![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Label all of these on heads
dorsal ventral lateral medial anterior posterior
and draw these types of heads transverse plane sagital plane horizontal plane |

|
|
|
hypo |
under |
|
|
nervous system breakdown |

|
|
|
Central Nervous System |
Brain and Spinal Cord |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System |
Connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
contains the somatic and autonomic nervous systems |
|
|
Somatic Nervous system |
Consists of axons conveying messages from the sense organs to the CNS and from the CNS to the muscles |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
contains the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems |
|
|
Gray Matter |
inside spinal chord; dendrites and soma |
|
|
White Matter |
Outside spinal chord; myelinated axons |
|
|
nucleus (CNS) |
a cluster of neurons inside the CNS |
|
|
Ganglion |
a cluster of neurons outside the CNS |
|
|
Dorsal Root Ganglia |
Cluster of sensory neurons outside spinal cord |
|
|
afferent/efferent nerves
location |
afferent nerves = sensory nerves = dorsal horn efferent nerves = motor nerves = ventral horn afferent + efferent nerves = spinal nerve
Dorsal-Afferent Ventral-Efferent = DAVE’s spine
sensory outside spinal cord motor inside spinal cord
|
|
|
pons
other name |
(metencephalon)
means bridge |
|
|
contralateral |
when connected from different side |
|
|
ipsilateral |
when connected on the same side |
|
|
Cranial nerves |
nerves that originate from cranial area |
|
|
medulla
other name |
myelencephalon
vital functions |
|
|
7th cranial nerve |
has to do with facial muscles |
|
|
bell's palsy |
paralysis on one side of face
more common after birth |
|
|
cranial nerve #10
other name |
vagus nerve
wandering nerve; goes everywhere |
|
|
raphe nucleus |
cluster of neurons (nuclei) |
|
|
hindbrain other name components |
rhombencephalon
medulla pons cerebellum |
|
|
cerebellum other name |
metencephalon
involved with coordination |
|
|
midbrain other name components |
mesencephalon
tectum on dorsal side tegmentum on ventral side |
|
|
tectum |
composed of
superior coliculi involved with vision
inferior coliculi basic auditory function |
|
|
tegmentum components |
contains periaqueductal gray
substantia nigra
red nucleus
3rd and 4th cranial nerves |
|
|
periaqueductal gray |
in tegmentum
surrounds spinal fluid involved with pain regulation |
|
|
substantia nigra |
in tegmentum
dopamine producing neurons motor movement
|
|
|
red nucleus |
in tegmentum
deals with motor movement |
|
|
connections between cerebral hemispheres |
corpus callosum (main connection) anterior commissure massa intermedia (connects 2 thalami) |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
layered highest level of processing |
|
|
basal ganglia parts what it does |
complex motor movements
caudate nucleus putamen globus palidus |
|
|
limbic system parts what it does |
motivation and emotion
olfactory bulb hypothalamus hippocampus amygdala cingulate gyrus (part of cerebral cortex)
|
|
|
forebrain parts, other name |
prosencephalon
basal ganglia limbic system cerebral cortex
divided into diencephalon telencephalon |
|
|
diencephalon |
part of forebrain towards medial area
contains thalamus, hypothalamus |
|
|
thalamus |
sensory relay station
all sensory info besides olfactory system goes here to be analyzed first before going to primary corticol areas to be more thoroughly analyzed
motivational behavior
4f's |
|
|
hypothalamus |
bosses around pituitary and tells it to release hormones
divided into clusters of nuclei |
|
|
telencephalon |
part of forebrain
contains pituitary, basal forebrain, hippocampus |
|
|
basal forebrain |
cluster of neurons that creates acetylcholine |
|
|
hippocampus |
involved with memory |
|
|
ventricles (ventricular system) |
hollow area with cerebral spinal fluid
4 of them
|
|
|
what creates spinal fluid? |
choroid plexus cells in the ventricular system |
|
|
how is spinal fluid recycled? |
enters arachnoid circulation diffuses into blood system pee it out |
|
|
hydrocyvalis |
disease where spinal fluid does not exit head caused by obstruction in spinal fluid circulation |
|
|
meninges parts |
protective covering around brain, made up of:
dura mater (hard covering)
arachnoid membrane (spongy; spinal fluid fills up here)
pia mater (soft, many blood vessels |
|
|
cerebral cotex parts |
frontal lobe parietal lobe occipital lobe temporal lobe |
|
|
frontal lobe |
contains primary motor cortex prefrontal lobe
|
|
|
prefrontal lobe |
planning actions use of logic use of working memory doesn't fully mature until later teens |
|
|
parietal lobe |
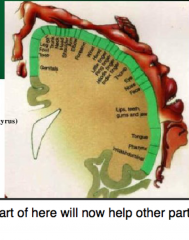
houses primary somatosensory cortex
primary somatosensory cortex: involved with basic processing of touch information
|
|
|
occipital lobe other name |
Striate cortex
basic vision analysis most of it is within grooves of brain; calcarine fissure is deepest groove
|
|
|
cortical blindness |
blindness resulting from damage of occipital lobe |
|
|
temporal lobe |
upper part analyzes auditory in sophisticated ways
bottom part analyzes vision in sophisticated ways
emotions, motivational behaviors |
|
|
kluver bucy syndrome |
characterized by loss of fear and mating with weird sh1t;
caused by damage of temporal lobe |
|
|
Brain imaging techniques
recording brain activity techniques |
Imaging:
CT scan MRI
Recording Activity:
EEG MEG PET scan fMRI
|
|
|
MRI scan |
turn on magnet affects hydrogen put in energy source hydrogen absorbs energy hydrogen releases energy detectors detect energy
detectors make picture
best resolution
expensive |
|
|
EEG (Electroencephalograph) |
put electrodes on brain those electrodes measure average activity of cells under them |
|
|
evoked potential |
EEG in response to stimulus |
|
|
MEG (magnetoencephalography) |
creates picture of how magnetic fields are changing with brain
can show changing brain activity over time
functional and structural information |
|
|
PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
|
person drinks glucose tagged with radioactive substance active brain areas suck up glucose radioactive substance decays positron released comes into contact with electron and is anihilated 2 gamma photons shoot out from each collision computer detects gamma rays gives an image to show which areas of brain are most active
exposed to radiation expensive to create cyclotron
|
|
|
fMRI |
which brain areas are sucking up most oxygen?
deoxygenated blood acts differently in magnetic field
computer creates image where most activated areas are
functional and structural information |
|
|
quasai experiment |
compare people who have and don't have brain damage
|
|
|
stereotaxic aparatus |
keeps head steady/still while doing surgery |
|
|
bregma |
area where skull plates come together
can see under skin
can find brain parts from there |
|
|
lesion |
causing brain damage
can do this with:
asperation (sucking up brain tissue)
electrolytic lesion (electrode to burn)
kainic acid (overstimulates and kills)
6-HD (selectively kills certain neurons related to DA and NE |

