![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the spectrum of visible light
|
430-750nm
|
|
|
sclera
|
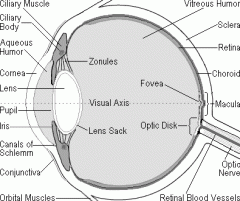
outer coat
tough, opaque connective tissue |
|
|
cornea
|
front surface
transparent fixed lens to focus light |
|
|
choroid
|
inner of the scelra
sheet of cells filled with black pigment absorbs light blood vessels |
|
|
ciliary body
|
anterior part of choroid
consists of ciliary muscle smooth muscle responsible for changing the shape of the lens changes focus of the eye for near and far vision ciliary processes secrete aqueous fluid |
|
|
iris
|
pigmented( eye color)
anterior to ciliary body diaphram muscular region regulates size of pupils |
|
|
pupils
|
in the center of the iris
|
|
|
retina
|
covers the inside of the choroid
light sensitive structure 2 types of photoreceptors (rods and comes) location of specialized neurons in the eye |
|
|
rod cells
|
1. doesnt detect color
2. detects shape and movement 3. responds well at low light level 4. when light falls on rod cells rhodopsin changes shape--> depolarization occurs |
|
|
comes
|
1. color vision
2. bright and light vision 3. fine detail |
|
|
macula
|
area near the center of retina
1. absorbs UV light ---sunblock |
|
|
fovea
|
center of macula
tightly packed comes no rods images clearly focused |
|
|
optic discs (blind spot)
|
where optic nerve leave eye
no rods or comes light that focuses on that part of the retina is not detected-->blind spot |
|
|
lens
|
-attached to ciliary body by suspensory ligament
-devides eye into two -anterior(aqueous) and posterior(vitreous) cavity -fluids- liquid lens focuses light on retina |
|
|
glaucoma
|
can occur by blockage of ducts that drain aqueous fluid
1. increase pressure 2. damages retina 3. blindness |
|
|
conjunctive
|
anterior to cornea
moisture |
|
|
optic nerve
|
rods and comes synapse with bipolar neurons
ganglian cell(unite)-->optic nerve--> out of the eyeball-->brain summary on pg 930 |

