![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
GENETICS |
the scientific study of heredity -explains shy offspring share similar traits to their parents, grandparents & other family members |
|
|
|
GE ETIC INFORMATION |
DNA- wound tightly during mitosis (forms chromosomes) chromatin- DNA in it's loose, unwound |
|
|
|
HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES |
Have the same genes but might have different versions (alleles) of those genes |
|
|
|
DIPLOID CELLS |
Have two alleles for each gene -might be identical (AA) or different (Aa) |
|
|
|
LOCUS |
In each gene it's location on a chromosome |
|
|
|
GREGOR MENDEL (1822-1884) |
-was born in Silesia (now part of the Czech Republic) -he founded the science of genetics -he ide tidied many of the rules of heredity that explain bkw traits are passed through generations of living things |
|
|
|
GREGOR MENDEL- HERITABLE VARIATION & PATTERNS OF INHERTIANCE |
Heredity- transmission of traits from one generation to the next -he published a paper in 1866 & correctly argued that parents pass on discrete, hereditable factors to their offspring -his work was rejected at first in the scientific community & wasn't widely accepted until after he died. During his own lifetime, most biologists held the idea that all characteristics we're passed to the next generation through blending inheritance, in which the traits from each parent are averaged together. His work was rediscovered in the 1900s & it's importance recognized |
|
|
|
MENDEL'S GARDEN PEA EXPERIMEMT |
He studied garden peas because -are easy to grow -come in many readily distinguishable varieties -easily manipulated -can self-ferilize Character- veritable feature that varies among indivisuals Trait- variation of the character -each of the 7 characters occurrednin two distinct forms |
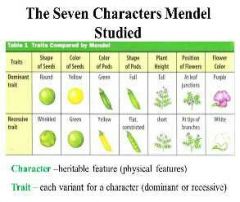
|
|
|
GREGOR MENDEL- BASIC LAW OF INHERITANCE |
True-Breeding Varieties- plants bred true for a specific trait -crossed two true-breeding varieties to produce Hybrids Hydrids- offspring True-Breeding- plants produce offspring identical to themselves |

P parental generation F1 first hybird generation F2 second generation resulting from a cross of two F1 individuals |
|
|
MONOHYBRID CROSSES |
-cross between parent plants that differ in only one character -parent plants differ only in colour (one characteristics) -demonstrated that there are alternate versions of genes (the units that determine inheritable traits Alleles- alternative versions of a gene |
|
|
|
GREGOR MENDEL'S FINDINGS |
He developed many hypotheses from experimentation 1. There are alternative versions of genes (alleles) 2. For each character, an individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from mother & fathe 3. An individual homozygous for the gene if he/she inherits the same version of the gene from the parents 4. An individual hetrozygous for the gene if he/she inherits two different versions of the gene, one version from mother & father |

|
|
|
GREGOR MENDEL'S LAWS |
1. Law of Segregation- in diploid organisms, chromsomes pair (& their alleles) are seperated into individual gamete (egg or sperm) during Meiosis I. Gametes carry only one allele (haploid) 2. Law of Independent Assortment- states that the alleles of one gene sort into the gametes independently of the alleles of another gene 3. Law of Dominance- dominant allele completely makes the effects of a recessive allele. A dominant allele produces the same phenotype in homozygotes & hetrozygotes |

|
|
|
BASIC LAW OF INHERITANCE |
Genotype- individual's two alleles from one gene Phenotype- orservable characteristics Homozygous Dominant- two dominant alleles of a gene Heterozygous- one dorminant & recessive allele Homozygous Recessive- two recessive alleles |

|
|
|
DOMINANT |
alleles exert their effects whenever they are present |
|
|
|
RECESSIVE |
allele is one whose effect is masked -dominant allele is present |
|
|
|
PUNNETT SQUARE & DIHYBRID CROSS |
Punnett Square- highlights the four possible combinations of gametes & their probabilities that result from each cross Dihydird Cross- crossing of parental varieties differing in two characters |

|
|
|
TESTCROSS |
mating between an individual of dominant phenotype (unknown genotype) & homozygous recessive individual |
|
|
|
WILD-TYPE TRAITS |
-most often in nature & aren't necessarily specified by dominant alleles |
|
|
|
PEDIGREE |
-depicts family relationships & phenotypes -tracks an autosomal recessive disorder |

|
|
|
CYSTIC FIBROSIS |
-most common lethal genetic disease -caused by recessive allele |
|
|
|
HUNTINGTON'S DIEASE |
Dominant -leads to degeneration of the nervous system, begins at middle age |
|
|
|
ACHONDROPLASIA |
Form of dwarfism -homozygous dominant genotype chases death of the embryo -only hetrozygotes have this disorder |
|
|
|
GENETIC TESTING & EUGENICS |
Amniocentesis- collects cells from smniotic fluid Chorionic Villus Sampling- removes cells from placental tissue -genetic counseling helps patients understand the results & implications of genetic testing |
|
|
|
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE |
F1 hybirds have an appearance in between the phenotypes of the two parents |
|
|
|
HYPERCHOLESTROLEMIA |
-characterized by dangerously high levels of cholesterol in the blood -incompletely dominant -heterozygotes have blood cholesterol levels a out twice normal -homozygotes have blood cholesterol levels about five times normal |
|
|
|
ABO BLOOD GROUPS |
-human blood type alleles IA & IB exhibit codominace Codominance- both alleles are expressed in the phenotypes -notation used to indicate the alleles is slightly different because there is more than two alleles -immune system produces blood proteins called ANTIBOTICS that can bind specifically to blood cell carbohydrates -blood cells may clump together if blood of a different type enter the body -clumping reaction is the basis of a blood-typing lab test |
|
|
|
PIEOTROPHY |
impact of a single gene on more than one character |
|
|
|
SICKLE-CELL DISEASE |
-exhibits pieotropy -results in abnormal hemoglobin production -causes disk-shaped red blood cells to deform into a sickle shape with jagged edges |

|
|
|
POLYGENIC INHERITANCE |
addictive effects of two or more genes on a single phenotype |

|
|
|
POLYGENIC TRAITS |
-skin color -affected by more than one gene |
|
|
|
SEX CHROMOSOME |
-influence the inheritance of certain traits Males- XY Females- XX |
|
|
|
SEX-LINKED GENES |
any gene located Lon sex chromosome -often found on the X chromosome Red-Green Color Bindness- common human sex-linked disorder |
|
|
|
HEMOPHILIA |
sex-linked recessive blood-clotting trait that may result in excessive bleeding & death after relatively minor cuts & bruises |
|

