![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Law of Conservation of Energy states that______ cannot be created or_______ but it can be changed from one_______ to ________. |
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
he kinetic energy of an object is theenergy that it possesses due to its motion
|
|
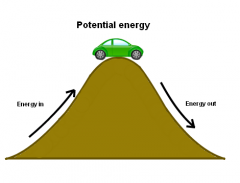
Potential Energy |
potential energy is a result of gravity pulling downwards.
|
|
|
entropy |
lack of order or predictability; gradual decline into disorder.
|
|
|
ATP is the energy_____________ of cells. |
|
|
|
ATP contains a sugar and nitrogen base and three__________. |
|
|
|
ATP can be broken down by breaking last phosphate group bond to form______. |
ADP |
|
|
It can be rebuilt. |
ATP |
|
|
Enzymes |
a.This has an active site where substrate binds. b.can be part of a metabolic pathway c.can be inhibited by an inhibitor (competitive and noncompetitive) feedback inhibition |
|
|
metabolic pathway |
|
|
|
diffusion |
the movement from a high to low concentration
|
|
|
osmosis |
the movement involving water from a high to low concentration
|
|
|
solvent |
a substance that dissolves another
|
|
|
solution |
solvent+solute =
|
|
|
solute |
a substance being dissolved by another
|
|
|
hypotonic solutions |
contain less solute than the cell (water will flow into the cell) |
|
|
hypertonic solutions |
contain more solute than the cell (water will flow into the cell) |
|
|
What happens with a hypertonic solution? |
plant cells become plasmolysed, red blood cells become shriveled or undergo crenation |
|
|
isotonic solutions |
contain the same number of solute molecules as the cell |
|
|
endocytosis |
the transport of solid matter or liquid into a cell
|
|
|
exocytosis |
the transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is extruded through anopening in the cell membrane
|
|
|
phagocytosis |
the ingestion of a smaller cell or cell fragment
|
|
|
pinocytosis |
the transport of fluid into a cell
|
|
|
Receptor-mediated endocytosis |
targets specific organelles to enter through membrane
|
|
|
active transport |
the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy.
|
|
|
The four phases of the breakdown of glucose are: |
Glycolysis transition reaction (prep step)
krebs (citric) cycle electron transport chain |
|
|
products of glycolysis |
two Pyruvate, two NADH, and two ATP
|
|
|
What is substrate level ATP synthesis? |
|
|
|
How many ATP are invested in glycolysis? |
2
|
|
|
Products of the electron transport chain |
|
|
|
photosynthesis |
the complex process by which carbon dioxide, water, and certain inorganic salts are converted into carbohydrates by green plants,algae, and certain bacteria, using energy from the sun and chlorophyll.
|
|
|
fermentation |
The process by which complex organic compounds are broken down by the action of enzymes into simpler compounds without the use of oxygen. It results in the production of energy in theform of two ATP molecules, and produces less energy than the aerobic process of cellular respiration
|
|
|
What organisms can photosynthesize? |
|
|
|
chloroplast |
has a double outer membrane and an interior membrane which makes up thylakoids |
|
|
Light reactions of Photosynthesis occur in the... |
______membrane |
|
|
Calvin Cycle occurs in the |
Stroma of Chloraplast
|
|
|
light reactions |
two photosystems which contain an electron acceptor and pigment |
|
|
The electron transport chain releases energy in the form of a |
H+ gradient (important in ATP production) |
|
|
codon |
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.
|
|
|
anticodon |
a sequence of three nucleotides forming a unit of genetic code in a transfer RNA molecule, corresponding to a complementary codon in messenger RNA.
|
|
|
genetic code |
the nucleotide triplets of DNA and RNA molecules that carry genetic information in living cells.
|
|
|
RNA polymerase |
A polymerase that catalyzes the synthesis of a complementary strand of RNA from a DNA template, or, in some viruses, from an RNA template
|
|
|
ribosome |
a minute particle consisting of RNA and associated proteins, found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells. They bind messenger RNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and proteins.
|
|
|
tRNA |
Small RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the ribosome for polymerization into a polypeptide.Anticodon of the this pairs with a codon on the mRNA being translated
|
|
|
amino acid |
building block of protein (monomer)
|
|
|
Adenine------------------------------------> |
<------------------------------------Thymine |
|
|
Guanine------------------------------------> |
<------------------------------------Cytosine |

