![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why are traditional phylogenies of protists to create accurately |
There are very few fossil records of protists. although the endosymbiont theory helps explain how eukaryotes acquired particular traits, we dont have a physical record of the earliest ancestral species. Biologists are now using DNA and RNA analysis to define groups of eukaryotes of which protists dominate |
|
|
Which of the 7 eukaryote groups would you find organisms that have a primary plastid containing chlorophyll |
Archaeplatida- contains protists like red and green algae, but also land and aquatic plants |
|
|
how many clades of protists exist today |
11 |
|
|
describe how the Unikonta are a unique group of protists |
The unikonta group contains a variety of fungi, animals and amoebozoans (cellular and plasmodial slime molds). Unikonts are believed to be the first eukaryotes to emerge, sharing a common ancestor with amoebaes and protists |
|
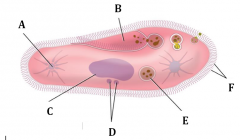
Label the cillate
|
A. Contractile Vacuole B. Oral Groove C. Macronucleus D. Micronuclei E. Food Vacuole F. Cilia |
|
|
What are the opisthokonts and amoebozoans |
opis are fungi and animals along with a variety of protists, amoe include some of the amoebas, slime molds, and a number of parasitic protists |
|
|
what are hydrogenosomes |
Mitochondrial relics that anerobically generate energy |
|
|
What are apicomplexans? and an example |
Apicomplexans are large groups of organisms that obligate parasites of vertebrates and invertebrates. An example of an apix. is plasmodiu, which is a parasite that causes malaria |
|
|
a major characteristic of excavates is the diverse range of |
mitochondria |
|
|
How does brown algae differ from most other protists |
Brown algae has unique properties that lead to it often being thought of as a plant. It is multicellular and grows to very large sizes. It includes root-like, stem like and leaf like structures. It also uses cellulose for structural support |
|
|
how did scientists that excavates should be grouped together |
It is based on studies of gene expression patterns in various protists. The decision has has its controversy and scientists continue to propose alternative theories |
|
|
Which of the following algae are archaeplastid |
Red and green Algae |
|
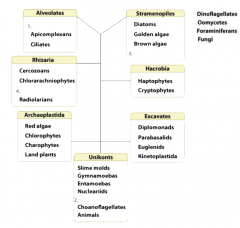
fill the blanks |
1. dinoflagellates 2.fungi 3.oomycetes 4.foraminiferans |
|
|
Briefly describe the group excavates |
contain altered mitochondria and unusual flagella. They are unicellular organisms. Their mitochondria may not be able to generate ATP. Some are anaerobic, some are parasitic, some photosynthetic and some are free living |
|
|
Which of the following is not clade of escavates |
mitosomes |
|
|
characterize cellular slime molds |
a haploid unicellular organism which prefers wet or moist regions, can join together with others of its kind when food is scarse and form a slimy mobile colony distinct from plasmodial slime molds |
|
|
hydrogenosomes |
mitochondrial relics that anaerobically generate energy
|
|
|
alveolates are characterized by |
membrane lined sacs (alveoli) that selectively filter larger molecules |
|
|
Alveoli function |
regulate the diffusion of materials across the plasma membrane, selectively filtering larger molecules, only allowing water and small ions to enter the cell |
|
|
aquatic alveolates definition and example |
sturdy plates that protect the contents of their bodies
dinoflagellates |
|
|
appox. half of dino. are |
photoautotrophic- converting light energy from the sun into the chemical energy of carbs by fixing carbon from carbon dioxide) |
|
|
A sudden spike in population size of dinos cause |
red tides which secrete lethal toxins that can harm any species that eat shellfish |
|
|
obligate parasites example |
apicomplexans |
|
|
the most famous apicomplexans are |
plasmodium which causes malaria |
|
|
ciliates use ____ for ____ and have specialized ____ |
cilia, locomotion, vacuoles |
|
|
process of contractile vacuole |
water enters and fills vacuole ----> vacuole contracts and pushes water out<---- |
|
|
process of food vacuole |
food from environment goes into oral groove undergoes endocytosis forms food vacuole lysosomes supplies digestive enzymes undergoes exocytosis which releases digested nutrients in and releases waste out |
|
|
ciliates had ____ nuclei |
two- a smaller micronucleus which maintains the genetic information of the individual and is transferred during reproduction and a larger macronucleus which is responsible for growth and other cellular functions |
|
|
the best known lineage of stramenopiles |
diatoms (photosynthetic, silica based structure) |
|
|
pigmented stramenopiles, including fresh water groups are.. |
golden algae, use flagella for locomotion, photoautrophic, some mixotrophic..switching from phagocytosis to photosynthesis unicellular or as colonies |
|
|
other stramenopiles include |
brown algae such as kelp or seaweeds, multicellular and have differentiated tissue structures include rootlike holdfasts to anchor the algae to the sea floor and stem like components to reach surface of water and leaf like structures to harvest sunlight |
|
|
another group of stramenopiles are |
oomycetes- making a living by decomposing materials that are alive or dead |
|
|
oomycetes examples |
sudden oak death bitter crab disease water molds...white rusts and downy mildews |
|
|
Hacobia members include |
photosynthetic cryptophytes and haptophytes |
|
|
scientists have grouped ____based on DNA |
rhizarians |
|
|
Rhizarians |
cellular extentions, pseudopodia used for locomotion (thinner) |
|
|
Rhizarians consist of three groups |
Radiolaria Foraminifera Cercozoa |
|
|
Radiolaria |
silica based skeleton |
|
|
Foraminifera |
calcium carbonate based skeletons, the shell contains pores that water and nutrients can pass through |
|
|
Cercozoa |
wide range of habitats and resource use, heterotrophs |
|
|
Archaeplastida includes all organism |
with a primary plastid for photosynthesis, including green and red algae |
|
|
green algae |
include common ancestor that lead to land plants, primarily photosynthetic organisms with chloroplasts |
|
|
red algae |
pigment carrying archaeplastids that thrive in aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
2 pigments in red algae are |
phycoerythrin and cholophyll |
|
|
red algae that thrive closer to the surface |
posses roughly equal amounts of both pigments |
|
|
red algae in deeper areas carry |
less chlorophyll resulting in red pigment |
|
|
green algae primarily use |
chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis |
|
|
green algae are divided into |
charophytes and clorophytes char-are found in fresh water, unicellular clor-singlecelled to multicellular |
|
|
unikonta |
a group consisting of an enormous variety of eukaryotic organisms ranging from amoebas to animals |
|
|
2 major unikont clades |
amoebozoans and opisthokonts (true amoebas) (fungi and animals) |
|
|
amoebozoans are |
pasmodial slime molds and cellular slime molds
|
|
|
describe the developing cytoplasmic mass |
otherwise called the plasmodium, easily spreads over a substrate and eventually develops buds, also known as sporangia. These structures increase the likelihood of survival |
|
|
cellular slime molds |
haploid, municellular eukaryotes, thrive in moist areas, exits individually and then forms a slug with a reproductive stalk than can move |
|
|
the end |
end |

