![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two ways diffused substances are transported across cells are?
|
OSMOSIS and DIFFUSION
|
|
|
Definition of diffusion
|
The movement of fluid across a concentration gradient
|
|
|
Definition of Osmosis?
|
The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane
|
|
|
When does Active Transport take place?
|
When substances need to be transported against a concentration gradient or semi permeable membrane
|
|
|
Because they are being transported against a gradient, it requires?
|
Energy to carry the molecule across
|
|
|
Where does the energy required for active transportation come from?
|
Cellular respiration The rate of active transport and the rate of respiration in cells is closely linked. The process of Respiration releases energy so the more respiration that is happening means the more active transport takes place.
|
|
|
What provide a lot of energy for Respiration?
|
Mitochondria
|
|
|
Example of Active transport in our bodies?
|
Glucose is moved out of your gut and kidney into your blood even though it is against a gradient.
|
|
|
When you breathe in...
|
your ribs move up and out
diaphragm flattens air is pulled into the lungs (so opposite happens for breathing out) |
|
|
How have the Lungs adapted to make gas exchange more efficient?
|
1. Alveoli- lungs are made up of clusters of alveoli which are tiny air sacs with large surface areas and are kept moist
2. Rich blood supply which maintain a concentration gradient in both directions. 3. Oxygen is constantly being removed from the lungs and carbon dioxide is constantly entering the lungs which means gas exchange can happen at the highest concentration gradients to make it rapid and effective |
|
|
Alveoli adaptions to make gas exchange more effective...
|
1. spherical shape gives large surface area
2.moist surface makes diffusion easy as gases can dissolve 3.thin walls to make diffusion easy 4.good blood supply |
|
|
What do the foods we eat break down into by the gut?
|
form simple sugars; Amino acids, glucose, fatty acids and glycerol
|
|
|
How do the molecules from the food enter the bloodstream?
|
A combination of active transport and diffusion
|
|
|
After being broken down the food molecules are small enough to?...
|
pass through the walls of the small intestines and into the blood vessels.
They can move this way because there is a high concentration of food molecules in the gut and a low concentration in the blood so to move along the concentration gradient, diffusion occurs |
|
|
The lining of the small intestine is folded into?...
|
Thousands of Villi. These increase the uptake of digested food by diffusion.
|
|
|
Why is diffusion very rapid and efficient in the gut?
|
It has a rich blood supply so digested food molecules are carried away as soon as it diffuses from one side to the other. So a steep concentration gradient is constantly maintained.
|
|
|
How is carbon dioxide obtained in plants?
|
Through diffusion in the leaves. The flattened shape of the leaves increases the surface area for diffusion to occur. The leaves are flat also to keep the distance between the air and the photosynthesising cells as short as possible
|
|
|
What does the stomata do in the plant?
|
Open and close at specific times to let the carbon dioxide
|
|
|
Adaptions of plants
|
1.Stomata to let carbon dioxide in and out
2.Waxy cuticle that is waterproof and gas proof 3.Roots adapted for uptake of water and mineral ions. The roots are thin and have a large surface area 4. Root hair cells have also been adapted to increase efficiency of water uptake. The cell membranes of root hair cells have Microvilli which increase surface area even more for diffusion and osmosis 5. Plants wilt when water is being lost faster than it is gained so hang down to prevent more water loss by minimising the surface area |
|
|
What is Transpiration?
|
The loss of water vapour through the surface of the leaves.
|
|
|
What is a Transpiration stream?
|
As water is lost through the opening in the stomata more water is pulled up through the xylem to take its place. The constant movement of water around the plant is a Transpiration Stream
|
|
|
What three components is the blood circulation system made up of?
|
The heart, Blood vessels, The blood
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the double circulation system in our bodies?
|
ONE transports blood from the heart to the lungs and back again,
the OTHER takes blood around the rest of the body |
|
|
Name the three main blood vessels
|
1. The Arteries. They carry blood away from the heart and to the rest of the organs in the body. This is usually oxygenated blood
2. The Veins. Carry blood towards the heart, usually low in oxygen 3. The Capillaries. Usually found in junctions between the veins and arteries. These are found in huge networks. The walls are a single cell thin so substances that need to get out of the blood and into our body cells can diffuse out easily. |
|
|
Properties of Arteries
|
1. Thick walls
2.Small lumen 3.Thick layer of muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
Properties of Capillaries
|
1. Thin walls a single cell thick
2.Tiny vessel with narrow lumen |
|
|
Properties of Veins
|
1.Thin walls
2. Large lumen |
|
|
The blood is a liquid tissue consisting of?
|
Plasmas, Red blood cells, White blood cells and Platelets
|
|
|
Stages of the Heart
|
1. First the blood travels through the vena cava, then the Deoxygenated blood enters the Right Atrium (the blood travels through the pulmonary vein, then the oxygenated blood enters the Left Atrium)
2.Right atrium contracts to pump blood through the valve into the right ventricle (so the left atrium contracts to pump blood through the valve into the left ventricle) 3.The right ventricle contracts, the valve opens and the deoxygenated blood travels through the pulmonary artery lungs ( the left ventricle contracts, the valve opens and oxygenated blood travels around the body again) |
|
|
What does the liquid part of out blood do?
|
The Plasma ( liquid part of our blood ) transports red and white blood cells, and platelets
|
|
|
What is Blood plasma?
|
yellow liquid which transports all blood cells and other substances around the body
|
|
|
What is Urea?
|
Waste product formed in the liver that is carried in the plasma to the kidneys
|
|
|
In the kidney, Urea removed and ...
|
transformed into urine
|
|
|
During exercise...
|
Heart rate increases, rate and depth of each breath increases, arteries supplying muscles dilate, blood flow to muscle increased and rate of removal of carbon dioxide increases
|
|
|
Respiration happens in...
|
the Mitochondria
|
|
|
Anaerobic respiration causes...
|
Poisonous lactic acid to build up in the muscles and cause painful cramps. When exercise stopsthere is an oxygen debt – you must keep breathing in order to get oxygen to the muscles andoxidise the lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water.
|
|
|
The three waste products the body must excrete are?
|
Urea
Carbon dioxide Sweat |
|
|
What is homeostatis?
|
controlling conditions inside the body
|
|
|
What can glycogen be converted into and where is it stored?
|
stored in the muscles and can be converted into glucose.
|
|
|
Why is anaerobic respiration not as efficient as aerobic respiration?
|
Because the glucose molecules are not fully broken down so less energy is released.
|
|
|
Why are the kidneys vital?
|
1.They filter out Urea and remove it in urine because it is poisonous
2.They remove excess water and release it from the body in urine 3.They filter the blood then reabsorb everything the body needs (sugar, amino acids, mineral salts and urea) |
|
|
What is selective Re absorption?
|
re absorbing certain amounts of water. mineral ions etc depending of how much is needed by the body
|
|
|
What is a dialysis machine?
|
It performs the function of a normal healthy kidney
There are two ways we can deal with this problem, the first being dialysis. The machineused in dialysis is called the dialysis machine, and relies on a process called dialysis to cleanthe blood.A person’s blood leaves their body and flows into the machine, through partially permeablemembranes. After the membranes comes the dialysis fluid, which contains a certainconcentration of substances to ensure diffusion of unwanted substances from the bloodinto the fluid. However, glucose remains in the blood. A kidney dialysis machine provides an artificial kidney for the sufferers of kidney failure. Thepatient must use a dialysis machine for 3-4 hours three times a week. |
|
|
How does Dialysis make sure the patient doesnt lose vital substances like glucose?
|
this is done by having the dialysis fluid at the right concentration so there is no net movement of glucose and mineral ions from the blood plasma out into the fluid.
There is no Urea in the dialysis fluid so there is a very strong concentration gradient for the urea. |
|
|
Disadvantages of Dialysis
|
Repeated use at 8 hours per use
Must follow a strict healthy diet after some years the levels can be hard to maintain |
|
|
Disadvantages of Kidney Transplants
|
Immune system may reject the kidney as it may be seen as foreign which means the body will destroy it.
To avoid this it means you have to take immunosuppressant drugs for the rest of your life This also means your more prone to disease |
|
|
How to avoid Rejection in Kidney Transplants
|
Take Immunosuppressant drugs for the rest of your life
choose a donor similar to the recipient in terms of body tissue |
|
|
Comparisons of Kidney transplants and Dialysis
|
Dialysis advantages: can be carried out at home, no hospital visits required, longer living livesDialysis disadvantages: takes up a lot of time, risk of infection side affects; nausea, cramps etc Transplant adv: fewer diet and fluid restrictions more energy better quality of life Transplants Disadv: surgery risks risk of rejection take drugs for life Dialysis is more readily available whereas kidney transplants have a long waiting list because you have to find a suitable donor |
|
|
Where is the Urea produced?
|
Produced in the liver, and is made up of waste product from the breaking down of amino acids)
|
|
|
Stages of Blood Filtration in the Kidneys
|
1. Ultrafiltration , Blood is brought to the kidneys to be filtered, it passes through tiny tubules and water, salt glucose and urea and squeezed out
2. Selective re absorption kidney sends all of glucose and as much of water and salt the body needs into the blood. sugar and dissolved ions may be actively absorbed against a concentration gradient 3. Waste Water, salt and urea are left – this is urine. Urine is sent to the through the ureterto the bladder where it is stored before being excreted |
|
|
What may Kidney Failure be caused by?
|
infections, toxic substances or genetic reasons. Patient can soon die if urea and salt not gotten rid of from their body.
|
|
|
How can yeast cells be used to make bread?
|
Yeast is used to produce bread and alcoholic drinks. In bread production, the yeast growsand respires – producing carbon dioxide which causes the bread to rise. The gas bubblesexpand when baked due to the high temperatures, giving the bread its light, wafery texture.All yeast cells are killed by the heat in the cooking process.
|
|
|
What is mycoprotein?
|
Mycoprotein is a low-fat, protein-rich food suitable for vegetarians. Itis made from the fungus Fusarium.The fungus grows and reproduces rapidly on a cheap energy supply(sugar syrup) in a fermenter.It requires aerobic conditions to grow. Its mass doubles every 5 hoursor so.The biomass is harvested, purified and dried to leave mycoprotein –colours and flavours are added to enhance it.
|
|
|
How can you make yoghurt?
|
You can make yoghurt by:
1 adding a culture of the right type of bacteria to warm milk 2 keeping the mixture warm so the bacteria grow, reproduce and ferment 3 as the bacteria break down the lactose, lactic acid is produces (this gives yoghurt thesharp, tangy taste) – this process is lactic fermentation 4 the lactic acid causes the milk to clot and solidify to form a yoghurt 5 further bacterial action gives the yoghurt its creamy texture |
|
|
How is biogas formed?
|
Biogas, a flammable mixture of gases (mostly methane), forms when bacteria break down thewaste material of dead animals or plants in anaerobic conditions.
|
|
|
what temperature does a biogas generator work best at? and what reaction is it?
|
30 degrees
exothermic |
|
|
What do industrial fermenters have?
|
Industrial fermentersusually have:
1 An oxygen supply so the microorganisms can respire 2 A stirrer to keep the microbes in suspension – this maintains a constant temperatureand makes sure that the oxygen and food are evenly spread out throughout theculture 3 A water-cooled jacket which removes excess heat produced from the respiration 4 Measuring devices for pH and temperature so changes can be made if necessary (i.e.when a dependent change is caused) |
|
|
what two main types of biogas generators are there? and define them
|
Batch process:make biogas in small batchesThey are manually loaded up with waste,which is left to break down, and the by productsare cleared away at the end ofeach season
cheaper than continuous not as efficient Continuous process: These make biogas constantlyWaste is continuously fed in, and biogasis produced at a steady rateThese are more suited to large-scaleprojects more expensive more efficient |
|
|
What conditions does a large fermenter for mycoprotein require?
|
aerobic respiration so micro organisms can respire
|
|
|
What is mycoprotein?
|
produced using fungus Fusarium
Its a High protein, Low fat meat substitute ideal for dieters and vegetarians |
|
|
why is; Animal waste, dead animal and plant material and garden waste
a good energy source for biogas generators? |
All contain carbohydrates which is a good energy source
|
|
|
what are the blood glucose levels monitored by?
|
the pancreas
|
|
|
how does the pancreas control the blood glucose levels?
|
produces hormone insulin which allows glucose to move from blood to our cells
when blood sugar levels fall, the pancreas secretes second hormone, GLYCOGEN which is stored in the muscles. |
|
|
what is Type 1 diabetes?
|
when persons blood glucose concentration may rise to a high level because pancreas doesnt produce enough insulin
so type 1 controlled by controlling diet and injecting insulin |
|
|
ethanol can be created from?
|
fermenting sugar solution with yeast
Alcohol is fractionally distilled |
|
|
biofuel have environmental and economic benefits as?
|
doesnt release sulfur oxides which cause acid rain
carbon neutral |
|
|
Properties of fusarium used to make mycoprotein
|
fungus
grown in glucose syrup is grown in anaerobic conditions with supply of nitrogen and ammonia fungi grow rapidly in warm conditions so production rates quite efficient but does need land for where Maize is grown for glucose syrup which is where fusarium is made from |
|
|
glucose syrup is made from?
|
breaking down maize starch with the correct enzyme containing microorganisms
|
|
|
before the mycoprotein forming fungi is introduced to the fermenter, you must ...
|
heat and sterilise all ingredients including fermenter to kill all micro organisms and the air filtered to remove airborne mircoorganisms
|
|
|
What is a semi permeable membrane?
|
Some membranes in plant and animal cells allow certain particles to pass through them but notothers.
|
|
|
In active transport, Particles move from an area of...
|
low concentration to an area of high concentration
|
|
|
Plants absorb water from the soil by...
|
Osmosis through root hair cells
|
|
|
The movement of water from a high concentration to a low concentration through a semi permeable membrane is...
|
Osmosis
|
|
|
What does Blood plasma transport?
|
Carbon dioxide from the organs to lungs
soluble products of digestion from the small intestine to other organs urea from the liver to the kidneys hormones |
|
|
The diagram of a heart
|
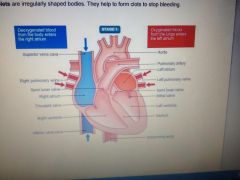
|
|
|
How do Blood vessels control our body temperature?
|
When we are too hot they dilate
When we are too cold they constrict |
|
|
If we are too hot...
|
If the body is too hot, glands in the skin secrete sweat onto the surface to increase heat loss by evaporation. This cools the body. Sweat secretion slows when the body temperature returns to normal.
|
|
|
If we are too cold...
|
Hairs on the skin trap more warmth if they are standing up, and less if they are lying flat. Tiny muscles in the skin can quickly pull the hairs upright to reduce heat loss, or lay them down flat to increase heat loss.
Also shivering reduces heat loss during respiration |
|
|
Ethanol can be used for...
|
Ethanol is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic drinks such as wine and beer. It is also useful as a fuel. It is usually mixed with petrol for use in cars and other vehicles.
|
|
|
Ethanol is made by
|
Ethanol can be made by a process called fermentation. This converts sugar into ethanol and carbon dioxide if conditions are anaerobic.
Single-celled fungi, called yeast, contain enzymes that are natural catalysts for making this process happen:In some countries, eg Brazil, the source of sugar is sugar cane - which yeast can directly ferment into ethanol. In other countries, plants such as maize are used. Because maize contains starch rather than sugar, the enzyme amylase must first break down the starch into sugar before the yeast can ferment it into ethanol.The ethanol produced by yeast only reaches a concentration of around 15 per cent before the ethanol becomes toxic to the yeast. In order to make it sufficiently concentrated to be burnt as a fuel, the ethanol must be distilled. |

