![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two forms of energy
|
Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
|
|
|
Thermodynamics
|
Study of energy transformations
|
|
|
First law of thermodynamics
|
Energy can not be created or destroyed
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics
|
Energy transformations increase the overall disorder of the universe
|
|
|
Entropy
|
Amount of disorder
|
|
|
What do chemical reactions do?
|
Store or release energy
|
|
|
Endergonic reactions
|
require energy input
|
|
|
Exergonic Reactions
|
Give off energy
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Controlled breakdown of glucose to form ATP
|
|
|
Cellular metabolism
|
The sum of all controlled chemical reactions in cells
|
|
|
What does ATP shuttle within the cell?
|
Energy
|
|
|
What is ATP?
|
Adenosine triphosphate
|
|
|
Where is the energy stored in ATP?
|
Between the P bonds of the ATP molecule
|
|
|
How does ATP release energy?
|
Breaks P bonds
|
|
|
What does ATP become after it breaks off a P bond?
|
ADP= Adenosine diphosphate
|
|
|
How do cells control chemical reactions?
|
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions.
|
|
|
How do Enzymes promote chemical reactions?
|
They lower the energy of activation
|
|
|
Enzyme inhibitors
|
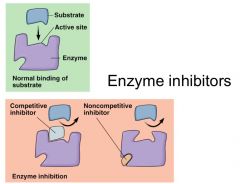
|
|
|
Energy coupling
|
Energy from exergonic are used to drive endergonic reactions
|
|
|
Efficiency of energy use
|
ratio of energy actually used to the total amount available at start
|
|
|
What efficency do cells have?
|
40%
|
|
|
Can cells access all of the energy of glucose?
|
No they must harvest it in small steps
|
|
|
Glycolysis
|
anaerobic
Glucose breakdown into pyruvic acid Occurs in cell cytoplasm |
|
|
Krebs Cycle
|
aerobic
Further breaksown of pyruvic acid derivative occurs in mitochondria |
|
|
Electron transport chain
|
anaerobic
In mitochondria |
|
|
What does Glycolysis start with?
|
1 molecule of glucose
|
|
|
How many intermediate steps are in glycolysis?
|
9
|
|
|
How many steps of glycolysis are endergonic and how many are exergonic?
|
4 are endergonic and 5 are exergonic
|
|
|
What does Glycolysis end with?
|
2 molecules of ATP
2 molecules of NADH 2 molecules of pyruvic acid |
|
|
What happens to the pyruvic acid from glycolysis?
|
2 molecules of pyruvic acid from glycolysis break down further in the mitochondria and the energy is then harvested in krebs cycle
|
|
|
Who is Krebs cycle named after?
|
Hans Krebs
|
|
|
What does Krebs cycle start with?
|
2 molecules of pyruvic acid derivative (Acetyl CoA)
|
|
|
How many intermediate steps does Krebs cycle have?
|
5
|
|
|
What does Krebs Cycle end with?
|
2 ATPs
6 NADH 2 FADH |
|
|
Krebs Cycle Diagram
|
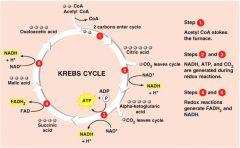
|
|
|
Electron transport chain
|
Last step of cellular respiration
occurs in mitochondria Starts with: NADH FADH2 Ends with: 32-34 ATPs |
|
|
Chemiosmosis
|
Major mechanism of ATP production
|
|
|
Anaerobic metabolism
|
metabolism without oxygen. involves fermentation
|
|
|
Fermentation produces
|
alcohol
lactic acids |
|
|
Polysaccharides are broken into what?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
What makes glucose in plants and animals?
|
Starch in plants
Glycogen in animals |
|
|
What are fats broken down into?
|
glycerol and fatty acids
|
|
|
What are proteins broken down into?
|
amino acids
|
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
making of new organic molecules
|

