![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Explain the Gaia Hypothesis and how does it relate to Unit 1? (Chapter 1)
|
noun
noun: Gaia hypothesis 1. the theory, put forward by James Lovelock, that living matter on the earth collectively defines and regulates the material conditions necessary for the continuance of life. The planet, or rather the biosphere, is thus likened to a vast self-regulating organism. |
Earth
|
|
|
What are the three components of the biosphere? (Chapter 1)
|
Lithosphere, Atmosphere, Heliosphere
|
Lith, At, Hel
Ends with -Sphere |
|
|
Explain the difference between biotic and a biotic factors. (Chapter 1)
|
Biotic = Living
a Biotic = Never lived. |
One lived, One hasn't lived yet.
|
|
|
List some alternative names for a producer? (Chapter 1)
|
Autotrophs and chemotrophs.
|
No hints.
|
|
|
What is an indicator species and what is their significance? (Chapter 1)
|
An Animal in an area that shows the environment is changing there.
|
Involves animals in an area.
|
|
|
What does a decomposer feed on? (Chapter 1)
|
Dead or decaying matter.
|
No hint.
|
|
|
Explain bio magnification, using a diagram? (Chapter 1)
|
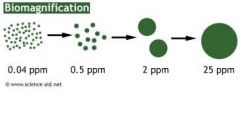
|
Gets bigger.
|
|
|
What is Dynamic Equilibrium? (Chapter 1)
|
A state of balance between continuing processes.
|
|
|
|
What is detritus? (Chapter 1)
|
waste of any kind.
|
Garbage
|
|
|
Explain the meaning and significance of biodiversity. Include an Example. (Chapter 1)
|
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
|
Rain forest.
|
|
|
Why are producers and decomposers needed for an ecosystem to function but not for a consumer? (Chapter 1)
|
Consumers are the middle step but it can be removed, the decomposer and Producer can do it by themselves.
|
|
|
|
In a food chain, what is the overall effect of low levels of precipitation on the top carnivore? (Chapter 1)
|
Dehydration and possibility of not getting prey as easily.
|
|
|
|
Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis and explain why this process is so important in an ecosystem. (Chapter 2)
|
6 CO2(gas) + 12 H2O(liquid) + photons → C6H12O6(aqueous) + 6 O2(gas) + 6 H2O(liquid)
It converts CO2 into Oxygen |
|
|
|
Define chemosynthesis. (Chapter 2)
|
Synthesis of carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water using energy obtained from the chemical oxidation of simple inorganic compounds. This form of synthesis is limited to certain bacteria and fungi.
|
|
|
|
Differentiate between a food web and a food chain. (Chapter 2)
|
A food chain is a single line of organisms, where each is preceded by something that it consumes and is followed by something that consumes it. A food web branches out in all directions with arrows pointing from organisms to any number of organisms that consume it.
|
|
|
|
Which of the ecological pyramids that we studied is the most accurate? (Chapter 2)
|
Energy Pyramid, Shows that 10% of Energy is transferred to the next trophic level.
|
|
|
|
Referring to fig. 3 on pg. 23. place the following labels. autotroph, primary consumer, secondary consumer. (Chapter 2)
|
PRODUCER -> Primary Consumer -> Secondary Consumer.
|
Plant, deer, wolf.
|
|
|
What are the first and second laws of Thermodynamics? (Chapter 2)
|
Law 1: Energy can not be created or destroyed.
Law 2: During any energy transformation some energy is converted into an unusable form, mostly thermal energy. |
Energy
|
|
|
In a food pyramid, the amount of energy available as you move up a pyramid is reduced. What "Rule" and "Law of Thermodynamics" does it follow?
|
2nd law, energy will be converted into unusable energy when being transferred.
|
|
|
|
What class of organism is always first Trophic level? (Chapter 2)
|
Producers.
|
|
|
|
Why are monocultures considered to be a factor that decreases biodiversity? (Chapter 2)
|
It isn't diverse it is one plant or crop.
|
|
|
|
Give an example of a substance with a high albedo. (Chapter 3)
|
Fresh snow.
|
|
|
|
Difference between Ozone Depletion and Global Warming. (Chapter 3)
|
Ozone depletion is the reduction of ozone in the upper atmosphere that would normally screen out ultra violet light that can cause sunburns and skin cancer.
Global Warming is an increase in temperature due to have a lot of Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. |
|
|
|
Difference between Greenhouse effect and Global Warming. (Chapter 3)
|
Greenhouse Effect is the cause of Global Warming.
|
|
|
|
Explain the process of denitrification. (Chapter 3)
|
Removing nitrogen from the soil.
|
|
|
|
Why is nitrogen and phosphorous important to organisms? (Chapter 3)
|
Phosphorus is a Nutrient for plants and animals, Nitrogen is in the air constantly that we are breathing (helps create food).
|
|
|
|
How does deforestation affect the atmosphere? (Chapter 3)
|
It increases CO2 levels and Deceases Oxygen levels.
|
|
|
|
What groups in Canada might not favor reducing carbon emissions? Why? (Chapter 3)
|
Oil companies.
|
|
|
|
What are the layers of soil? Why is top soil important? (Chapter 4)
|
Topsoil (A Horizon)
Subsoil (B Horizon) Weathered rock fragments (C Horizon) Bed rock (D Horizon) |
|
|
|
What are the factors affecting terrestrial ecosystems? (Chapter 4)
|
Moisture, Temperature, Soil, Relief, Drainage.
|
|
|
|
What are the four factors affecting biotic potential? (Chapter 4)
|
1. Male to female population.
2. Number of offspring produced at a time, 3. Time between births, 4. Age at which reproduction begins. |
|
|
|
What is the carrying capacity and what happens if it is exceeded? (Chapter 4)
|
Number of things that can be held inside a container. if it is exceeded the container will break.
|
|
|
|
What are the density-dependent and density-independent factors? (Chapter 4)
|
Dependent: Effects whose intensity changes with increasing population density.
Independent: A factor that affects the size of a population independent or regardless of the population density. |
|
|
|
If an ecosystem is changed in some way, what usually happens? (Chapter 4)
|
Creatures in the Ecosystem leave or adapt.
|
|
|
|
What is an ecotone and what is the significance? (Chapter 4)
|
Where two biomes meet and integrate.
|
|
|
|
What is a niche? (Chapter 4)
|
the role of an organism within its ecosystem that allows that ecosystem to survive and function efficiently
|
|
|
|
What is a biome? What Biome do we live in? (Chapter 4)
|
A Biome Grasslands.
A Biome is an area where animals and plants are adapted to living in that area. |
|
|
|
Explain the law of the minimum and law of tolerance. (Chapter 4)
|
law of tolerance: How much a species can take before dying
law of minimum: growth and development of plants and animals are determined by the availability of that essential nutrient which is present in the smallest amount. |
|
|
|
Why is Evolution a theory? (Chapter 5)
|
It isn't proven, species adapt but it can't be credited to Evolution.
|
|
|
|
Taxonomy System (Chapter 5)
|
Domain
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species |
|
|
|
What regulates the movement of your stomach? (Chapter 8)
|
sphincters
|
|

