![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two types of fermentation |
Lactic acid fermentation, fermentation in food such as cheese, yogurt, and bread |
|
|
What is fermentation? |
Another type of process that can occur to continue the breakdown of sugars |
|
|
Anaerobic v aerobic |
Anaerobic doesn't use oxygen, aerobic does, aerobic creates much more energy |
|
|
Where does the Krebs cycle take place |
The mitochondrial matrix |
|
|
Where does glycolysis occur |
The cytosol |
|
|
How many atp are created from the electron transport chain or cellular respiration? |
About 30 |
|
|
Glycolysis |
Splits glucose into 3-carbon molecules called pyruvate, produces 2 atp |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Transfers energy from pyruvate to electron transport chain, breaks down the 3-carbon molecules from glycolysis |
|
|
Electron transport chain |
Creates a large amount of atp to be used by the cell |
|
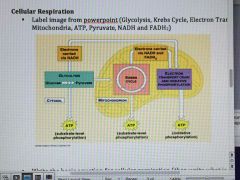
Memorize |
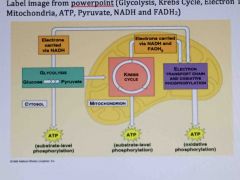
(Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, cytosol, mitochondria, atp, pyruvate, Nadh and fadh2) |
|
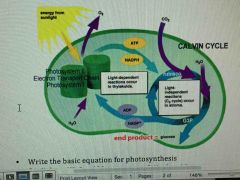
Know it |
Know it |
|
|
What comes in and out of cellular respiration |
Oxygen and sugar go in, water, carbon dioxide, and energy come out |
|
|
Where do light independent reactions take place? |
The stroma, the fluid outside the thykaloids |
|
|
What process in photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight and transfers it to electrons |
Light dependent reactions |
|
|
What goes in and out of photosynthesis? |
Sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide go in, oxygen and sugar come out |
|
|
Where do light dependent reactions take place? |
In the thylakoids |
|
|
Purpose of photosynthesis |
Make sugars with stored energy and become the food source for every living thing on the planet |
|
|
Where is chlorophyll and what is its purpose |
Chlorophyll is in the chloroplasts, and it's purpose is to absorb light energy and make energy carrier molecules |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
The conversion of solar energy into chemical energy |
|
|
How do hydrothermal vents sustain an ecosystem? |
They release superheated chemical rich water at the bottom of the ocean. |
|
|
What is the energy source of hydrothermal vents? |
Chemical energy |
|
|
Basis for the ecosystem of hydrothermal vents |
Bacteria |
|
|
How is energy released? |
A phosphate group is released from atp and it becomes adp |
|
|
What happens to the molecule after it is used? |
Adp recycles to atp when a new phosphate group is added |
|
|
What biomolecule is most commonly used to make atp? |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
What biomolecule is most commonly used to make atp? |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
Which biomolecule provides the most atp per molecule? |
Lipids |
|
|
What biomolecule is most commonly used to make atp? |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
Which biomolecule provides the most atp per molecule? |
Lipids |
|
|
Label atp |
Phosphate groups, sugar, base, atp, adp |

