![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anabaena |
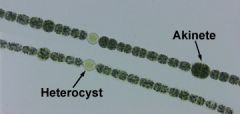
a type of cyanobacteria that exists as a plankton
vegetative cells: photosynthesis
akinete: hypnospore
heterocyst: N2 fixation
muciliaginous sheath: protection |
|
|
rhodospirillum rubrum |
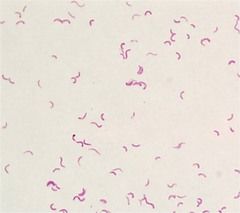
gram-negative, pink colored bacteria
spririllum shape
|
|
|
euglena |
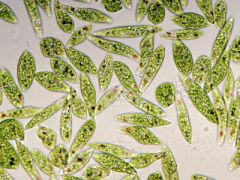
supergroup: excavata
methylcellulose was added to slow its movement
has a pellicle, eyespot, and posterior flagellum, green in color |
|
|
euglena detailed structures |
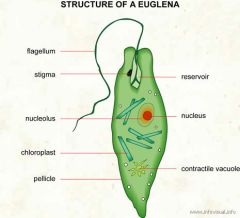
|
|
|
trypanosoma sp. |
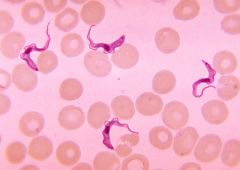
supergroup: excavata
type of kinetoplastid
was viewed in blood with red blood cells surrounding it
appear eel-like
undulating membrane |
|
|
trypanosoma detailed structures |
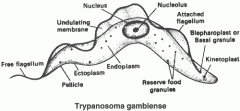
|
|
|
giardia lamblia |
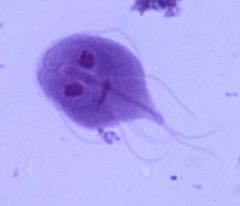
supergroup: excavata
causes giardiasis |
|
|
giardia lamblia detailed strucutres |
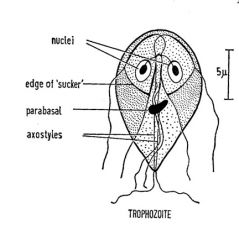
|
|
|
chlamydomonas sp
unicellular |
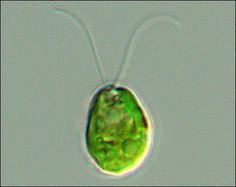
supergroup: land plants and relatives (chlorophyta)
methyl cellulose added to slow movement
have two flagella
stigma
type of green algae |
|
|
chlamydomonas sp detailed structures |
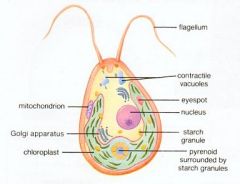
|
|
|
spirogyra sp
filamentous |

supergroup: land plants and relatives (chlorophyta)
has unbranched filaments
two types: vegetative and conjugating |
|
|
spirogyra sp detailed structures |
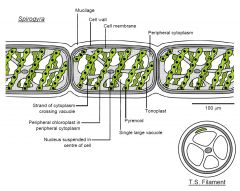
|
|
|
volvox sp
colonial |
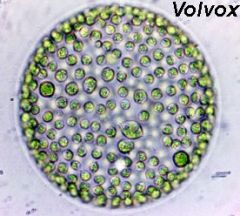
supergroup: land plants and relative (chlorophyta)
colonial, each cell synchronously beats its two flagella, propelling it in a spinning motion
daughter colonies: the smaller spheres inside the colony, product of asexual reproduction |
|
|
volvox sp detailed structures |
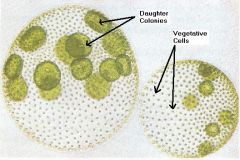
|
|
|
ulva lactuca
multicellular |

supergroup: land plants and relative (chlorophyta) |
|
|
dinoflagellates |

supergroup: alveolata
primary producers, endosymbionts with coral, and toxins like red tide
secondary endosymbiosis from red algae
cellulose plates
perpendicular flagella |
|
|
dinoflagellates detailed structures |
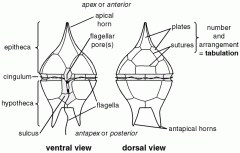
|
|
|
stentor sp |
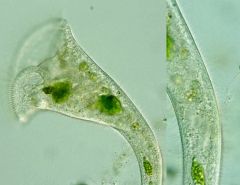
supergroup: alveolata |
|
|
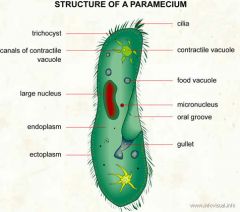
paramecium sp |
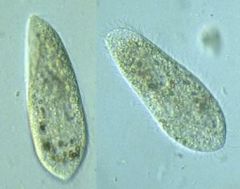
supergroup: alveolata
exhibit taxis |
|
|
paramecium detailed structures |
|
|
|
diatoms |

supergroup: stramenopila
unicellular algae, chlorophyll a and c and xyanthophyll
cell wall of silicone dioxide
lack stramenopila as adults, so they move with currents
25% of carbon fixation
can be pennate or centric |
|
|
brown algae |
supergroup: stramenopila
fucus sp.
brown in color |
|
|
amoeba sp |
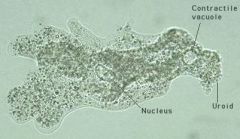
supergroup: amoebozoa
move using pseudopodia
contractile vacuole to expel excess water |
|
|
radiolarian |

supergroup: rhizaria |
|
|
foraminiferan |

supergroup: rhizaria |
|
|
marchantia sp antheridia |
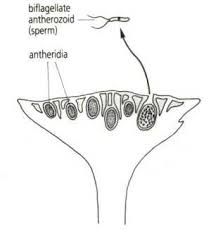
liverworts, phylum hepatophyta
male sex organs produce sperm |
|
|
merchantia sp archegonia |
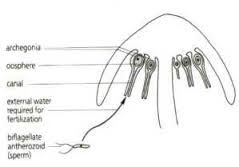
female sex organs, produce egg
the sporophyte forms on the archegonia after fertilization |
|
|
polytrichium sp |

bryophtya phylum
sporophyte: capsule on top
gametophyte: more abundant greenery on bottom |
|
|
fern sporophyte anatomy |
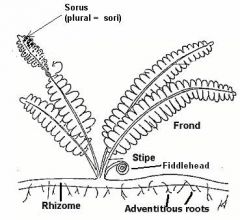
|
|
|
fern prothallus |

has archegonia and antheridia
is the gametophyte generation
produced when sori mature |
|
|
young fern sporophyte |
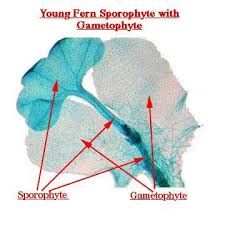
rhizoids located on bottom |
|
|
horsetails (equestium sp) |

it does not have true leaves, photosynthesis occurs at the stems
only extant species left
strobili cones at the tip of reproductive stems
|
|
|
lycopodium sp |

phylum lycophyta
needle-like |
|
|
selaginella sp |

phylum lycophyta
scale-like |
|
|
female cone vs male cone |

conifers |
|
|
pine pollen |
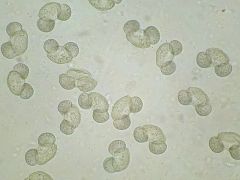
the large air bladders on the side help make it airborne |
|
|
female cone with megasporocyte |
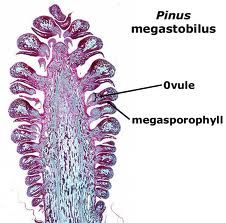
|
|
|
pine ovule |
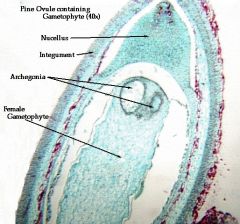
|
|
|
mature pine embryo |

|
|
|
anther cross section |
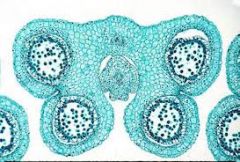
|
|
|
anther cross section detailed structures |
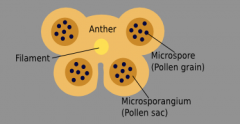
the four sacs are pollen sacs where only one will survive |
|
|
tomato cross section |
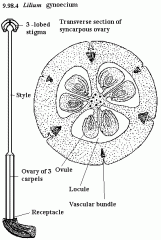
|
|
|
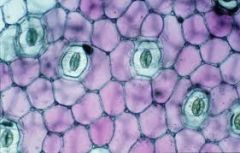
stomata and guard cells |
|
|
|
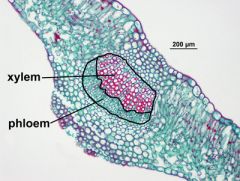
xylem and phloem |
|
|
|
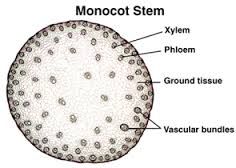
monocot stem |
|
|
|
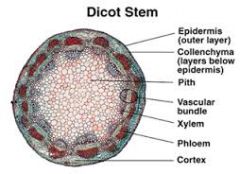
dicot stem |
|
|
|
monocot vs dicot stem |
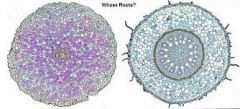
dicot has a star shape center
monocot is circular |

