![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is homeostasis? |
homeostasis is how the body creates and controls a stable internal e |
|
|
describe negative feedback |
receptors detect a change in levels(stimulus) the coordination center organises a response an effector produces a responce to counteract the change in level/ |
|
|
What does the nervous System do? |
detect stimuli
|
|
|
what is the CNS |
the CNS consists of the brain and spinal chord. It is connected to the body by sensory neurones |
|
|
what are sensory neurones |
they carry information from receptors to the CNS |
|
|
what are motor neurons? |
neurones that carry impulses from theCNS to effectors |
|
|
describe a reflex arc |
sensory neuron>relay neuron>motor neuron>effector |
|
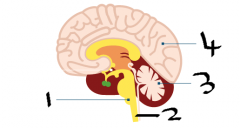
Lable |
1)medulla 2)spinal chord 3)cerebellum 4)cerebral cortex |
|
|
give 3 methods of studying the brain |
1)using brain damaged people 2)electrically stimulating parts of brain-observing 3)MRI scans form a picture |
|
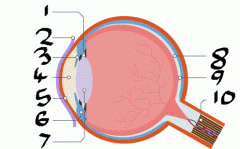
lable |
1)suspensory ligaments 2)don't need to know 3)Iris 4)pupil 5)cornea 6)cilliary muscle 7)Lens 8)Retina 9)dont need to know 10)Optic nerve |
|
|
how does your eye look at near objects? |
muscles tighten,ligaments relax |
|
|
how can you counteract hyperopia |
farsightedness can be fixed with a convex lens |
|
|
how can you counteract myopia |
short sightedness can be fixed with a concave lens |
|
|
give two surgical ways to fix eye problembs |
laser eye surgery changes cornea shape replacement lens surgey gives you an artificial lens |
|
|
what acts a as a coordination center for change in temperature |
thermoregulatory center |
|
|
how does you body keep cool/cool down |
hairs lie flat sweating blood vessels near skin dilate to allow heat to escape |
|
|
how do you heat up/stay hot |
hairs stand up stop sweating blood vessels near skin constict shivering |
|
|
what are hormones |
chemical messages sent in bloodstream |
|
|
name 6 endocrine glands and their purpose |
Pituitary-regulate body conditions ovaries-oestrogen Testes-testosterone Thyroid-thyroid Adrenal-adrenaline pancreas-insulin |
|
|
how does you body lower blood sugar levels? |
by producing insulin to turn glucose into glycogen which is absorbed mainly ito the liver
|
|
|
how does your body raise blood-sugar levels? |
by producing glucagon which turns glycogen into glucose which goes back into bloodstream |
|
|
what is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes? |
1)pancreas produces little or no insulin 2)cells don't respond properly to insulin |
|
|
what do kidneys do? |
they filter the blood |
|
|
what is urea? |
because protein cant be stored it is coverted to fats and carbohydrates. it also produces ammonia which is toxic so it's converted to urea,which is then filtered out of the blood by the kidneysand into the urine |
|
|
what else does the kidney filter out? |
Ions(from food) have to be kept in balance with water, too much or little will upset osmosis. so some ions are lost in sweat but the rest is maintained by the kidneys.-ions>reabsorbed/+ions lost in urine water going out has to balance going in and we dont lose enough from sweat so the kidneys get rid of it in urine |
|
|
describe the 4 stages of the menstrual cycle |
1)1-menstruation starts(uterus lining breaks down for 4 days) 2)4-14 uterus lining builds up again 3)14-developed egg released(ovulation) 4)14-28-wall maintained. If no fertilised egg lands on by by 28 it begins again. |
|
|
where is FSH made and what does it do? |
pituritary gland, causes egg to mature in a follicile in an ovarie and stimulates oestrogen |
|
|
where is oestrogen made and what does it do? |
ovaries, causes uterus lining to grow and stimulates LH. an inhibits FSH |
|
|
where is LH produced and what does it do? |
pituitary gland. stimulates ovulation |
|
|
where is progestrone made and what does it do? |
made by remains of follicle in ovarie. maintains uterus lining and inhibits production of FSH and LH |
|
|
how can hormones be used to reduce fertility |
if enough is taken it inhibits production of FSH. It also produces a thick mucus that prevents sperm from reaching egg. side effects |
|
|
how can hormones be used to increase fertility? |
some women have low FSH levels so they can be given to them as drugs along with LH to stimulate ovulation. side effects |
|
|
How does IVF work |
eggs collected from ovaries are fertilised(ICSI may be used which injects sperm into egg) in lab. they are grown into embryos in an incubator. once they are more developed they are put into the uterus to grow. |
|
|
what does adrenaline do? |
increases supply of O2 and glucose to brain and muscles. |
|
|
how does negative feedback regulate thyroxine |
thyroxine controls basal metabolic rate and is regulated by TSH. when thyroxine levels are too high TSH is inhibited so thyroxine falls to normal. |

