![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Through what organ does air move into the lungs |
The windpipe/ trachea |
|
|
What is the proper term for breathing |
Ventilation |
|
|
What are the tiny air sacs in the lungs called |
Alveoli |
|
|
What are the products of aerobic respiration |
Carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
Where does respiration happen |
Mitochondria, Cytoplasm |
|
|
Which organ system helps us breathe |
Gas exchange system |
|
|
What does the trachea do divide into |
Two bronchi |
|
|
What happens to the diaphragm when you breathe in |
Contracts and moves downwards |
|
|
Name an adaption of the lungs |
They have tiny air sacs called alveoli which have a large surface area to make gas exchange easily and efficiently |
|
|
What happens to the diaphragm when you breathe out |
Relaxes and moves up |
|
|
What is another word for thorax |
Chest |
|
|
What two jobs do the lungs have |
To collect oxygen from the air To deliver carbon dioxide to the air |
|
|
What is respiration |
Respirationnis the chemical process that releases energy from glucose |
|
|
Carbon dioxide |
Poisonous by product of respiration |
|
|
Transport system |
Takes materials to and from respiring cells |
|
|
Oxygen |
Is needed to release energy from glucose in the body |
|
|
Respiration |
Is the process which releases energy from food |
|
|
Water |
Made when energy is released from food |
|
|
Energy |
Is needed to do anything |
|
|
Equation for respiration |
Glucose + oxygen - carbon dioxide water energy |
|
|
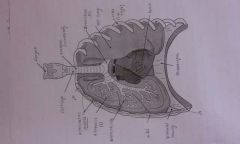
Intercostal muscle |
The muscles found between the ribs involved in ventilation |
|
|
Bronchiole |
The smaller tubes that the bronchi split into |
|
|
Trachea |
The windpipe is the passage of air from outside to inside |
|
|
Diaphragm |
A muscular sheet at the bottom of the thorax involved in ventilation |
|
|
Bronchi |
The two tubes that the trachea splits into |
|
|
Pleural membrane |
Moist membrane between the inside of the thorax and lungs that provide lubrication to prevent the lungs from sticking |
|
|
Alveoli |
Air sacs where gas exchange occurs |
|
|
Ribs |
Bones that surround the lungs which act as protection and involved in ventilation |
|
|
Name three things energy is needs for |
Growth and repair Movement Control of body temperature in mammals |
|
|
Connecting the outside to the inside |
Trachea- bronchi - bronchioles - alveoli |
|
|
What is blood |
A mixture of different types of cells suspended in plasma It is the transport system used to provide cells with the reactants for respiration and to remove waste products It transports substances to and from respiring cells |
|
|
The main function of blood is to..... |
Carry oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells Remove waste products Protect the body from infection |
|
|
Red blood cells |
Contain chemical called haemoglobin which helps them absorb and release oxygen Their shape increases their surface area for absorbing oxygen Carry oxygen around the body They are biconcave meaning they are disc shaped with a dimple on each side |
|
|
White blood cells |
Defend the body from infection from microorganisms |
|
|
What are the two types of white blood cells |
Phagocytes Lymphocytes |
|
|
Explain phagocytes |
Have to be very flexible as they kill microorganisms by surrounding and engulfing them |
|
|
Explain lymphocytes |
Produce chemicals called antibodies They stick onto the foreign microorganisms in the blood. This either kills them or causes them to clump together making it easier for phagocytes to kill. Lymphocytes also protect the body as they are able to neutralise toxins produced by the microorganisms |
|
|
Platelet |
Are small fragments of cells Help to clot blood at a wound to prevent cells blood being lost when vessels become damaged |
|
|
Plasma |
A straw coloured liquid Carries substances dissolved in it including glucose for body's cells It carries the other types of blood cells which are suspended in it |
|
|
Aorta |
Main artery carrying the blood around the body |
|
|
Arteries |
Carry blood away from the heart |
|
|
Veins |
Bring in the blood towards the heart |
|
|
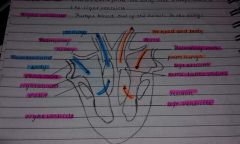
Left atrium |
Collects blood from the lungs and pumps blood to the left ventricle |
|
|
Left ventricle |
Pumps blood out of the heart and into the body |
|
|
Right atrium |
Collects blood from the body amd pumps blood to the right ventricle |
|
|
Right ventricle |
Pumps blood out of the heart to the lungs |
|

|
|
|
|
Three blood vessels |
Capillary Vein Artery |
|
|
Vein |
Large lumen Often have valves Relatively thin walls |
|
|
Artery |
Small lumen Thick walls Thick layer of muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
Capillary |
Walls a single cell thick Tiny vessel with a narrow lumen |
|
|
Cc |
|
|
Aerobic respiration equation |
Glucose+ oxygen - carbon dioxide water |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration |
Glucose - lactic acid |
|
|
Ventilation |
Ventilation or breathing involves movements of the ribs intercostal muscles and diaphragm to move air into and out of the lungs |
|
|
Cc |
|
|
When we inhale what happens to the pressure in the thorax |
Decreases |
|
|
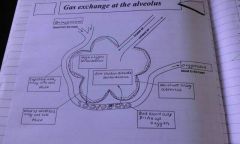
What happens during gas exchange in the lungs |
Oxygen passes into the blood and carbon dioxide passes out of the blood |
|
|
During exercise what happens to breathing in humans |
The depth of breathing Increases and the breathing rate increases |
|
|
Tobacco smoke contains carbon monoxide what problems does this cause |
The carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin in the red cells reducing the ability of blood to carry oxygen |

