![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define ecosystem |
All living and non living components in a habitat and their interactions |
|
|
Define community |
All populations of different species that live in an area and can interact |
|
|
Define niche |
Role each specie plays in an ecosytem |
|
|
What is a biotic factor |
Living factor e.g. disease |
|
|
What is intraspecies competition |
Competition within a specie |
|
|
What is npp |
Net primary productivity - rate at which carbohydrates accumulates in the tissue of plants |
|
|
What does npp equal |
pp - respiration |
|
|
Why does the pyramid of organisms get narrower nearer the top |
As energy is converted into e.g. heat so less is passed up the food chain so few tertiary consumers can survive |
|
|
What is a pyramid of biomass |
Area of bars are proportional to dry mass of organisms at each trophic level |
|
|
Describe the pyramid of energy |
Organisms are burnt to see how much energy is related and then calculated per gram by using the temperature rise of water |
|
|
What is primary productivity |
Total amount of energy fixed by photosynthesis |
|
|
How can you improve primary productivity |
Drought resistant crops Greenhouses Crop rotation Pesticides/fungicides/herbicides
|
|
|
How can you improve secondary productivity |
Consume younger animals as more energy for growth so more available Steroids but illegal causing quicker growth Antibiotics preventing pathogens Grow in a warm area so less energy for temp maintenance |
|
|
Describe primary succession |
Pioneer community live on bare rock e.g. algae Rotting and erosion form soil so moss and ferns can grow larger plants succeed that making a stable community |
|
|
What is secondary succession |
Succession on damaged habitat |
|
|
How can we study ecosystems |
Quadrat Transects - either note species touching line at regular intervals (line) or place a quadrat along it or measure continously (belt) |
|
|
Describe saprotrophs |
Secrete enzymes on to material which caused it to be broken down and is then absorbed into body for storage or respiration |
|
|
Describe the nitrogen cycle |
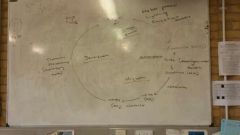
|
|
|
Describe nitrogen fixation |
Mostly done by nitrogen fixing bacteria like rhizobium in root nodules in peas or beans Converts nitrogen in air into ammonia Can occur through lightning or the haber process. The ammonia is the added to urea (from excretion or dead matter) to form ammonium ions in ammonification |
|
|
Describe nitrification |
Chemoautotrophic bacteria absorbs ammonia They gain energy by oxidising ammonium ions into nitrites using nitrosomonas or oxidising nitrites into nitrates by nitrobacter Some nitrates absorbed by soil to make e.g. proteins IT IS AN AEROBIC PROCESS |
|
|
Describe denitrification |
Converting nitrates to nitrogen When bacteria are growing in anaerobic conditions nitrates are used as a source of oxygen producing nitrogen and nitrous oxide |
|
|
Define carrying capacity |
The maximum population size that can be sustained in an area at a specific time |
|
|
Describe what k strategists believe |
Population is determined by carrying capacity and will level out |
|
|
What do r strategists believe |
Boom and bust Once carrying capacity has been exceeded population will die out due to a lack of resources |
|
|
Describe the relationship between predators and prey |
As population of predators increase prey will decrease but when prey runs out predators will begin to die so prey can increase again |
|
|
Describe the competitive exclusion principle |
If 2 species have the same niche one would die out |
|
|
What is allelopathy |
Where plants release chemicals to inhibit other plants from using resources, growth or uptake |
|
|
Name and describe 3 ways of sustainable small scale timber production |
Coppicing - cutting a tree closer to the ground promoting new growth e.g. deciduous trees Pollarding - tree is cut higher up to prevent deer from eating new shoots Rotational coppicing - provides continuous wood, cut every 20 years allowing biodiversity
|
|
|
Name and describe 2 ways of sustainable large scale timber production |
Clear felling - clearing all trees destroying soil Selective cutting - cutting only certain plants |
|
|
How can we conserve |
National parks Zoos Sites of special scientific interest Food Vaccines Culling predators Prevent poaching |
|
|
List reasons to conserve |
Right to live Our responsibility Food Drugs Tourism Jobs Climate control Natural pest control maintain biodiversity and gene pool protect indigenous people aesthetics |
|
|
how can you measure energy content |
bomb calorimeter known dry mass burnt in oxygen and measure rise in temperature of water |
|
|
what plants contain rhizobacterium |
legumes in the root nodules e.g. peas |
|
|
what is the difference between abundance and distribution |
abundance - no. of individuals distribution - presence or absence of an organism |
|
|
what is ecology |
the study of interactions between organisms and their environment |
|
|
explain how to work out the distribution and abundance of plants in an area |
lay tape measure continuous line transect using a quadrat work out % cover use quadrat for ACFOR scale use a key to identify species ensure a data recording sheet is present |
|
|
what is the benefit of coppicing/pollarding and selective cutting |
prevents disruption to habitat maintain biodiversity prevents soil erosion pollarding prevents deer from eating shoots |
|
|
Name and describe different isolating mechanisms |
Geographical isolation Seasonal - mating seasons mechanical gamete compatibility behavioural - pheremones |
|
|
describe a mutualistic relationship |
rhino and oxpecker birds |
|
|
what is conservation |
the process of managing an ecosystem sustainably to protect biodiversity |
|
|
Why can speciation occur |
geographical isolation reproductive isolation climate/environment seasons - breeding |
|
|
Name native species of animal on the Galapagos islands |
lava lizards Cacaotillo shrub Scalesia trees land iguana sea cucumber |
|
|
name some invasive species to the Galapagos islands |
Red quinine feral goats pigs |
|
|
what do decomposers do |
bacteria/fungi they are saprotrophic so secrete enymes on to dead or waste matter releases CO2 and H2O makes ammonium |
|
|
define producer |
autotrophic synthesise their own complex organic molecules |
|
|
define consumer |
they feed on the the organisms |
|
|
define trophic level |
level in a food chain |
|
|
whats the difference between the pioneer and climax community |
pioneer - lower biomass, succession and less stable, first organisms climax - opp. |
|
|
what does decomposition and denitrification do differently |
decomposition increases nitrates but denitrification lowers the amount |
|
|
name the two types of sampling |
systematic random |

