![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypothesis |

A tentative conjecture explaining an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further observation, investigation, and/or experimentation |
|
|
Scientific journal |

allows other scientists to determine what has been don previously and where their own research fits in the larger study |
|
|
Peer Review |

The scholarly process whereby manuscripts intended to be published in an academic journal are reviewed by independent researchers to evaluate the contribution, importance, and accuracy of the manuscript's contents |
|
|
Theory |

a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world based on knowledge that has been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experimentation |
|
|
element |

pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical means (they are composed entirely of 1 type of atom) |
|
|
polymer |

a long or larger molecule consisting of a chain or network of many repeating units. Synthesized by dehydration synthesis and broken down by hydrolysis |
|
|
monomer |

a relatively small molecule which can be covalently bonded to other monomers to form a polymer |
|
|
dehydration synthesis |

chemical reaction involving the loss of a water molecule as two molecules are bonded together (used during polymerization of monomers) |
|
|
hydrolysis |

chemical reaction that splits a large molecule into smaller ones and requires the addition of a water molecule |
|
|
diffusion (simple) |

a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an are of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
osmosis |

the movement of water through a semi-permable membrane according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane |
|
|
aerobic respiration |

the process in which organisms convert energy in the presence of oxygen- and glycolysis is their sole source of ATP. |
|
|
The Scientific Method |

a method of discovering knowledge about the natural world based on making falsifiable predictions, testing them, and developing theories that match known data from repeatable physical experimentation |
|
|
CHON |
make up 96% of the human body and most life: Oxygen -65% Carbon - 18% Hydrogen- 10% Nitrogen - 3% |
|
|
4 types of organic macromolecules |
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids |
|
|
Lipids |

long-term shortage of energy |
|
|
Proteins |

polymers made from amino acid monomers. requires proper shape to function |
|
|
DNA and RNA |

polymers made from nucleotide monomers. Consist of strand of nucleotides (AGTC) bonded in a 5' to 3' direction |
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |

energy can neither be created nor destroyed |
|
|
ligand |

a molecule that binds another specific molecule, in some cases, delivering a signal in the process |
|
|
receptor protein |

a molecule usually found embedded within the plasma membrane surface of a cell that receives chemical signals from outside the cell. |
|
|
signal transduction |

propagation of the signal through the cytoplasm ( and sometimes also the nucleus) of the cell |
|
|
haploid |

cell, nucleus, or organism containing one set of chromosomes (n). Undergo fertilization to produce a diploid zygote |
|
|
diploid |

cell,nucleus, or organism containing two sets of chromosomes (2n) |
|
|
gamete |

haploid reproductive cell or sex cell (sperm, pollen grain, or egg) |
|
|
zygote |

is cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. |
|
|
crossing over |

process by which homologous chromosomes undergo reciprocal physical exchanges at their arms. recombines genetic information from the 2 parents |
|
|
dominant/recessive |

to a genetic feature that hides the recessive trait in the phenotype of an individual / an allele that causes a phenotype. |
|
|
allele |

gene variations that arise by mutation and exist at the same relative locations on homologous chromosomes |
|
|
homozygous |

having two identical alles for a given gene on the homologous chromosome |
|
|
heterozygous |

having two different alles for a given gene of on the homologous chromosome |
|
|
genotype/phenotype |
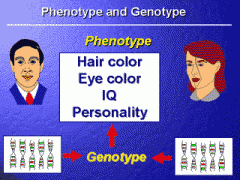
underlying genetic makeup, consisting of both physically visible and non-expressed alleles, of an organism/ observable traits expressed by an organism |
|
|
linked genes |

alleles that are located in close proximity to each other on the same chromosome are more likely to be inherited together |
|
|
Mitotic cell cycle |
produces 2 cells with identical genetic information |
|
|
Chargaff's Rule |
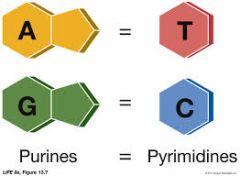
A=T and G=C. Bases are complementary |
|
|
semi-conservative replication |

each of the two parental DNA strands acts as template for new DNA to be synthesized; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes on parental or "old" strand and one "new" strand. |
|
|
transcription |

process through which messenger RNA forms a template of DNA |
|
|
Translation |

process through which RNA directs the formation of protein |
|
|
mRNA |

coped from the DNA, is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and contains info for the construction of protiens |
|
|
tRNA |

RNA that carries activated amino acids to the site of protein synthesis on the ribosome |
|
|
codon |

three consecutive nucleotides in mRNA that specify the insertion of an amino acid or the release of a polypeptide chain during translation |
|
|
The Genetic Code |

the DNA alphabet (ATCG), the RNA alphaget (AUCG) and the polypeptide alphabet (20 amino acids) |
|
|
mutation |

changes to an organism's DNA and are an important drive of diversity in populations. |
|
|
Fossils |

the preserved remains of once-living organisms - the age of fossils can be estimated |
|
|
phylogeny |
adding new intermediate forms, allowing a better picture of how organisms are related to one another |
|
|
homology |
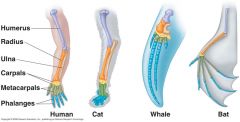
structures with different appearances and functions that all derived from the same body part in a common ancestor |
|
|
microevolution |

changes in allele frequences/phenotypes within a population. Happens quickly |
|
|
macroevolution |

(speciation) requires a considerable amount of time to witness |
|
|
Evolution |
the core concept that allows proper understanding of biology |
|
|
Biology |
the study of life |

