![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
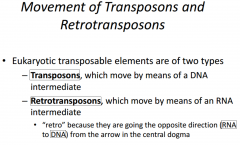
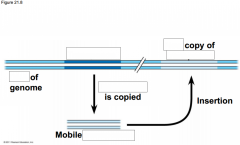
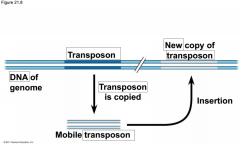
-The first evidence for mobile DNA segments -______________________ identified changes in the color of ______________ --she postulated that some genetic element move from other genomes locations into the genes for ______________ -These ____________ elements move from one site to another in a cell's ________; they are present in _______________________ |
-The first evidence for mobile DNA segments -Barbara McClintock identified changes in the color of corn kernels --she postulated that some genetic element move from other genomes locations into the genes for kernel color -These transposable elements move from one site to another in a cell's DNA; they are present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
|

|
|
|
|
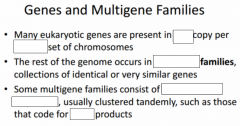
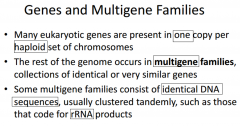
-Multiple copies of _____________ elements and related sequences are scattered throughout the ___________ genome -In _____________, a large portion of transposable element-related _______ consists of a family of similar sequences called _____________ -Many _____________ are transcribed into _______ molecules; however their function, if any, is unknown |
-Multiple copies of transposable elements and related sequences are scattered throughout the eukaryotic genome -In primates, a large portion of transposable element-related DNA consists of a family of similar sequences called Alu elements -Many Alu elements are transcribed into RNA molecules; however their function, if any, is unknown |
|
|
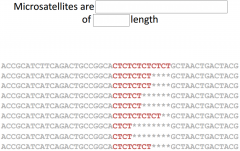
A series of repeating units of 2 to 5 nucleotides is called a _____________________ |
A series of repeating units of 2 to 5 nucleotides is called a short tandem repeat (STR) |
|
|
A _______________________________ is called a short tandem repeat (STR) |
A series of repeating units of 2 to 5 nucleotides is called a short tandem repeat (STR) |
|
|
-____________ mutate at a higher frequency (~10^-2 to 10^-6 per generation) than ____________ (~2 x 10^-8 per generation) -Many ____________ at each marker, so lots of information per marker -Easy to ____________ by measuring length differences -Many _______-wide scans performed with these markers -Can't be highly ____________, so not often used for large scale genotyping today -High ____________ obscures relationship among alleles in population (many alleles are identical by ____________ but not ____________) |
-Microsatellites mutate at a higher frequency (~10^-2 to 10^-6 per generation) than SNPs (~2 x 10^-8 per generation) -Many alleles at each marker, so lots of information per marker -Easy to genotype by measuring length differences -Many genome-wide scans performed with these markers -Can't be highly multiplexed, so not often used for large scale genotyping today -High mutation rate obscures relationship among alleles in population (many alleles are identical by state but not descent) |
|
|
|
|
|
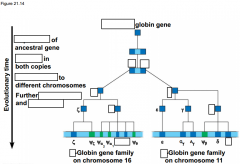
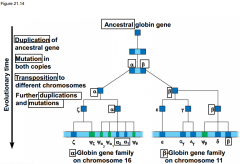
-The basis of change at the genomic level is ____________, which underlies much of genome ____________ -The size of genomes has ____________over evolutionary time, with the extra genetic material providing raw material for gene ____________ |
-The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, which underlies much of genome evolution -The size of genomes has increased over evolutionary time, with the extra genetic material providing raw material for gene diversification |
|
|
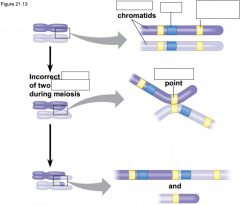
-Accidents in _________ can lead to one or more extra sets of chromosomes, a condition known as _________ -The genes in one or more of the extra sets can diverge by accumulating _________; these variations may persist if the organism carrying them _________ and _________ |
-Accidents in meiosis can lead to one or more extra sets of chromosomes, a condition known as polyploidy -The genes in one or more of the extra sets can diverge by accumulating mutations; these variations may persist if the organism carrying them survives and reproduces |
|
|
-____________in meiosis can lead to _______________________________, a condition known as polyploidy -The genes in ____________________________ can ___________by accumulating mutations; these variations may __________if the organism carrying them survives and reproduces |
-Accidents in meiosis can lead to one or more extra sets of chromosomes, a condition known as polyploidy -The genes in one or more of the extra sets can diverge by accumulating mutations; these variations may persist if the organism carrying them survives and reproduces |
|
|

|
|
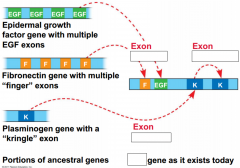
|
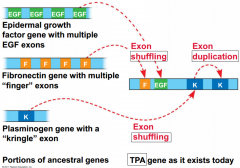
|
|

|
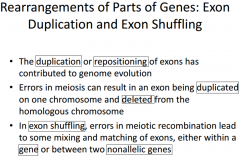
|
|
|
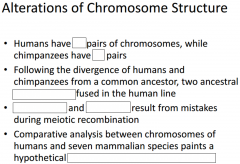
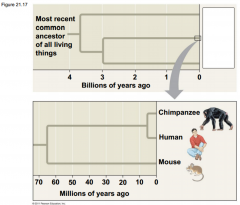
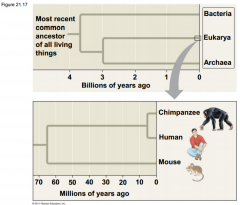
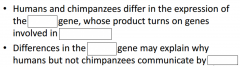
-Human and chimpanzee genomes differ by 1.2%, at ____________, and by 2.7% because of __________ and __________ -Several genes are evolving faster in __________ than __________ -These include genes involved in defense against __________ and __________, regulation of __________ size, and genes that coded for _______________ |
-Human and chimpanzee genomes differ by 1.2%, at single base-pairs, and by 2.7% because of insertions and deletions -Several genes are evolving faster in humans than chimpanzees -These include genes involved in defense against malaria and tuberculosis, regulation of brains size, and genes that coded for transcription factors |
|

|
|
|
|
About _____________ of repetitive DNA is made up of _____________ elements and sequences related to them. |
About three-fourths of repetitive DNA is made up of transposable elements and sequences related to them. |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
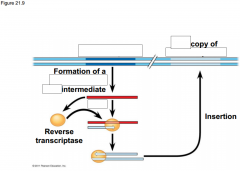
The human genome also contains many sequences of a type of ________________ called _____________ |
The human genome also contains many sequences of a type of retrotransposon called LINE-1 (L1) |
|
|
About 15% of the human genome consists of |
About 15% of the human genome consists of |
|
|

|
|
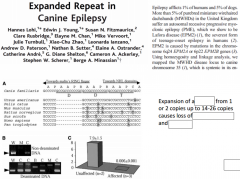
|
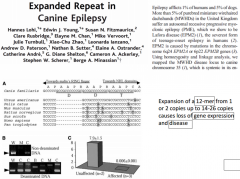
|
|
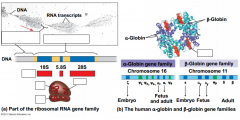
|

|
|

|

|
|
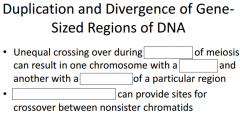
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|
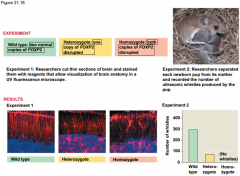
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
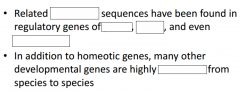
|

|
|

|

|

