![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
light microscope (LM) |
visible light is passed through a specimen 1000x magnification 2um distance of resolution |
|
|
Electron Microscope (EM) |
focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen or onto its surface. 100,000x magnification 2nm |
|
|
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) |
Uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a cell or other sample, which is usually coated with a thin film of gold. The beam excites electrons on the surface, and these electrons are then detected by a device that translates their pattern into an image projected onto a video screen. |
|
|
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) |
used to study the details of internal cell structure. Aims an electron beam through a very thin section of a specimen, just as a light microscope aims a beam of light through a specimen. The section is stained with atoms of heavy metals, which attach to certain cellular structures more than others. Electrons are scattered by these more dense parts, and the image is created by the pattern of transmitted electrons. |
|
|
Size scale |
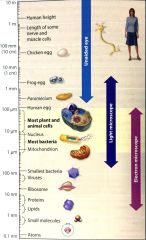
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane |
Forms a flexible boundary between the living cell and its surroundings. It would take a stack of more than 8,000 plasma membranes to equal the thickness of a thin piece of paper |
|
|
cytosol |
jelly like fluid in which cellular components of the cell are suspended |
|
|
Chromosomes |
all cells have one or more chromosomes, which carry genes made of DNA |
|
|
Ribosomes |
tiny structure that make proteins according to instructions from the genes. |
|
|
cytoplasm |
the inside of cells |
|
|
Fimbriae |
attachment structures on the surface of some prokaryotes |
|
|
Nucleoid |
region where the cell's DNA is located (not enclosed by a membrane) |
|
|
Cell Wall |
rigid structure outside the plasma membrane |
|
|
Capsule |
Jellylike outer coating of many prokaryotes |
|
|
Flagella |
Locomotion of some bacteria |
|
|
Bacterial Ribosomes |
Prokaryotic ribosomes differ somewhat from those of eukaryotic ribosomes. These molecular differences are the basis for the action of some antibiotics, such as Tetracycline and Streptomycin. Stops protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells but not eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
Cell Wall |
Protects the prokaryotic cell and helps it maintain its shape. Some antibiotics, such as Penicillin, prevent the formationof theseprotective walls. |
|
|
Organelles |
(little organs) |
|
|
Function of Nucleus and Ribosomes |
carry out the genetic control of the cell |
|
|
Function of Endoplasm Reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and peroxisomes |
involved in the manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules |
|
|
Function of Mitochondria in all cells and chloroplasts in plant cells |
Function in energy processing |
|
|
Functions of the Cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, and plant cell wall. |
structural support, movement, and communication between cells |
|
|
Cellular metabolism |
Many of the chemical activities of the cells. Many of the enzymes essential for metabolic processes are built into the membranes of organelles |
|
|
Organelles found in animal cells, but not plant cells |
Lysosomes, centrosomes, and flagella or cilia |
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
cytoplasmic channels through cell walls that connect adjacent cells. |

