![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
John ray |
Described many plants as monocots and dicots |
|
|
|
Caroleus Linnaeus |
Father of taxonomy Published systema naturea 17,500 plants |
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
Classification of organisms |
|
|
|
Ancient |
Usefulness for any reason |
|
|
|
Artificial |
One or very few attributes |
|
|
|
Natural |
As many attributes as possible Has to be a physical trait not mental |
|
|
|
Phylogenetic |
Characteristics with common evolutionary history such as a race or tribe |
|
|
|
Cladisitics |
Arrange in order and time with evolution |
|
|
|
Cladogram |
Drawing of phylogenetics |
|
|
|
Dichotomous keys |
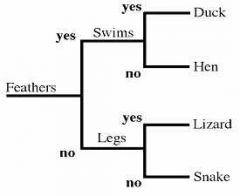
a key used to identify a plant or animal in which each stage presents descriptions of two distinguishing characters, with a direction to another stage in the key, until the species is identified |
|
|
|
Couplets |
Two items of the same kind. |
|
|
|
Leads |
A dichotomous key is a list of paired statements (each statement is called a lead) that guides you to the identification of a specimen. The paired leads (the pair of leads together is called a couplet) are contrasting descriptions of certain characteristics. In a good key, couplets are written so that you must choose one or the other of the leads as being true for your specimen. Couplet leads should always be mutually exclusive |
|
|
|
Naming major ranks |
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: plantae Division: coniferophyta Class: coniferopsida Order: coniferales Family: Taxodiaceae Genus: sequoiadendron Specific epithet: giganteum |
|
|
|
Binomial system |
Genus and specific epithet Italicized or underlined or both |
|
|
|
Genus |
General name Last name First word Capitalized |
Morgan |
|
|
Specific epithet |
First name Second word Not capitalized |
Hollis |
|
|
Author |
Whomever named the organism |
|
|
|
Early scientific views |
Christianity/Religion |
|
|
|
Thales |
Father of speculative science Life is from water Study nature by nature not supernatural |
|
|
|
Anaximander |
Thales student Simple life forms preceded complex forms |
|
|
|
Aristotle |
Father of biology Published scala naturae |
|
|
|
Theological views |
313AD Constantine grants religious freedom for all which means more people in his kingdom for more tax. Rome falls and the catholics take over. |
|
|
|
St. Augustine |
1) study nature to know god 2) god created perfect ideal types 3) perfect types won't change 4) humans created in image of God |
|
|
|
Catastrophism |
The world is shaped by catastrophic events. The earth sits at center of the universe and at most 6000 years old. |
|
|
|
The Roman Catholic church |
The dark ages from about 410ad-1500ad Suppression of free thinking |
|
|
|
The inquisitions |
Catholic church policed and killed those who they thought were against the church |
|
|
|
The Darwinian west |
The Roman Catholic Church breaks up and there's a new way of thinking. Philosophical views are scientific. Start to question St. Augustine. |
|
|
|
James Hutton |
The father of historical geology Published theory of the earth |
|
|
|
Uniformitarianism |
Same natural laws and processes that operate in the universe now and have always operated in the universe and apply everywhere. |
|

