![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dizzy Kangaroos Punch Children on Family Game Shows |
Taxonomic Groups from Broad to Narrow (8) |
|
|
Cladistics |
- Provided infinite levels unlike taxonomy to classify organisms |
|
|
Phylogeny |
Evolutionary history of a species or a group of relates species |
|
|
Systematics |
- Classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships using fossil, molecular, and genetic data |
|
|
Root Tree |
- Includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree |
|
|
Basal Taxon "OUTGROUP" |
- Diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group - Not necessarily less evolved or more ancestral |
|
|
Polytomy |
- Branch from which more than two groups emerge- - Unresolved pattern of divergence |
|
|
1. Sister Taxa 2. Polytomy 3. "Outgroup" |
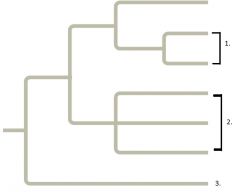
|
|
|
A. Show patterns of descent |
What can be learned from phylogenetic trees? A. Show patterns of descent B. Show phenotypic similarity C. Indicate when species evolved D. Show how much change occurred in a lineage after the branch point E. Allows assumption that taxon evolved from taxon next to it |
|
|
Morphological Molecular |
2 Types of Data used to infer phylogenies |
|
|
Homologies |
Phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared similarity |
|
|
Analogies/Homoplasies |
- Analogous structures or molecular sequences that evolve independently |
|
|
Homoplasy |
- Analogy in a gene |
|
|
Cladistics |
- groups organisms by common descent |
|
|
Clade |
Group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants- - Evolutionary history that implies what you look like Ex: Tetrapods |
|
|
Monophyletic |
-Taxon is equivalent to a clade only if it consists of an ancestral species and all of its descendants |
|
|
Paraphyletic |
- Consists of ancestral species, and some, but not all, of its descendants - Leaves out descendant that should be included |
|
|
Polyphyletic |
- Includes distantly related species but does not include most recent common ancestor - Includes descendant that doesn't belong |
|
|
Ancestral Character |
- characters shared by the outgroup and ingroup that predate the divergence of both groups |
|
|
Derived character |
evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade (defines a branch point) |
|
|
Maximum Parsimony |
Assumes that the tree requires the fewest evolutionary events (appearances of shared derived characters) is the most likely |
|
|
Grade |
- What you look like - Group whose members share key biological features Ex: Coelomates and Pseudocoelomates |
|
|
Phylogenetic bracketing |
- Allows us to predict features of an ancestor from features of its descendants Ex: Infer characteristics of dinosaurs from birds and crocodiles |
|
|
Gene Duplication |
- Provides more opportunities for evolutionary change - Can result in gene families |
|
|
Orthologous Genes |
- Genes found in a single copy of the genome and are homologous between species - Only diverge after speciation |
|
|
Paralogous Genes |
- Genes resulting from gene duplication, so are found in more than one copy in the genome
- Can diverge within the clade that carries them and often evolve new functions Ex: Humans and mice |
|
|
2. Versatility of the gene 3. Complex control of genes |
Complexity of an organism is linked to the 1. Gene number 2. Versatility of the gene 3. Complex control of genes Select all that apply. |

