![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acid |
A substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution |
|
|
Amino acid |
Monomer sub unit of a protein. Contains and amino a carboxyl and a unique side group |
|
|
Atom |
The smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element |
|
|
Base |
A substance that reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution |
|
|
Carbohydrate |
Energy rich molecules that is the major source Of be energy for the cell. |
|
|
Cell |
Basic unit of life an organism's fundamental building block units. |
|
|
Cell wall |
Tough but elastic structure surrounding plant and bacterial cell membrane. |
|
|
Chloroplast |
And organelle found in plant cells that absorbs sunlight and uses the energy derived to produce sugars. |
|
|
Compound |
A substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. |
|
|
Convalent Bond |
A type of strong chemical bond in which two atoms share electrons. |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The entire contents of the cell ( except the nucleus ) surrounded by the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) |
Molecule of heredity that stores the information required call making all of the proteins required by the cell. |
|
|
Electron |
A negatively charged subatomic particle. |
|
|
Element |
A substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance. |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum ( ER ) |
A network of membranes in eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum ( ER ) |
A network of membranes in eukaryotic cells. When rough, or studded with ribosomes, or smooth , it functions in phospholipid and steroid synthesis and detoxification. |
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Water hating molecule. |
|
|
Ionic bond |
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction of oppositely charged ions. |
|
|
Lipids |
Hydrophobic molecules including fats phospholipids and steroids. |
|
|
Lysosome |
A membrane - bounded sac of hydrolytic enzymes found in the cytoplasm of many cells. |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Large molecules including Polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids composed of subunits joined by dehydration synthesis. |
|
|
Metabolism |
All chemical reactions occurring in the body. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Organelles in which products of the digestive system are converted to ATP. |
|
|
Molecule |
Two or more atoms held together by convalent bonds. |
|
|
Nonpolar |
Water hating. |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Polymers of nucleotides that comprise DNA and RNA. |
|
|
Enzyme |
Protein the catalyzes and regulates the rate of metabolic reactions. |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Building blocks of nucleic acids that include a sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogenous base. |
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Cells that have a nucleus and membrane- bounded organelles. |
|
|
Fat |
Hydro phonic molecule composed of a three carbon glycerol skeleton bonded to three fatty acids. Energy source that contains more calories than an equal weight of carbohydrates or proteins. |
|
|
Fatty acids |
A long acidic chain of hydrocarbons bonded to glycerol. Fatty acids vary on the basis of their length and on the number and placement of double bonds |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of a flattened membranous sacs The modified as sort proteins and other substances. |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The steady-state condition an organism works to maintain. |
|
|
Hydroph |
A molecule consisting of carbon and hydrogens. |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
A type of weak chemical bond. In DNA this type of bond forms between nitrogens bases across the width of the helix. |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Water loving molecule. |
|
|
Nucleus |
Cell structure that houses DNA; found in eukaryotes. |
|
|
Organelle |
Sub cellular structure found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that performs a specific job. |
|
|
Peptide bond |
Chemical bond that joins adjacent amino acids. |
|
|
pH |
A measure of the hydrogen ion concentration ranging from 0 - 14 with the lower numbers equaling higher hydrogen ion concentrations. 7 is Neutral |
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer |
The membrane that surrounds cells and organelles and is composed of phospholipids ( along with proteins and sometimes cholesterol ) . |
|
|
Phospholipid |
Molecules that make up the plasma membrane, with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. |
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Structure that encloses a cell, defining the cells outer boundary. |
|
|
Polar |
Water loving. |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
Complex carbohydrate. |
|
|
Active transport |
The movement of a substance that requires an input of energy. |
|
|
Defusion versus osmosis( what moves?) |
Molecules. |
|
|
Selective permeability |
Some substances can cross the membrane others are excluded and still others can pass through the membrane when they are aided by transport proteins. |
|
|
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes |
All living organisms can be sorted into one of two groups. Mycoides and all other bacteria are prokaryotes, but virtually all the organisms you see every day, including all plants and animals are eukaryotes. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
A network of protein cylinders and filaments. |
|
|
Diffusion |
Passive and random movement of the molecules from an area of its own higher concentration to an area of its own lower concentration. |
|
|
Model Theory |
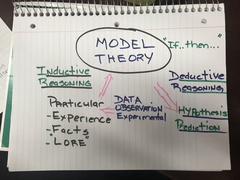
|
|
|
Dissecting Microscope |
Object - Solid or Flat "View" - Stereo ➡️ " 3D" Magnify - Low - Medium 10x ➡️ 30x Light - Above/or Below Moves lens UP and DOWN
|
|
|
Compound Microscope |
Object - Flat View - 1 View No Stereo "2 D" Magnify - 40x ➡️ 400x Light - From below transmitted Moves object UP and DOWN Red Ring - Low Yellow Ring - Medium |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cell |
This cell is larger and more complex than then prokaryotes. This cell is 10 times wider with a cell volume of a thousand times greater. ( A Membrane - enclosed NUCLEUS ) |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
This cell lacks a ( NUCLEUS ) or membrane - bounded organelles. |
|
|
Carbon Dioxide + water |
6CO2 + 6H2O >>>>>>>>>>>>>>> photosynthesis |
|
|
Glucose Oxygen |
C6H12O6+6O2 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<< Respiration |
|
|
Calvin Cycle or light independent reactions. |
A is a series of enzymes driven reactions in which each ions and energy rich molecules from the light reaction help convert carbon dioxide into sugars. |

