![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? |
6CO₂ + 6H₂O→6O₂ + C₆H₁₂0₆
|
|
|
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
|
Carbon Dioxide + water→ Oxygen + glucose
|
|
|
What happens during photosynthesis?
|
Light energy is converted into chemical energy through the bonds in glucose.
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis catalysed by?
|
Enzymes
|
|
|
Why is glucose used in plants?
|
Respiration
Makes cellulose Makes fats and oils |
|
|
How do CO₂, light intensity and temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
Rate of photosynthesis can be increased by increasing any of these factors until one of them becomes the limiting factor
|
|
|
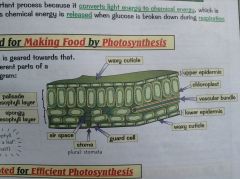
How are leaves adapted for photosynthesis?
|
Thin/transparent epidermis - allows more light to reach palisade cells
Thin, waxy cuticle -reduces water loss through evaporation Leaves - broad - LSA - exposed to light |
|
|
Describe a photosynthesis experiment containing pond weed.
|
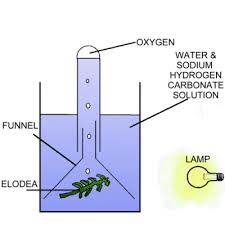
Submerge a funnel and test tube in water and turn over so funnel is on bottom of tank with tube stood on end.
Place pondweed under submerged funnel. Oxygen will displace water in test tube. After 20 mins measure water displaced. This will tell you how fast the rate of photosynthesis is. |
|
|
How do you test a leaf for starch? |
1. Kill the leaf - dunk it in boiling water 2. put leaf in ethanol and heat in water bath - gets rid of chlorophyll turning leaf pale white 3. rinse leaf in cold water and add a few drops of iodine solution- leaf will turn black if starch is present |
|
|
Why do you test for starch? |
Shows that photosy. is happening - glucose + O2 are products of photos. and glucose is stored by plants as starch |
|
|
Experiment - showing chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis |
1. take a leaf from plant thats been exposed to light- record which bits are green 2. test for starch - you'll see that only the green bits turn black 3. suggesting that only the parts containing chlorophyll can photosy. and produce starch |
|
|
Experiment - showing CO2 is needed for photosynthesis
|
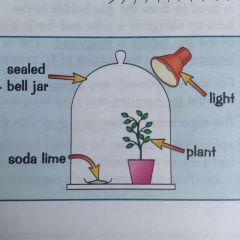
1. use the apparatus shown to left 2. the soda lime will absorb CO2 3. leave plant in jar then test for starch - wont turn black 4. showing no starch has been made meaning CO2 is needed |
|
|
Experiment - showing light is needed for photosynthesis
|
1. get a plant thats been grown without light e.g. in cupboard 2. test for starch - leaf wont turn black 3. showing light is needed |
|
|
Where are minerals found and how can you increase them? |
Found in the soil - enter plants through their roots using diffusion or active transport
You can add fertiliser or manure to the soil to increase minerals |
|
|
What are the 4 important minerals?
|
Nitrate - (to make amino acids for growth or will have yellow leaves)
Magnesium - (to make chlorophyll - for photosynthesis - yellow leaves) Phosphates - (Makes DNA/cell membrane - respiration and growth - purple leaves)Potassium - (help enzymes needed for photosyn. and respiration - discoloured leaves) |
|
|
What does it mean that a plant is deficient?
|
There are not enough minerals
|
|
|
When plants photosynthesise what do they use up and produce? |
Use up CO2 from atmosphere Produce P2 as a waste product |
|
|
When plants respire what do they use up and produce?
|
Use - O2 Produce - CO2 |
|
|
How do plants exchange gases? |
Diffusion - the movement from an area of HC to LC |
|
|
How are leaves adapted for gas exchange? |
Broad - LSA for diffusion Thin - gases only have to travel short distance to where they are needed Air spaces in leaf - lets CO2+O2 move easily in between cells Lots of stomata |
|
|
What are stomata? |
Let gases diffuse in and out allow water to escape - transpiration |
|
|
How are stomata specialised? 1. |
They close at night - photosynthesis happening in dark - so they dont need to let CO2 in Also stops when they close they stop water from escaping - plant doesn't dry out |
|
|
How are stomata specialised? 2. |
Close when water supply from roots dries up - stopping plant from photosynthesising but keeping plant from dying |
|
|
What controlls the stomata opening and closing? |
Guard cells - cells around them |
|
|
WHat is the aerobic respiration equation? |
Reverse of photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the anaerobic equation in plants? in animals? |
Glucose ~> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide Glucose ~> Lactic Acid |
|
|
What is respiration? |
The process of releasing energy from glucose, which happens constantly in every living cell |
|
Label the leaf |
|

