![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Genetic Material Must... |
Replicate Contain Information Be stable "Universal" Allow for variability |
|
|
Viruses have ____ not _____ |
RNA, DNA |
|
|
Gene has _______ in it, the gene tells _______ what to do |
Information, cells |
|
|
DNA is very simple |
Makes it easy to manipulate |
|
|
1868 - Johann Miescher investigated.... |
The chemical composition of the nucleus |
|
|
Johann Miescher... |
Isolated an organic acid (high in phosphorous) = Nuclein (actually DNA) |
|
|
Early candidates for the genetic material were |
Macromolecules -> proteins/nucleic acids -> DNA |
|
|
Nuclein is.... |
Substances from the nucleus of the cell |
|
|
Griffith's experiment was... |
The transformation of pneumonia-causing bacteria (in vivo/used mice) |
|
|
Avery, McLeod, and McCarty experimented.... |
Cell extraction |
|
|
Hershey and Chase experimented with... |
Bacteriophage (Bacteria/viruses that infect cells) |
|
|
1928 - Griffith |
Isolated Streptococcus pneumonia Rough = Harmless (avirulent) Smooth = Pathogenic (virulent) |
|
|
R/S Strands of Pneumonia = Transforming Principle |
Rough = Harmless Smooth = Pneumonia Heat killed S = No pneumonia Heat killed S and R = Pneumonia |
|
|
Avery, McLeod, McCarty and Transforming Principle |
In vitro = In glass (test tubes, etc) Used Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|
|
Avery, McLeod, McCarty and the Experiments |
Heat Killed S-strands No Protein + R-strands = Transformed No RNA + R-strands = Transformed No DNA + R-strands = No transformation |
|
|
Hershey and Chase Experiments |
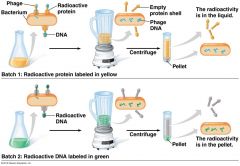
|
|
|
Hershey and Chase Experiments |
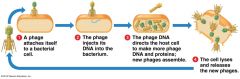
|
|
|
1953 - Watson and Crick |
Proposed structure of DNA Made of nucleotides, didn't know how they were arranged |
|
|
Watson and Crick - Nucleotides contain... |
Phosphate Deoxyribose - Pentose sugar Nitrogen - Containing base A, T, G, C |
|
|
Watson and Crick - DNA Nucleotide |
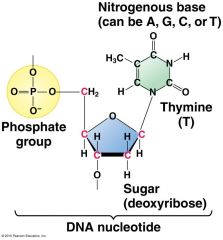
|
|
|
Watson and Crick - Pyrimidines/Purines |
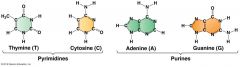
|
|
|
Watson-Crick Model |
The double strands (double helix) Strands are complementary to each other Bonds are Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
1940 - Chargaff |
%age of each type of nucleotide differs from species to species Within a species there is the same base composition %age of A = T %age of G = C |
|
|
1940 - Chargaff |
Percentage of A + G = 50% Percentage of T + C = 50% |
|
|
Watson-Crick Model |
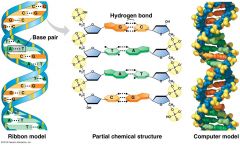
|
|
|
RNA vs DNA |
RNA = 2nd Nucleic acid that is involved in how genes function RNA = Sim. structure to DNA (no T, instead U) RNA = Ribose as the pentose sugar |
|
|
The ___________ is the information contained within the DNA |
Genotype |
|
|
__________ is the physical traits that are seen in organisms. |
Phenotype |
|
|
____________ (genotype) directs the synthesis of proteins (phenotype) |
DNA |
|
|
Proteins are synthesized by... |
A two-step process Transcription Translation |
|
|
Central Dogma - CRITICAL |
The keystone of how life functions. Explains how DNA functions, the structure of it, but it mostly talks about how DNA is able to function as genetic material. |
|
|
DNA is... |
An informational molecule and it directs the synthesis of proteins |
|
|
Transcription (Central Dogma) |
First event when our genes function Occurs within the nucleus |
|
|
Translation (Central Dogma) |
After Transcription DNA code is interpreted in order to know how to synthesize protein (At no time during these two processes does DNA become any other molecule, stays DNA) |
|
|
Central Dogma |
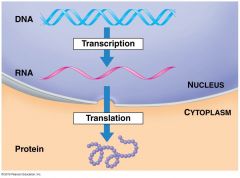
|
|
|
Three classes of RNA's are needed to synthesize a protein... |
Messenger RNA Ribosomal RNA Transfer RNA |
|
|
Messenger RNA |
Carries protein-building instructions Complementary to the DNA that it was transcribed from |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA |
Major component of ribosomes |
|
|
Transfer RNA |
Delivers amino acids to ribosomes Complementary to messenger RNA Synthesizes in the nucleus Transfers our amino acids into proteins Interpreter DNA > RNA > Protein |
|
|
Central Dogma - Co-linearity of protein synthesis |
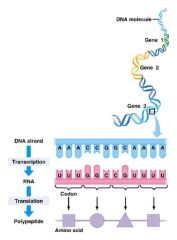
Linear = It's a sequel Colinear = It's a copy of that sequence Proteins are synthesized by a sequence of amino acids
|
|
|
The genetic code is the amino acid translations of the.... |
Nucleotide triplets (three nucleotides specify one amino acid)
|
|
|
61 codons correspond to amino acids and ___ is the start |
AUG Information in DNA is arranged in triplets Three parts of a triplet = one amino acid Three stop codons signal the end of translation |
|
|
If we look at the DNA, we can..... |
determine that there are 61 possible triplets that provide information in the DNA molecule Language of the gene = Genetic code |
|
|
The genetic code is... |
Redundant (more than one codon for some amino acids) Unambiguous (any codon for one amino acid does not code for any other amino acid) Nearly universal |
|
|
AUG = Start ___, ___, and ___ = Stop |
UAA, UGA, UAG |
|
|
When transcription takes place, there is only one section that is transcribed = Template strand |
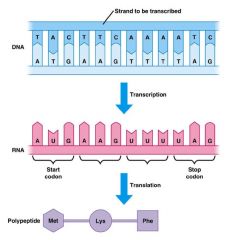
RNA doesn't have T, instead is has U |
|
|
In Transcription.... |
A base sequence in DNA serves as a structural pattern or template for assembling a strand of RNA from the cell's pool of free nucleotides. Happens in the nucleus.
|
|
|
In Translation.... |
Occurs in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. RNA directs the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains. Newly formed chains become folded into the 3D shapes of proteins. |
|
|
Transcription.... |
Occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotes DNA is transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA Only one strand of DNA is transcribed |
|
|
Graph showing Central Dogma |
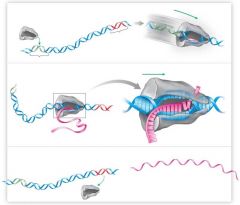
|
|
|
Transcription - mRNA |
Encodes amino acid sequences Conveys genetic messages from DNA to the translation machinery of the cell Must exit the nucleus via nuclear pores |
|
|
Transcription - mRNA |
Contains introns and exons Introns - just there to take up space Exons - Actual information of the messenger |
|
|
Transcription - Picture |
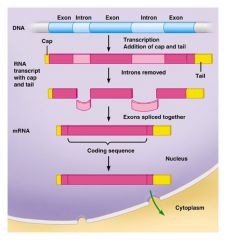
Once finished the RNA transcribed in processed into a functional mRNA molecule |
|
|
mRNA undergoes processing before leaving the nucleus |
RNA splicing - removes introns/splices exons together Cap/Tail of extra nucleotides are added to the ends of the (not translated) Cap/Tail help facilitate the export of mRNA from the nucleus, protect the mRNA from degregation, and help ribosomes to bind to the mRNA |
|
|
Cap/Tail on mRNA |
Cap helps the RNA get out of the nucleus and helps them bond to ribosomes Tail consists of a sequence of Adenine nucleotides (Poly A) called Exonucleases, these are enzymes that can break apart RNA/DNA Poly A chain protects the messenger RNA from Exonucleuses. Tail protects the RNA from breakdown. |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
Functions as an interpreter of mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein |
|
|
tRNA functions by.... |
Picking up the appropriate amino acid Using a special triplet of bases called an anticodon, recognizing the appropriate codons in mRNA |
|
|
Proteins synthesize one ______ at a time |
Amino acid |
|
|
Transfer RNA.... |
Translates the messenger RNA into a sequence of amino acids Each tRNA has a specific amino acid that it bonds to |
|
|
RNA is _________ stranded. DNA is _________ stranded. |
Single, Double |
|
|
Translation occurs.... |
On the surface of the ribosome |
|
|
Ribosomes coordinate the functioning of mRNA and tRNA, resulting in the synthesis of a _______. |
Protein |
|
|
Ribosomes have two _______; small and large. |
Subunits |
|
|
Each subunit is composed of ________ and proteins |
rRNA. And have binding sites for mRNA and tRNA |
|
|
Ribosomes.... |
Do protein synthesis Are synthesized within the nucleus of Eukaryotic cells Have binding spots for tRNA and mRNA |
|
|
Ribosome - Diagram |
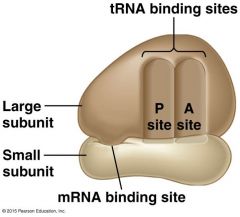
P site and the A site can only accommodate one protein at a time. |
|
|
Ribosome - Diagram |
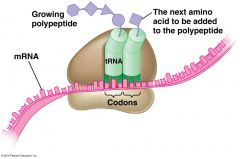
The Anticodon on the tRNA can recognize and compliments the codons on the mRNA |
|
|
Translation can be divided into three phases: |
Initiation, Elongation, Termination |
|
|
Initiation brings together... |
mRNA A tRNA bearing the first amino acid The two subunits of the ribosome
|
|
|
Initiation establishes.... |
Where translation will begin |
|
|
Initiation occurs in two steps - first step... |
An mRNA molecule binds to a small ribosomal subunit and a special initiator tRNA binds to the mRNA at the start codon |
|
|
The start codon... |
Reads AUG and codes for methionine The first tRNA has the anticodon UAC |
|
|
Initiation occurs in two steps - second step... |
A large ribosomal subunit joins the smaller subunit allowing the ribosome to function
|
|
|
The first tRNA occupies the ___ site.... (Initiation step two) |
P, which will hold the growing polypeptide |
|
|
An ___ site is available to..... (Initiation step two) |
A, receive the next amino-acid-bearing tRNA |
|
|
Translation - Diagram |
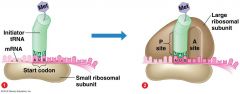
|
|
|
Each cycle of Elongation has three steps....Step 1 |
The anticodon of the incoming tRNA molecule, carrying its amino acid, pairs with the mRNA at the A site of the ribosome |
|
|
Each cycle of Elongation has three steps....Step 2 |
The polypeptide separates from the tRNA at the P site and attaches by a new peptide bond to the amino acid carried by the tRNA in the A site |
|
|
Each cycle of elongation has three steps....Step 3 |
The P site tRNA now lacking an amino acid the ribosome and the ribosome translocates the remaining tRNA from the A to the P site |
|
|
Elongation - Diagram |
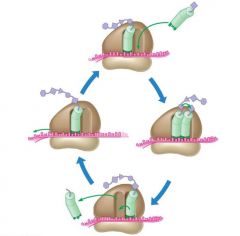
|
|
|
Elongation continues until.... |
Termination |
|
|
Termination..... |
The ribosome reaches a stop codon The completed polypeptide is freed from the last tRNA The ribosome splits back into its separate subunits |

