![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lab safety |
1. Food and drinks are never allowed 2. You cannot stay if you arrive after the pre lab lecture 3. Safety glasses, you must wear them always when you're told |
|
|
What are SDS sheets and what are they used for? |
Safety Data Sheets. list of characteristics of a chemical, including hazards and safety info |
|
|
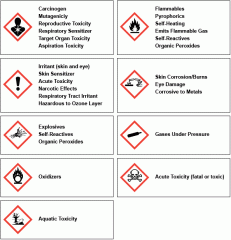
Be able to identify 9 GHS pictograms and their associated hazards |
|
|
|
What is the scientific method? |
Steps to form a hypothesis |
|
|
Know steps of the scientific method in order |
Observation. Ask questions. Form hypothesis. Experiment. Conclusion. |
|
|
The conclusion is based on what step of the scientific method? |
The hypothesis |
|
|
What is the purpose of the "control" in an experiment? How does this differ from the test/experiment group? |
A sample that goes through all steps. The comparison group. |
|
|
What is the chemical name for vitamin c? |
Ascorbic acid |
|
|
What is the name of the indicator used to test for the presence of Vitamin C in a solution? |
Indophenol (blue color that changes) |
|
|
mechanical stage |
table for slides |
|
|
objective lens |
4 levels of magnification |
|
|
eye piece/occulars |
what you look in |
|
|
diaphragm |
amount of light that comes through |
|
|
course focus knob (which objectives can you use this knob for) |
brings objects into focus....only use this knob when scanning lens is in place. |
|
|
fine focus knob (which objectives can you use this knob for) |
brings object into best resolution possible....this can be used with any of the objectives in place. |
|
|
light switch |
turns light on |
|
|
stage adjustment |
moves stage back and forth |
|
|
Be able to calculate the total magnification of a microscope |
multiply x 4 |
|
|
Distinguish between Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells |
Eukaryotic - nucleus Prokaryotic |
|
|
Nucleus |
Storage genetic function |
|
|
cytoskeleton |
shape, support and membrane of structures within the cell |
|
|
ribosome |
protein synthesis |
|
|
vacuole |
for water and mineral storage |
|
|
mitochondria |
ATP synthesis |
|
|
chloroplasty |
for photosynthesis |
|
|
if provided with pictures of specimens, be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells |
Animal cells are circles, plants are squares |
|
|
Know how to test for the basic organic compounds: what indicator is used to test for each organic compound and the positive/negative test results (colors) PROTEINS |
Biuret test (blue) - turns purple |
|
|
Know how to test for the basic organic compounds: what indicator is used to test for each organic compound and the positive/negative test results (colors)
CARBOHYDRATES |
Benedicts reagent (blue) - turns orange/green simple sugars (saccharides/glucose) Benedicts reagent (blue) - turns orange/green complex sugars (starch) iodine brown to a very dark color
|
|
|
Know how to test for the basic organic compounds: what indicator is used to test for each organic compound and the positive/negative test results (colors) LIPIDS |
spot test - persists (unsaturated fat) -evaporates (saturated fat) |
|
|
Negative tests |
Blue |
|
|
Positive tests |
Orange and green |
|
|
What is the main difference between fermentation and cellular respiration |
Fermentation without oxygen Cellular respiration WITH oxygen |
|
|
Know the reactants and end products of cellular respiration. How many ATP's are produced from each molecule of glucose. |
36-38 ATP's (glucose+oxygen-->water+energy) |
|
|
What is the purpose of KOH in the respirometer chambers? |
Removes carbon dioxide |
|
|
Know the reactants and end products of fermentation. How many ATP's are produced from each molecule of glucose? |
Glucose-->carbon dioxide+ethanol+2ATP 2 molecules of glucose |
|
|
Know the relationship between time and the amount of oxygen consumed in cellular respiration and the amount of carbon dioxide produced by fermentation. |
MORE TIME, LESS O2. MORE TIME, MORE CO2. |
|
|
prophase |
nuclear membrane disappears |
|
|
metaphase |
chromosomes align at the cell equator |
|
|
anaphase |
DNA/chromosomes separate |
|
|
telophase |
cytokinesis occurs |
|
|
How can you tell the difference between a plant and animal cell during cytokinesis? |
Plant - binary fision Animal - cleavage furrow |
|
|
Mitosis |
diploid 2n-->2n growth and repair crossing over occurs in prophase I ends with 2 diploid cells |
|
|
Meiosis |
haploid 2n-->n used for reproduction crossing over occurs in prophase I ends with 4 haploid cells |
|
|
Be able to calculate the number of chromosomes a cell would have after it undergoes mitosis/meiosis |
mitosis, 46 chromosomes -->46 chromosomes meiosis, 46 chromosomes -->23 chromosomes |
|
|
homozygous recessive |
2 alleles are same in the gene. can only be expressed when no dominant present |
|
|
homozygous dominant |
always expressed in the phenotype |
|
|
heterozygous |
2 alleles are different in that gene |
|
|
genotype |
all alleles present in a cell |
|
|
genotypic ratio |
expected numbers of different genotypes produced by a particular cross. 1:2:1 |
|
|
Phonotype |
physical characterisitics of an organism |
|
|
phenotypic ration |
number of different phenotypes in a particular cross |
|
|
complete dominance |
dominant allele covers recessive allele |
|
|
incomplete dominance |
heterozygous condition where both alleles are partially expressed |
|
|
co-dominance |
relationship between 2 versions of a gene |
|
|
identify parts of a virus |
contain 1 nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA capsid- protein coat envelope- lipid layer that covers the capsid no envelope- naked virus some have spikes |
|
|
identify the 3 bacterial shapes |
cocci spirilla bacilli |
|
|
gram negative bacteria |
resistant to drugs in the penicillin family |
|
|
gram positive bacteria |
sensitive to penicillin |
|
|
classify viruses |
neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic |
|
|
classify bacteria |
prokaryotic |
|
|
classify protists |
eukaryotic |
|
|
Prostist locomotion phylum sarcodina |
pseudopodia |
|
|
Prostist locomotion phylum mastigophora
|
flagella |
|
|
Prostist locomotion phylum ciliphora
|
cilia |
|
|
Prostist locomotion phylum apicomplexa
|
no locomotion |
|
|
classify fungi and plants |
both eukaryotic |
|
|
what are lichens |
they are mutualistic relationship between a sac fungi and photosynthetic green algae |
|
|
3 different types of lichens |
crutose (crusty) foliose (leafy) fruticose (shrubby) |
|
|
What are some common diseases associated with fungi |
thrush, oral candididasis, ringworm, athlete's foot |
|
|
order in which each land plant evolved |
1. Bryophytes 2. Ferns 3. Gymnosperms 4. Angiosperms |
|
|
dominant generation (gametophyte (2n), sporophyte (n) |
Gametophyte 2n- Ferns, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms Sporophytes (n)-Bryophytes |
|
|
Vascular or nonvascular plants |
Vascular-Ferns, gymnosperms, Angiosperms Nonvascular-Bryophytes |
|
|
Type of reproduction |
Seedless/flagellated sperm/spores-Fern, Bryophytes Naked seed-Gymnosperm Protected seed with ovary-Angiosperm |
|
|
Examples of Plants |
1. Bryophyte (Moss) 2. fern (Fern) 3. Gymnosperm (Pine Trees) 4. Angiosperm (flowering plants) |
|
|
Monocot vs. eudicot |
Monocot- Flower parts in 3, Leaf veins parallel Eudicot-Flower parts in 4 or 5, leaf veins reticolated |
|
|
Identify Parts of flower |
Female: Style-stem Stigma-Sticky Ovary-Outside Ovule-Inside Male: Anther-yellow top Filament-stems of pollen |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Sponges |
Phylum Porifera |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Jellyfish
|
Cnidaria |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Flatworms
|
Phylum Platyhelminthes |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Roundworms
|
Phylum Nematoda |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Segmented worms
|
Phylum Annelida |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Clams, snails
|
Phylum molluska |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Insects, crabs, spiders
|
Phylum Arthropoda |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Starfish
|
Phylum Echinodermata |
|
|
Classify Organism into phylum: Chordates
|
Phylum chordata |
|
|
Classify organisms from phylum chordate into classes |
Bilateral symmetry, spinal chord |
|
|
Directional Selection |
One extreme phenotype is favored over all other phenotypes |
|
|
Diversifying Selection |
Extreme phenotypes favored over intermediate phenotype. |
|
|
Stabilizing Selection |
Favors intermediate phenotype instead of extremes. |
|
|
Natural Selection |
Organisms adapt to their environment and produce more offspring. |
|
|
Mutation |
The changing of the structure of a gene, resulting in variant form that may be transmitted to sybsequent generations. |
|
|
Conditions that lead to evolution |
1. Genetic Drift 2. Mutation 3. gene Flow 4. Non-random mating 5. Natural selection |
|
|
What would happen if a breeding pair of finches were placed under ideal conditions? Given enough time... |
The finch population would increase dramatically. |
|
|
Finches require food and water. |
When food is scarce, some birds will not survive. |
|
|
Once the birds have lived on an island for many years... |
the population remains relatively stable, with some fluctuations. |
|
|
What are primary changes that occur in the finches? |
Proportions of finches having different traits within a population change. |
|
|
How did they get different beaks? |
By chance |
|
|
What type of variation in finches is passed to the offspring? |
Characteristics that are genetically determined. |
|
|
What caused different beak shapes and sizes? |
The features that were best suited to the available food supply on each island reproduced most successfully. |
|
|
Cultural Eutrophication |
Water pollution that occurs when excessive fertilizers run into lakes and rivers. It encourages growth of algae. |
|
|
Effects of eutrophication on an ecosystem. |
Reduces water clarity and harms the water. Algae blooms, limiting light penetration. Fish die. Depletes oxygen causing a 'dead zone' |

