![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Label |
|
|
|
How can residual volume be measured? |
Gas dilution test (breathes into a container and changes in volume is measured) and body plethysmography (sits in an airtight room and breathes through a mouthpiece while the pressure and air flow is measured) |
|
|
What is breathing rate? |
Number of breaths taken per minute |
|
|
What is ventilation rate and how do you calculate it? |
Total volume of air inhaled in 1 min Tidal volume * Breathing rate |
|
|
What are 4 limitations for insects for gaseous exchange? |
The have high oxygen demands because they are active Low SA:V Tough exoskeleton so no gaseous exchange No blood pigments so oxygen is delivered directly to cells |
|
|
What are spiracles? |
Small openings along the thorax where gases and water can leave and enter. |
|
|
What are tracheae? |
They carry air into the body, running both into and along the body. Tubes are lined with spirals of chitin which is relatively impermeable to gases and keep them open if bent/pressed (1mm wide) |
|
|
What are tracheoles? |
A single greatly elongated cell (0.7mm wide)so they are freely permeable to gases. They run inbetween cells and are the main site of gaseous exchange. Large SA as there are many of them and air moves along here via diffusion |
|
|
What is the function of tracheal fluid? |
Oxygen dissolves into the moisture at the ends of tracheoles and this limits penetration of air for diffusion But when oxygen demands of high fluid moves out of the tracheoles Via osmosis exposing more exchange surface, increasing SA |
|
|
How is gas exchange controlled in insects? |
The opening and closing of spiracles using sphincters |
|
|
What are the other methods of increasing levels of gaseous exchange? |
Mechanical ventilation- Air is actively pumped into the system by muscular pumping of the thorax/abs. This changes the pressure of the system
Collapsible enlarged trachea or air sacs- These act as reservoirs and are used to increase the amount of air through the system |
|
|
What are the limitations of gaseous exchange in water? |
Water is 1000 times denser than air It is 100 times more viscous than air It contains less oxygen Lung like respiratory organs would use up far too much energy |
|
|
Why do fish need transport systems? |
They are very active so oxygen demands are high They have a low SA:V Scaly outside prevents gaseous exchange |
|
|
What is the operculum? |
A bony flap that protects the Gill cavity which is also active in maintaining the direction of flow of water It allows fish to move water over their gills all the time (even when stationary) |
|
|
What is ram ventilation? |
When cartilaginous fish rely on continual movement to ventilate their Gills |
|
|
What is the function of the Gill Arch? |
It supports the structure of the Gills |
|
|
What is the function of the gill lamellae? |
They are the main site of gaseous exchange in a fish (appendages on gills) |
|
|
What is the function of Gill filaments? |
It relies on the flow of water to keep them apart to increase SA for higher rates of diffusion |
|
|
How does the fish breathe? |
1. The mouth opens and the floor of the buccal cavity is lowered this increases the volume of the buccal cavity and the pressure decreases so water moves in 2. The operculum shuts and the opercular cavity expands lowering the pressure of the cavity 3. The floor of the buccal cavity moves up increasing the pressure so water flows over the Gills |
|
|
Why are cartilaginous fish less effective at gaseous exchange? |
Because blood and water flow in the same direction |
|
|
What 3 things determine the structure of an exchange surface in an organism? |
Size of organism Where it lives The metabolic demands of the organism |
|
|
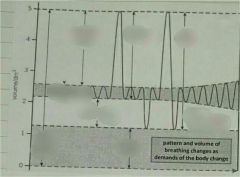
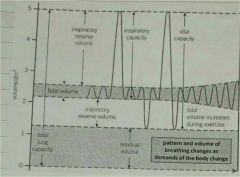
How is a single breath showed on a spirometery trace? |
The peak of expiration to the trough of inspiration |
|
|
How can the volume of initial oxygen in the tank be measured? |
Difference between the trough of the first inspiration to the trough of the last inspiration |
|
|
How is the breathing rate measured? |
The number of inspirations taken (troughs) within a certain time, divided by that time |
|
|
What are the extra adaptations gills have for effective gaseous exchange? |
The tips of adjacent Gill filaments overlap increasing the resistance to the flow of water and this slows the movement of water down, allowing more time for gaseous exchange to occur Countercurrent flow is when water and blood flow in opposite directions this adaptation ensures that a constant steep conc. gradients is maintained than if the blood was flowing parallel to the water making diffusion faster and more effective |

