![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a eukaryotic cell? |
describes a cell that contains a nucleus |
|
|
what is a small vacuole |
contains material being taken in or removed by cell |
|
|
what is a mitochondria |
power station of the cell - releases energy in a useable form via respiration |
|
|
what is the cytoplasm |
solution of numerous chemicals dissolved in water |
|
|
what is a large vacuole |
contains water with a few dissolved chemicals (sap) provides support together with the cell wall when full |
|
|
what is a cell walk |
provides essential support - made of strong cellulose fibres |
|
|
what’s a ribosome |
the site of protein synthesis |
|
|
what’s the cell membrane |
selectively permeable barrier to chemicals |
|
|
what is a nucleus |
controls the cells functions - contains the genetic material dna in chromosomes |
|
|
what is chloroplast |
contains green pigment (chlorophyll) - site of photosynthesis |
|
|
what are prokaryotes |
bacteria, they are smaller than eukaryotes |
|
|
what do prokaryotes have? |
a tail, known as a flagellum, to help it move |
|
|
what do prokaryotes have instead of a ‘true’ nucleus |
a circular stand of dna, they may also have one or more small rings of dna called plasmids |
|
|
what 3 things do prokaryotes have |
cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall |
|
|
what do prokaryotes have instead of a ‘true’ nucleus |
a circular stand of dna, they may also have one or more small rings of dna called plasmids |
|
|
describe what a prokaryotic cell looks like |
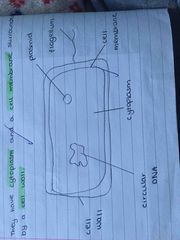
Back (Definition) |
|
|
how do you work out magnification? |
image size / actual size |
|
|
how do you work out image size |
actual size x magnification |
|
|
how do you work out actual size |
image size / magnification |
|
|
describe the units of measurements and how to convert them |
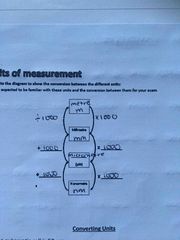
Back (Definition) |
|
|
why do we use iodine in an experiment with cells |
so you can stain the specimen to see the cells easier |
|
|
why do you use a thin slice of specimen |
so enough light could pass through so you can study the cells |
|
|
why do we use forceps to lower the cover slip slowly |
to avoid air bubbles |
|
|
give two reasons why cells need to divide |
• to produce more cells for growth of the organism • to produce new cells for the repair of damaged tissue |
|
|
describe the cell cycle |
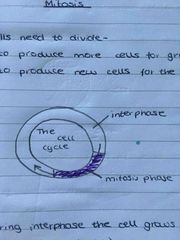
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what happens during interphase |
the cell grows larger and it carries out its function |
|
|
what happens just before mitosis |
the number of organelles increase and each chromosome is copied because the cell is about to divide and become 2 cells which are genetically identical |
|
|
what happens just before mitosis |
the dna is replicated |
|
|
what’s the second step that happens just before mitosis |
the long dna strands coil up into chromosomes |
|
|
what’s the first step of mitosis |
the nuclear membrane breaks down and the chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell |
|
|
what’s the second step of mitosis |
cell fibres attach to the chromosomes and pull them apart |
|
|
what’s the third step of mitosis |
membranes form around each set it chromosomes making the nuclei of the new cells |
|
|
what’s the fourth step of mitosis |
the cytoplasm then divides and makes two identical cells |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of sperm cells |
• in semen • microscopic tadpole • make babies |
|
|
what does a sperm cell look like |
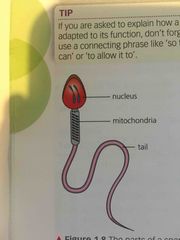
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a nerve cell |
• lots of ending • transmit electric impulses • make body move |
|
|
what does a nerve cell look like |
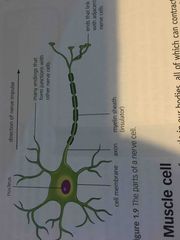
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a muscle cell |
• contract quickly • strands of protein • make us move • make energy |
|
|
what does a muscle cell look like |
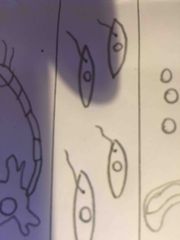
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a roof hair cell |
• plant roots • absorbs water and minerals • make plants grow healthy |
|
|
what does a root hair cell look like |
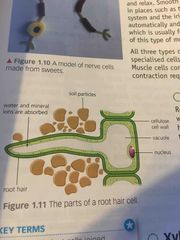
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a xylem cell |
• inside plants • transportation stream • transport mineral ions from the roots |
|
|
what does a xylem cell look like |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a phloem cell |
• inside plants • allows sap to flow • transports food |
|
|
what does a phloem cell look like |
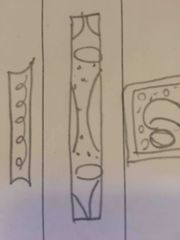
Back (Definition) |
|
|
what are the key features and functions of a palisade cell |
• at the top of any leaf • has chlorophyll and chloroplasts • makes glucose, oxygen and does photosynthesis |
|
|
what does a palisade cell look like |
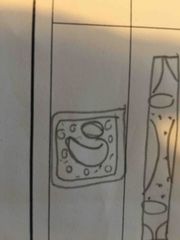
|
|
|
what is a stem cell |
a cell that has not yet become a specialised cell |
|
|
where do stem cells exist |
adults and embryos |
|
|
what can embryonic stem cells do |
differentiate into any kind of cell |
|
|
how would we describe embryonic stem cells |
totipoten |

