![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 Major Functions of Lipids |
1. Phospholipids serve as a structural component of membranes; 2. Triacylglycerols store metabolic energy and provide thermal insulation and padding; 3. Steroids regulate metabolic activities and; 4. Some fatty acids (eicosanoids) seven serves as local hormones |
|
|
Lipoprotein Density |
HDL - High Density - more protein than lipid within lipoprotein molecule. LDL - Low Density - more lipid than protein within lipoprotein molecule. |
|
|
Glucose vs. Fructose |
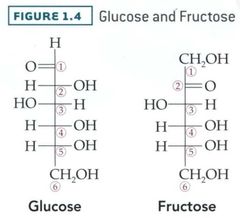
Glucose is more commonly metabolized than Fructose. (80% of the time) Glucose has 1 primary hydroxyl group and 1 primary sp2 Oxygen. Fructose has two primary Hydroxyl groups. |
|
|
Carbohydrates vs. Lipids |
More hydroxyl groups in Carbohydrates than Lipids. Think of carbohydrates as a compound with molecule with a fixed 1:1 ratio between water and carbon. More energy stored in Lipids because higher concentration of C-H bonds. |
|
|
Starch vs. Cellulose |
Starch = alpha linked molecule
Cellulose = beta linked molecule |
|
|
Alpha linkage vs. Beta linkage |
Beta stability > alpha stability Only bacteria can breakdown beta linkages. Only animals can eat alpha linkages. |
|
|
Division of Metabolism |
Catabolism - the breakdown of large molecule into smaller molecules (think catastrophic). Anabolism - the joining of smaller molecules, forming larger molecule (think Avengers). |
|
|
How do you break Peptide bonds? |

Hydrolysis - a water molecule is used to break the peptide bond, forming two separate compounds (amino acids). |

