![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is succession |
A directional change in the community of organisms over time It is a natural non-human event Occurs over a timescale of many years |
|
|
What is a climax community |
The final stage of succession. Manor stable community is reached populations exist in balance |
|
|
What is primary succession |
No soil plants ; uncolonised ground on newly formed Lake. For example sand dunes or volcanic eruptions |
|
|
What is secondary succession |
The destruction of a previously colonized area. For example forest fires , landslides |
|
|
What is a Pioneer species |
Species which are first to colonize the ecosystem and begin succession. They start to build up a layer of soil through death and decay |
|
|
What is deflected succession |
Burning, grazing, mowing, hopes succession as particular sere |
|
|
What is a sere |
Seral community. A community within a succession |
|
|
How are Pioneer species adapted |
To survive in a hostile abiotic Factors in the environment. For example xerophytes, root nodules, wind pollinaters. Can tolerate extreme conditions that are in favourable two other species. For example lack of nitrates in the soil. |
|
|
What is a niche |
The role of each species and ecosystem |
|
|
Give an example of a large medium and small scale ecosystem |
Large, African grassland all rainforest Medium, football pitch for garden Small, rockpool or tree |
|
|
What is the competitive exclusion principle |
Two species that compete for the exact same resources cannot stably coexist as one will be better adapted and out compete the other |
|
|
What is an abiotic Factor and give examples |
The effect of a non living component on an ecosystem. Rainfall, soil pH, temperatures, oxygen availability and pollutants |
|
|
What is a biotic factor and give an example |
Living factors which affect an ecosystem Producers, primary consumer, secondary consumer, competition, and disease |
|
|
What is a directional and cyclic change in an ecosystem |
Direction of change is a change in One Direction. For example the erosion of a coastline Cyclic changes or changes that repeat themselves in a rhythm |
|
|
What is each level of a food chain called |
Trophic level |
|
|
Why can counting the number of organisms in a food chain lead to an untrue representation of the biomass in an ecosystem |
It does not take into account the Life Processes that occur for example respiration, waste material, and death |
|
|
What is a more accurate way of measuring biomass in the ecosystem |
Measure the dry mass of each trophic level Collect all of them organisms and put them in the oven at 80 degrees until all the water has evaporated and it has reached a constant mass |
|
|
Why is a pyramid of biomass always pyramid shaped |
Each trophic level some of the biomass consumed is lost from the food chain and therefore unavailable to the next trophic level This occurs through processes such as respiration Waste products such as urine and faeces also contain biomass which is lost Undigested part of the plant such as bones and hair and tissues cannot be digested so are excreted and not eaten |
|
|
How do you calculate ecological efficiency |
Biomass at higher trophic level ----------------------------_-------------------- x100 Biomass at lower trophic level |
|
|
How can you manipulate the transfer of biomass through ecosystems in primary productivity |
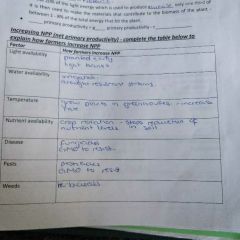
|
|
|
What is primary productivity |
Light energy converted into plant biomass through photosynthesis |
|
|
How do humans maximise secondary productivity |
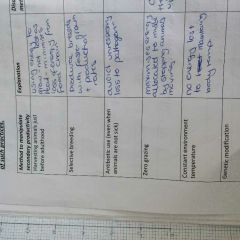
|
|
|
How is energy and materials lost from food chain |
Excretion, waste, death, inability to digest the full biomass |
|
|
What are saprotrophs |
Decomposers that feed saprotrophically |
|
|
How does saprotrophic decomposition work |
It secretes enzymes into the dead and waste material comma digesting the material into small molecules which are absorbed into the saprotroph body. These molecules are stored or respired |
|
|
Carbon cycle diagram |
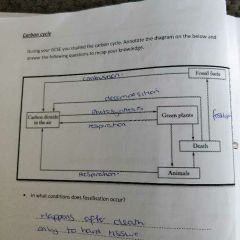
|
|
|
How do humans disrupt the carbon cycle |
The Burning of fossil fuels release more carbon dioxide Killing animals the decomposition releases more CO2 |
|
|
The nitrogen cycle diagram |
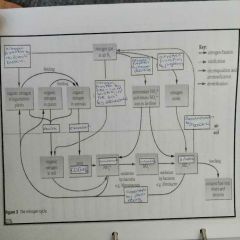
|
|
|
What is ammonification |
The release of ammonium ions by the decay of Dead Matter by bacteria which can undergo the process of nitrification |
|
|
What are ammonium ions oxidised into |
Nitrates |
|
|
Azobacter |
They live freely in the soil and fix nitrogen from the air |
|
|
What is a chemoautotrophic bacteria |
They obtain energy from the soil |
|
|
What is a decomposer |
Bacteria and fungi who feed on decomposing matter |
|
|
What is denitrification |
Conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas nitrous oxide and requires anaerobic conditions |
|
|
What is nitrification |
The oxidation of ammonium to nitrite and then nitrite to nitrate. Only happens in aerobic conditions |
|
|
What is the nitrogen cycle |
A series of processes by which nitrogen and it's compounds are interconverted in ecosystems |
|
|
What is nitrogen fixation |
Conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates or ammonium by nitrogen fixing bacteria such as a azobactor or rhizobium |
|
|
What is a nitrobacter |
Oxidises nitrites to nitrates |
|
|
What are nitrosomonas |
Converts ammonium to nitrites |
|
|
How to work out population size of a species |
Mean number of individuals of the species in each quadrat÷fraction of the total habitat area covered by a single quadrat |
|
|
How to use a line transect |
Measure at regular intervals, and make note of which species is touching the tape at that interval |
|
|
How to use a belt transect |
At regular intervals, place a quadrat next to the line (un interrupted belt transect) and measure from the quadrat. Or place a quadrat next to the line moving it along the line after looking at each quadrat (continuous belt transect) |

