![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are all organisms made of? |
Cells |
|
|
What is a cell? |
The smallest unit of life that can function independently. |
|
|
What is a Prokaryotic cells? |
A cell bound by a plans membrane enclosing the call contents. There is no nucleus or other organelles. |
|
|
Give me an example of a prokaryotic cell? |
Bacteria |
|
|
What is a eukaryotic cell? |
It has a central control structure called a nucleus which contains DNA |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells have compartments with specialized functions which are... |
It's larger than prokaryotic cells, it has a nucleus. Endosymbiosis theory is also the specialized function of the eukaryotic cell. |
|
|
What is a phospholipid? |
A lipid that is the major component of the plasma membrane; phosopholipids are structurally similar to fats, but contain a phosphorus atom and have two, not the, fatty acid chains. |
|
|
What is polar? |
Positive charged |
|
|
What is non polar? |
Negatively charged particles |
|
|
Give an example of a polar and non polar? |
Cell membrane |
|
|
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic? |
Water loving and water fearing |
|
|
What is a transmembrane proteins? |
It penetrates right through the lipid bilayer, from kn side to the other. Also know as a gatekepper. |
|
|
What are the 4 types of membrane proteins? |
Receptor proteins, recognition proteins, transport proteins, enzymatic proteins. |
|
|
How do people end up with faulty membranes? |
Malfunction of chloride passageways in a cells membrane that causes gradual accumulation of chloride ions within cells. |
|
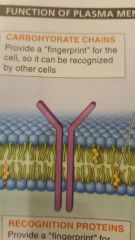
What do proteins do in the plasma membrane? |
It acts as receptors, help molecules gain entry into and out of the cell, and catalyze reactions on the inner and outer cells surfaces. |
|
|
What is the fingerprint that the membranes surfaces use to identify the cell? |
CD4 markers. This molecular fingerprint is there key to the function of your immune system. |
|
|
What is passive transport? |
The molecular movement occurs spontaneously, without the input of energy. |
|
|
Give an example of passive transport... |
Hair wet on a dry towel |
|
|
What are the two types of passive transport? |
Diffusion and osmosis |
|
|
Give two examples of diffusion and osmosis |
Rats in a corner of a room. Brine chicken in water. |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
The passive diffusion of water across a membrane |
|
|
What is active transport? |
Cells use energy to move molecules across a membrane. It pumps (requires energy) |
|
|
What are Endocytosis and Exocytosis are used for? |
Bulk transport. When material cannot get into a cell via diffusion or a pump cells can engulf the molecules or particles with their plasma membrane. |
|
|
What are the connections between cells that holds them in place and enables them to communicate with each other? |
Tight junctions, desmosomes, fall junctions. Most cells are connected to other cells. |
|
|
The nucleus is the cell's genetic what? |
Control Center. It is also the store house for all hereditary information. |
|
|
Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton form what |
the cell's internal environment, provides its physical support, and can generate movement. |
|
|
What does the mitochondria do? |
It converts protein molecules into energy |
|
|
What are lysosomes? |
The cell's garbage disposal |
|
|
The endoplasmic reticulum is what? |
The sites where cells build proteins and disarm toxins. |
|
|
What is the golgi apparatus? |
It processes products for delivery throughout the body. |
|
|
The cell wall provides what? |
Additional protection and support for plant cells. |
|
|
What do vacuoles do? |
They are multipurpose storage sacs for cells. |
|
|
What is chloroplasts? |
Are the plant cell's solar power plant |

