![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell |
The cell cytoplasm |
|
|
What is stage one of gycolysis |
Phosphylation. |
|
|
What must happen to glucose molecules in stage 1 of glycolysis |
It undergoes phosphorylation in order to activate the glucose and prevented from leaving the |
|
|
How many carbon atoms are within a glucose molecule and what is the term used to describe the sugar molecule |
6 carbons and hexose sugars |
|
|
What happens to an ATP molecule when it is hydrolysed |
ATP------ ADP+PI |
|
|
What happens to the glucose molecule when it is phosphorylated and what is the name given to the new molecule |
Two phosphates added from two ATP molecules to form a hexose bisphosphate |
|
|
What is Stage 2 |
Splitting of hexose 1 6 bisphosphate into two molecules of triose phosphate |
|
|
What is stage 3 |
The oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruvate |
|
|
What happens to triose phosphate |
Dehydrogenase and NAD are used in order to remove a phosphate group and two hydrogen molecules. This produces two molecules of reduced NAD |
|
|
How is a triose phosphate molecule converted to pyruvate |
Triose phosphate molecules undergo 4 enzyme catalysed reactions. During this process two molecules of ADP are phosphorylated by the addition of two phosphate groups forming two molecules of ATP. As one glucose molecules formed to provide molecules the total ATP molecules formed is 4 |
|
|
Summary of the link reaction |
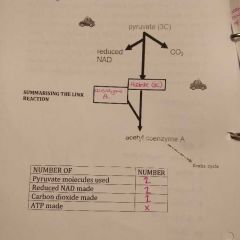
|

