
The coordination centre receives and processes information and organises a response
An effectors produces a response that counteracts the change and restores the optimum level (e.g. The level decreases) |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
How long will effectors keep producing responses |
For as long as they are stimulated by the coordination centre
This may cause the problem of making the level change too much. The receptor will detect if level is too different and the negative feedback will start again |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
How long will effectors keep producing responses |
For as long as they are stimulated by the coordination centre
This may cause the problem of making the level change too much. The receptor will detect if level is too different and the negative feedback will start again |
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do |
The nervous system detects and reacts to stimuli |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
How long will effectors keep producing responses |
For as long as they are stimulated by the coordination centre
This may cause the problem of making the level change too much. The receptor will detect if level is too different and the negative feedback will start again |
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do |
The nervous system detects and reacts to stimuli |
|
|
|
Why do organisms need to respond to stimuli |
To survive |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do |
The nervous system detects and reacts to stimuli |
|
|
|
Why do organisms need to respond to stimuli |
To survive |
|
|
|
As multicellular organisms e why did they develop nervous and hormonal communication systems |
They need to respond to stimuli to survive the cells of multi cellular organism need to communicate first |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do |
The nervous system detects and reacts to stimuli |
|
|
|
Why do organisms need to respond to stimuli |
To survive |
|
|
|
As multicellular organisms e why did they develop nervous and hormonal communication systems |
They need to respond to stimuli to survive the cells of multi cellular organism need to communicate first |
|
|
|
What does the central nervous system consist of in vertebrates |
* The brain *The spinal cord |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
How long will effectors keep producing responses |
For as long as they are stimulated by the coordination centre
This may cause the problem of making the level change too much. The receptor will detect if level is too different and the negative feedback will start again |
|
|
|
As multicellular organisms e why did they develop nervous and hormonal communication systems |
They need to respond to stimuli to survive the cells of multi cellular organism need to communicate first |
|
|
|
What does the central nervous system consist of in vertebrates |
* The brain *The spinal cord |
|
|
|
What are vertebrates |
Animals with backbones |
|
|
|
What is a stimulus |
A change in the environment |
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do |
The nervous system detects and reacts to stimuli |
|
|
|
Why do organisms need to respond to stimuli |
To survive |
|
|
|
As multicellular organisms e why did they develop nervous and hormonal communication systems |
They need to respond to stimuli to survive the cells of multi cellular organism need to communicate first |
|
|
|
What does the central nervous system consist of in vertebrates |
* The brain *The spinal cord |
|
|
|
What are vertebrates |
Animals with backbones |
|
|
|
What does the central nervous system consist of in mammals |
The central nervous system is connected to the body by *motor neurones *sensory neurones |
|
|
|
What are motor neurones |
The neurones that carry electrical impulses from the CNS to effectors |
|
|
|
What are sensory neurones |
What are sensory neurones |
The neurones that carry information as electrical impulses from the receptors to the CNS |
|
|
What are motor neurones |
The neurones that carry electrical impulses from the CNS to effectors |
|
|
|
What are sensory neurones |
What are sensory neurones |
The neurones that carry information as electrical impulses from the receptors to the CNS |
|
|
What are effectors |
All muscles and glands that respond to nervous impulses |
|
|
|
What are effectors |
All muscles and glands that respond to nervous impulses |
|
|
|
What do effectors respond to |
Nervous impulses and they bring about a change |
|
|
|
Give an example of two types of receptors |
*taste receptors on tongue * sound receptors in the ears |
|
|
|
Give an example of receptors used in a large complex organ |
The retina of the eye is covered in light receptor cells |
|
|
|
Give an example of two effectors |
Muscles Glands |
|
|
|
What do effector muscle do in response to a nervous impulse |
Contract |
|
|
|
What do effector glands do in response to a nervous impulse |
Secrete hormones |
|
|
|
Describe the response of the automatic control centre when a bird sees a cat coming towards it |
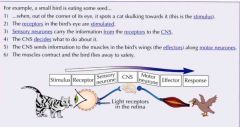
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What are reflexes |
Reflexes are rapid automatic responses to stimuli that don't involve the conscious part of the brain |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What are reflexes |
Reflexes are rapid automatic responses to stimuli that don't involve the conscious part of the brain |
|
|
|
Why are reflexes beneficial |
They reduce risk of injury |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What are reflexes |
Reflexes are rapid automatic responses to stimuli that don't involve the conscious part of the brain |
|
|
|
Why are reflexes beneficial |
They reduce risk of injury |
|
|
|
Explain what happens when a bright light is shone at eyes |
Pupils automatically get smaller so less light gets into the eye so it doesn't get damaged |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What are reflexes |
Reflexes are rapid automatic responses to stimuli that don't involve the conscious part of the brain |
|
|
|
Why are reflexes beneficial |
They reduce risk of injury |
|
|
|
Explain what happens when a bright light is shone at eyes |
Pupils automatically get smaller so less light gets into the eye so it doesn't get damaged |
|
|
|
What happens when the body gets a shock |
The body releases the hormone adrenaline automatically |
|
|
|
What is a synapse |
The connection between two neurones |
|
|
|
Explain what happens at a synapse |
The nerve signal is transferred by chemicals that diffuse across the gap These chemicals then set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone |
|
|
|
What are reflexes |
Reflexes are rapid automatic responses to stimuli that don't involve the conscious part of the brain |
|
|
|
Why are reflexes beneficial |
They reduce risk of injury |
|
|
|
Explain what happens when a bright light is shone at eyes |
Pupils automatically get smaller so less light gets into the eye so it doesn't get damaged |
|
|
|
What happens when the body gets a shock |
The body releases the hormone adrenaline automatically |
|
|
|
What is a reflex arc |
A reflex arc is the passage of information in a reflex (from receptor to effector ) |
|
|
|
Describe how a reflex arc goes through the central nervous system |
* the neurones in the reflex arc go through the spinal cord or an unconscious part of the brain
* when a stimulus is detected by receptors impulses are sent along a sensory neurone to the CNS
* when impulses reach a synapse between the sensory neurone and a relay neurone they trigger chemicals to be released these chemicals cause impulses to be sent along the relay neurone
*when impulses reach a synapse between a relay neurone and a motor neurone again chemicals are released and cause impulses to be sent along the motor neurone
* the impulses travel along the motor neurone to an effector
* muscle contracts / gland secretes hormone |
|
|
|
What do relay neurones do |
Relay neurones connect sensory neurones to motor neurones |
|

