![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of Osmosis? |
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a partially permiable membrane from a dilute solution (which has a high concentration of water) to a concentrated solution (with a low concentration of water) down a concentration gradient. |
|
|
What are stem cells? |
Stem Cells are undifferentiated cells with the potential to form a wide variety of different cell types. |
|
|
What are ribosomes? |
Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in a cell. |
|
|
What are the 4 main components in blood? |
Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, Platelets and Plasma |
|
|
Do Veins carry oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood? |
Deoxygenated blood. |
|
|
Do Arteries carry oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood? |
Oxygenated blood. |
|
|
Diagram of a leaf cross section. |
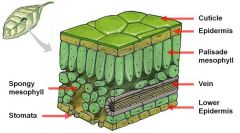
|
|
|
What are the four chambers in the heart. |
Right Atrium, Right Ventricle, Left Atrium, Left Ventricle |
|
|
In a cross section of a plant root what are the two features inside of the vascular bundle. |
Xylem and Phloem |
|
|
What are the 6 main food groups? |
Carbohydrates (Energy), Lipids (Reserve Energy), Protein (Structure of Body Tissues and Organs), Minerals (Strong bones, teeth, blood skin ect.), Vitamins (Metabolism and helps form blood cells), Fibre (Keep digestive system healthy) |
|
|
What does the Xylem do? |
Xylem transports water and solutes from the roots to the leaves. |
|
|
What does the Phloem do? |
The Phloem transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. |
|
|
What does the Stomata do? |
Stomata open and close to allow the intake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen. |
|
|
How do the White Blood Cells get rid of viruses in the blood? |
The White Blood Cell can either engulf the virus cell and destroy it or produce antibodies. |
|
|
What are the 4 layers of a leaf cross section in order from top to bottom? |
Waxy Cuticle, Palisade Metopyill, Spongy Mesopyoll, Lower Epidermis. |
|
|
How is an artery adapter to its job? |
It has thick walls and a small lumen. |
|
|
How is a Vein adapted to it's job? |
It has thin outer walls, valves inside and a large lumen. |
|
|
How are Capillaries adapted to their job? |
Walls a single cell thick and a tiny lumen. |
|
|
What is the definition of Diffusion? |
Diffusion is the spreading out of any substance in a solution, or particles of gas, resulting in a net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient. |
|
|
Where are Enzymes made? |
Enzymes are made in the Pancreas. |
|
|
What enzyme breaks down Carbohydrates? |
Carbohydraze. |
|
|
What enzyme breaks down Lipids? |
Lipase. |
|
|
What enzyme breaks down Protein? |
Protease. |
|
|
What do Lipids break down into? |
Fatty acids and Glycerol |
|
|
What is the definition of Transpiration? |
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the leaves of plants through the Stomata when they are opened to allow gas exchange for photosynthesis. It involves evaporation from the surface of the cells and diffusion through the Stomata. |
|
|
What is the definition of Translocation? |
Translocation is the movement of sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant through the phloem. |

