![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acquired characteristics/traits |
A modification or change in an organ or tissue during the lifetime of an organism due to use, disuse, or environmental effects, and not inherited. |
|
|
Adaptation |
Inherited characteristics that increases an organisms chance of survival |
|
|
Adaptive radiation |
process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms |
|
|
Allele |
one of a number of different forms of a gene |
|
|
Artificial selection |
selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms |
|
|
Coevolution |
process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other |
|
|
Convergent evolution |
process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments |
|
|
Directional selection |
form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve |
|
|
Disruptive selection |
form of natural selection in which a single curve splits into two; occurs when individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle |
|
|
Divergent radiation |
The process by which a species evolves unto two or more descenant or different forms |
|
|
Diversity |
A range of different species in a ecosystem |
|
|
DNA replication |
The process by which a double stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules |
|
|
Dominant |
The gene that controls the characteristics even if only one parent passes it on |
|
|
Endocrine system |
The collection of glands of an organism that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system |
|
|
Eukaryote |
organism whose cells contain nuclei |
|
|
Fitness |
ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment |
|
|
Gene pool |
combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population |
|
|
Genetic drift |
random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations |
|
|
Genotype |
genetic makeup of an organism |
|
|
Geographic isolation |
Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water |
|
|
Gradualism |
The hypothesis that evolution proceeds chiefly by the accumulation of gradual changes |
|
|
Heterozygous |
term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles for the same trait |
|
|
Homozygous |
term used to refer to an organism that has two identical alleles for a particular trait |
|
|
Hormones |
substance produced in one part of an organism that affects another part of the same organism |
|
|
Hybrid |
offspring of crosses between parents with different traits |
|
|
Index fossil |
distinctive fossil used to compare the relative ages of fossils |
|
|
Natural selection |
process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called survival of the fittest |
|
|
Nervous system |
The network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body |
|
|
Neurons |
cell that carries messages throughout the nervous system |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus |
|
|
Phenotype |
Physical traits of an organism |
|
|
Polygenetic |
trait controlled by two or more genes |
|
|
Prokaryote |
unicellular organism lacking a nucleus |
|
|
Protein synthesis |
The process by which individual amino acids are connected to each other in a specific order dictated by nucleotide sequence in DNA |
|
|
Punctuated equilibrium |
pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change |
|
|
Radioactive dating |
technique in which scientists calculate the age of a sample based on the amount of remaining radioactive isotopes it contains |
|
|
Relative dating |
method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock |
|
|
Relative frequency |
number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles occur |
|
|
Selective breeding |
method of breeding that allows only those individual organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation |
|
|
Single gene trait |
Trait controlled by a single gene that has two alleles |
|
|
Stabilizing selection |
Form of natural selection by which the center of the curve remains in its current position; occurs when individuals near the center of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end |
|
|
Temporal isolation |
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times |
|
|
Vestigial structure |
organ that serves no useful function in an organism |
|
|
Three parts of a nucleotide |
Nitrogen base, five base sugar phosphate group. Sugar to base. Phosphate sugar chain |
|
|
Blood type |
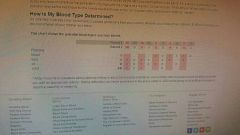
|

