![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Think about what a calibration curve of % change in mass (y-axis) against sucrose conc (x-axis) might look like for concentrations of sucrose from 0 to infinity? |
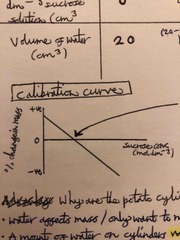
Back (Definition) |
|
|
The rate of reaction of an enzyme-controlled reaction is influenced by different factors. The effect of each of these can be determined by changing a single variable and measuring its effect on the rate of reaction. Why is it important to keep all other variables constant? |
So that they do not influence the results |
|
|
In RP1 we investigate the effect of temperature on rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction. Describe in note form how this is done? |
• Buffer solution • Water bath - to set the temperatures • Milk solution • Trypsin enzyme • Measure time taken for cross to appear - do several at each temp and take an average • Keep conc of enzyme + substrate constant • Leave enzyme + substrate separately in water bath for 10 mins before mixing • rate = 1/time |
|
|
Why is a buffer solution used in RP1? |
• Keep the pH constant • pH affects enzyme action, we’re investigating temperature effect on enzyme action |
|
|
In RP1, why do we leave the enzyme and substrate separately in the water bath (for 10 mins) before mixing? |
• allows solutions to equilibrate -> So reaction begins at the correct temperature |
|
|
What is the problem with RP1 if you use the appearing cross method of measuring rate of reaction? |
It’s subjective - people will say the cross is visible at different times • human error • not really accurate |
|
|
Sketch a graph you might expect to draw of the results in RP1? |
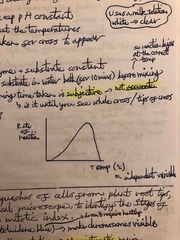
Back (Definition) |
|
|
How could you change the method of RP1 slightly to increase the accuracy of results? |
• use a colorimeter instead of an appearing cross • lower absorbance, more casein (substrate) broken down (white -> clear solution) |
|
|
In RP1, it is common at each temperature for 3 test tubes to contain milk solution and 1 test tube to contain only water. What is the water test tube there? |
As a control • shows the effect of an absence of enzyme activity |
|
|
Required practical 2? |
Preparation of stained squashes of cells from plant root tips; set-up and use of an optical microscope to identify the stages of mitosis in these stained squashes and calculation of a mitotic index |
|
|
Describe how you’d prepare a slide to show cells dividing mitotically? (RP2) |
• soak root tips in conc. HCl (15 mins) then rinse with distilled water • stain root tip with Toluidene blue (on microscope slide) • Macerate (tease tissues apart) • Lower the cover slip down carefully onto the slide. • squash cells under cover slip |
|
|
What is the purpose of Toluidene blue in RP2? |
Stains the chromosomes - making them visible |
|
|
Why is it important to use the root tip in RP2? |
Meristematic region (meristem tissue) • Is the part of the plant undergoing cell division constantly (growth region) • so we can see the stages of mitosis |
|
|
Why can’t we study mitosis in parts of the plant not undergoing cell division (non-meristematic regions)? |
Vast majority of cells in interphase |
|
|
Why can’t we study mitosis in parts of the plant not undergoing cell division (non-meristematic regions)? |
Vast majority of cells in interphase - chromosomes not visible |
|
|
Why do we use conc. HCl in RP2? |
Freezes the cells - stops all reactions in cells |
|
|
In RP2, why do we macerate the cells? |
Spreads out the cells - so not overlapping (We want a single layer of cells) |
|
|
In RP2 -> Why do we press down on the cover slip? |
Squashes cells to make a thin layer of cells - so that light can penetrate making the cells visible with a microscope |
|
|
In RP2: Why is it important to lower the cover slip carefully onto the sample? |
• Make sure there are no air bubbles in the slide which may distort the image • Need to make sure coverslip doesn’t slide sideways which could damage the chromosomes |

