![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition of homeostasis |
Maintaining a constant internal environment despite changes in the external or internal environments |
|
|
Example of internal conditions that homeostasis effects |
Body temperature Blood glucose concentration Blood salt concentration Blood water potential Blood pressure Carbon dioxide concentration |
|
|
What is a set point |
The desired level at which the system operates |
|
|
What is a stimulus |
The information from our environment that identifies a change away from the optimum |
|
|
What is a receptor |
A sensory cell that detects the stimulus |
|
|
What is an input |
The message sent by the cell signalling from receptor to the coordination Centre |
|
|
What is the coordination Centre |
Coordinates information from various receptors and sends instructors to the effectors |
|
|
What is an output |
The message sent by cell signalling from the coordination Centre to the effector |
|
|
What is the effector |
Target cells in the hormonal system or muscle cells in the nervous system that receives information from the coordination Centre and brings about the necessary change |
|
|
What is a response |
A change in the environment condition in relation to the optimum brought about by the effector |
|
|
What is a feedback loop |
Inform the receptor of the changes to the system brought about by the effector |
|
|
Explain positive feedback |
I change away from the optimum causes an increase in the original change. A small stimulus causes a large and Rapid Response away from the optimum. This can destabilize the system. |
|
|
Where is positive feedback beneficial |
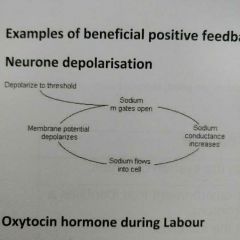
In neurones |
|
|
Explain negative feedback |
I change away from the optimum causes a return to the original value |
|
|
What are the four processes that account for heat exchange in the skin |

Conduction Convection Radiation Evaporation |
|
|
Explain vasodilation |
It is a physiological process in which arterioles and large to allow more blood to flow through capillaries flowing near the skin surface. Mohit leaves the Blood by conduction into the skin cells where it is Lost by convection and radiation |
|
|
Explain vasoconstriction |
It is a physiological process in which arterioles constrict so no blood flows through capillaries near the skin surface but instead through the subcutaneous fat layer where is his insulated allowing only a little heat to be conducted away from the blood into surrounding cells |
|
|
Explain sweating panting and licking as a mechanism for temperature control |
It is a physiological process in which organisms sweat when I have no fur or Feathers and the liquid on skin surface caused the skin by evaporating with the heat. Organisms with no sweat glands pant which causes evaporation from the mouth and tongue |
|
|
Explain shivering |
It's a physiological process in which rhythmic and control contraction of muscles produces heat energy in cold environments to increase body temperature |
|
|
Explain nocturnal behaviour |
It is behavioural and is done to avoid heat in the day |
|
|
Explain a countercurrent heat exchanger |
It is an anatomical feature in which veins and arteries positioned close together exchange heat. The heat in the artery blood going towards the limbs are transferred by conduction to call a blood returning to the core of the body |
|
|
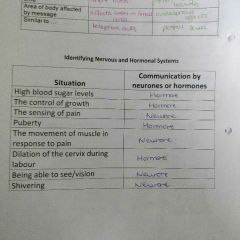
Identifying stimuli and responses |

|
|
|
Comparing the nervous system and hormonal system |

|
|
|
Identify nervous and hormonal systems |
|
|
|
Explain signalling between distant cells |
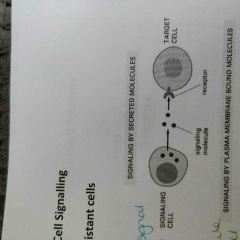
It requires signal molecules to be able to move between cells |
|
|
Explain signalling between adjacent cells |
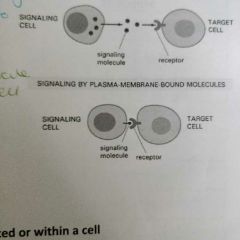
Signal molecules can be attached to self services and does not need to travel |
|
|
Explain hydrophilic and hydrophobic receptors |
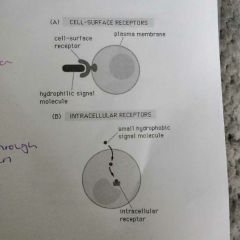
Hydrophilic requires the cell surface receptors Hydrophobic passes through plasma membrane to an intracellular receptor |
|
|
Explain ectotherms |
Receives heat primary from external sources Does not produce its own heat and regulates temperature via other means Circulatory system is Major and then she was a close connection between the blood vessels and their skin Heat exchange between blood and the environment occurs in animals extremities such as their feet and tail It prevents heat loss by constricting blood vessels and limiting the blood flow to the skin They increase the blood flow to get rid of excessive heat Fish Have a counter current heat exchange system |

