![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is science? |
Empirical observation of the universe and its components |
|
|
What is an empirical observation? |
An observation using your senses |
|
|
What is biology? |
The study of living things |
|
|
Name at least 6 characteristics of life |
Organization, replication, metabolism, growth and development, response to stimuli, homeostasis, evolution |
|
|
What are two arguable chars of life? |
Adaptation and regulation |
|
|
Name the three major forms of life |
Archaea, bacteria, eukarya |
|
|
What is a virus? |
Not living, dependant on other life for survival |
|
|
What is a viroid? |
Stripped down virus |
|
|
What is a prion? |
Infectious strand of protein, alters protein structure to make harmful proteins |
|
|
List the 10 levels of biological complexity |
Atoms and molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biosphere |
|
|
What are two approaches of the scientific method? |
Induction- collecting data without a goal Deduction-knowledge that brings on a question |
|
|
What are the 6 steps to experimental science? |
Observation, question, hypothesis,prediction, test, analysis |
|
|
What are the biologically most important elements? |
NaC HOPKINS CaFe & Cl and Mg |
|
|
What is electronegativity? |
The ability to hog electrons in a covalent bond |
|
|
What does electronegativity create? |
Polarity |
|
|
What is a shell of hydration? |
Water molecules attracted to ions |
|
|
What does the pH scale go up by |
Factors of 10 |
|
|
What is a vanderwaal bond? |
Bonds that form from weak polarities that roll down elongated molecules like waves, causing things to stick |
|
|
Give these bonds from strongest to weakest: covalent, vanderwaal, ionic, hydrogen |
Covalent, hydrogen, vanderwaal, ionic |
|
|
Name and describe the two types of biomolecules |
Organic- composed of carbon and hydrogen Inorganic-not composed of carbon and hydrogen |
|
|
What does water do in the body? List at least 4 |
Stabilizes body tempurature, metabolic reactions, lubrication, capillary action |
|
|
List the four organics |
Carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids |
|
|
Name the three functions of proteins |
Energy, cell to cell recognition pathways, structure |
|
|
Name 4 lipids |
Triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, waxes |
|
|
What is a wax? |
Long chain straight hydrocarbons that are semi solid at high tempuratures |
|
|
What is the structure of a phospholipid? |
Phosphate head with fatty acid tails, amiphipathic |
|
|
What is a steroid and what is its function? |
Molecules based on cholesterol, functions to build muscle |
|
|
List 5 functions of proteins |
Structure, energy, transportation, antibodies, immune function, enzymes |
|
|
What are the three protein structures? |
Primary- amino acid sequence Secondary- regular 3D pattern Tertiary- Complex 3D folding |
|
|
Name the six nucleic acids |
Guanine, cytosine, adenine, thiamine, uracil, inasine |
|
|
What are the two laws of thermodynamics? |
1st- energy of the universe is constant, cannot be created or destroyed 2nd- when energy is transformed you increase the entropy of the universe |
|
|
How do you know if a reaction is okay with the second law? |
If entropy is larger than enthalpy and gibbs free energy is negative |
|
|
How do enzymes lower activation energy? Give three ways |
Hold atoms with most venerable bonds showing, stabilize transition state, remove shells of hydration |
|
|
How do you find Km on a product substrate concentration graph |
Half of Vmax, find x coordinate |
|
|
What are the two types of inhibitors and how do they interact with the substrate? |
Competitive- competes with substrate for binding site, still reaches vmax Non-competitive- doesn't compete, attaches to back of binding site, vmax not reached |
|
|
What are the three postulates of cell theory? |
All living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure, all cells arise from other cells |
|
|
What are the three forms of prokaryotic cells? |
Coccus, bacillus, spirillium |
|
|
What does the term fluid mosaic model mean? |
Fluid means the components move freely, mosaic means there are a variety of molecules in it |
|
|
What increases fluidity in the membrane? |
Cholesterol |
|
|
What is passive transport? |
No energy, molecules move down a concentration gradient |
|
|
What three things affect the speed of diffusion? |
Size of molecule, temperature, distance |
|
|
What is an aquaporon? |
Specialized water channel |
|
|
What is a carrier? |
Large hydrophilic molecules |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
Diffusion of water down a concentration gradient across a semi permeable membrane |
|
|
When dealing with osmosis, what is used to determine whether the beaker is hypertonic or hypotonic to the cell |
Water percentage |
|
|
What is active transport? |
Situation where cell wants to move a hydrophilic ion or molecule against the concentration gradient |
|
|
Put the three levels of bulk membrane transport in order from smallest to largest: receptor mediated vesicles, phagocytosis, pinocytosis |
Receptor mediated, pinocytosis, phagocytosis |
|
|
What is receptor mediated transport? |
Process used to take in specific molecules at a greater rate than the surface membrane can allow |
|
|
What is pinocytosis? |
Technique that turns over entire membrane by absorbing extracellular fluid |
|
|
What is phagocytosis? |
Cell eats other cells |
|
|
Where does the citric acid cycle occur in the mitochondria? Where does the ETC occur? |
Stroma, inner membrane |
|
|
Describe anaerobic respiration, what does it create? |
Glucose-2×glyceraldehyde-3-P-2×Pyruvate, creates 2NadH+2H from 2NAD+ and 2ATP from 2ADP+2Pi |
|
|
Describe aerobic respiration |

|
|
|
What is a chemoheterotroph? |
Animals, uses organic molecules to make ATP and build other organic molecules |
|
|
What is a photoautotroph? |
Plants, uses energy to make ATP, Carbon of organic molecules comes from CO2 |
|
|
What is photosynthesis? |
Foundation of energy/organic molecules used by almost all organisms on earth |
|
|
Who discovered photosynthesis? |
Priestly |
|
|
Give the photosynthesis equation |

|
|
|
Where does photosynthesis occur? |
Chloroplasts |
|
|
State the two types of reactions in photosynthesis and where they occur |
Light dependant rections- occur on thylakoid membrane Light independant reaction- occurs in stroma |
|
|
What is a photosystem? |
A cluster of light absorbing pigments coupled to a type of ETC |
|
|
Describe the two metabolic pathways |
Cyclic photophosphorylation- only uses photosystem 1, makes ATP Non cyclic photophosphorylation- uses photosystem 1 and 2, makes ATP and NADPH |
|
|
Describe the cycle of cyclic photophosphorylation |

|
|
|
What is the function of the PQ/CC/PC? |
To pump hydrogens into the thylakoid space |
|
|
When a molecule gains electrons what happens to it? |
It is chemically reduced and at a higher energy |
|
|
When a molecule loses electrons what happens to it? |
It is oxidized and at lower energy |
|
|
What is C4 photosynthesis? |
Light dependant and independant rxns occur in different cells |
|
|
What is DNA? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
Name at least 3 people involved in the discovery of DNA |
Gregor Mendel, Thomas Morgan, Watson and Crick, Rosalind Franklin |
|
|
What does CRISPR stand for? |
Clustered Regularily Interspaced shift Palindrome Repeats |
|
|
What is a nucleotide made up of? |
Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base |
|
|
Name the four nitrogenous bases in DNA |
Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine |
|
|
In what direction does DNA replication occur in? |
3' to 5' |
|
|
What enzyme breaks H bonds in DNA replication? Which stops the helix from kinking? Which lays out primers? |
Helicase, topoisomerase, RNA polymerase, DNA polymerase |
|
|
What strands are on the lagging strand of DNA? |
Okazaki fragments |
|
|
Summarize DNA replication |

|
|
|
What is a telomere? |
Long stretch of DNA that gets shorter with every replication |
|
|
Summarize the process of DNA fingerprinting |

|
|
|
What are the three stop codons, what is the start codon? |
Start-AUG Stop- UAA UAG UGA |
|
|
Describe transcription |

|
|
|
What does the 3' end of a transcribed DNA get |
A poly a tail |
|
|
What is the function of a poly-A-tail? |
Affects longetivity of RNA in cytosol |
|
|
What are the three types of RNA? |
Messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA |
|
|
Describe translation |

|
|
|
How do prokaryotic cells divide? |
Binary Fission |
|
|
What are the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle? |
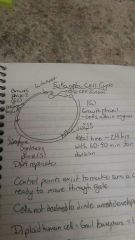
|
|
|
Where do cells not ready to be used in the cell cycle reside? |
G1 phase |
|
|
What is a chromosome? |
Condensed DNA and proteins |
|
|
What is a centromere? |
The point of contact between chromatids |
|
|
Define mitosis and meiosis |
Mitosis- cell division without a loss of genetic info Meiosis-cell division with a loss of cell division |
|
|
Cell division includes what two components |
Mitosis or meiosis and cytokinesis |
|
|
What are the phases of mitosis |

|
|
|
Define genetics |
The process of predicting how characteristics will transfer from one generation to the next |
|
|
Who founded genetics? |
Gregor mendel |
|
|
What is a genotype? A phenotype? |
Genotype-alleles of an individual Phenotype- physical traits |

