![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Function Modifying, sorting and packaging of proteins for secretion(Found in Eukartotic cell) |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Function To regulate gene expression; It also controls cellular growth replication(found in Eukartotic cell) |
|
|
|
Nucleolus |
Function Rewrite ribosomal rebonucleic acid(RNa) and combine it with proteins(found in Eukayotic cell) |
|
|
|
Ribosome |
Function Synthesize(make) proteins for use throughout the cell(found in both prokaryotic and Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Function Produces protein and helps them fold properly (found in Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
Function Produces membrane phospholipids and breaks down harmful substances(found in Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Lysosome |
Function Breaks down worn out cell parts that are no longer functioning properly(found in Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Vacoule |
Function Maintain the proper pressure within the plant cells to provide structure and support for growing plant(found in Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Function Produce energy currency of the cell(found in Eukartotic cells) |
|
|
|
Chloroplast |
Function Convert light energy of the sun into sugars that can be used by cells(found in prokaryotic cells) |
|
|
|
Flagella/Cilia |
Function Help bacterium move towards nutrients away from toxic chemicals(found in prokaryotic cells) |
|
|
|
Fluid mosaic model |
Fluid tends to move more than solids |
|
|
|
Components of a cellular membrane |
1) phospholipids bilayer=building a wall 2) transmembrane protein=both hydrophilic and hydrophobic 3) interior protein network 4) cell surface markers=antigens |
|
|
|
Peripheral membrane |
Can move around(antigen) |
|
|
|
Integral membrane protein |
1)Spins the whole membrane 2)Can't move 3)Transmembrane domain needs to be hydrophobic |
|
|
|
Biological molecules |
Larger molecules constructed from smaller subunits Consist of 1)carbon bonded to carbon 2)carbon bonded to hydrogen |
|
|
|
Isomers |
Molecules with the same formula/sterile isomers |
|
|
|
Chirai |
Molecules are mirror images |
|
|
|
Trans |
Switching molecules/changes the reactor of the molecule |
|
|
|
Monomer |
Single subunit Mono=1 Mer= unit |
|
|
|
Polymer |
More than 1 subunit Poly=many units |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis Dehydration=loose water Synthesis=come together |
Molecules are made by removing water That's how you make fat, lipids(etc) |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Carbo=carbon Hydrates=water |
|
|
|
Molecules |
2:1 ratio 2 hydrogen for every oxygen Molecules=carbon |
|
|
|
Glucose=Monosacharide =C6H12O6 |
Monosacharide=single sugars containing 6 carbons example(high fructose corn syrup) |
|
|
|
Disacharide |
2 molecules and 2 Monosacharide Both make fructose, lactose sucrose |
|
|
|
Lactase |
Enzymes that help break down lactose |
|
|
|
Polysacharides |
Used for structural support Short term energy storage |
|
|
|
Chitin |
Fingernails-which are carbohydrates |
|
|
|
Amalose/starch |
Have straight molecules |
|
|
|
Glycogen |
Have branched molecules |
|
|
|
Plants |
Uses 2 monosacharides at a time |
|
|
|
Lipids(fats,oils,laxis) |
Long term energy storage Lipids=group of molecules that are insoluble in water Reason of insolubility in water=polarity of water/what attracts water molecules |
|
|
|
Structural formula |
Show the shape of a molecule Have long fatty acid chains Categories=triglycerides(fats) Phospholipids |
|
|
|
Covalent bonding |
Sharing of molecules(not equal sharing) |
|
|
|
O1 |
Deadly molecule that destroys other molecules Free oxygen |
|
|
|
Triglycerides(fats and oils) |
Stores twice as much energy as carbohydrates Made of 1 glycerol+3 fatty acids |
|
|
|
Fatty acids |
Long hydrocarbon chains with saturated or unsaturated fat |
|
|
|
Saturated(coconut oil) |
Full/as much as you can hold Tend to be solid at room temperature Single bond |
|
|
|
Unsaturated |
Have double bonds(easier to break) |
|
|
|
Polyunsaturated(olive oil,grape seed oil) |
Little double bonds |
|
|
|
Transfat |
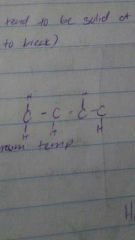
Unsaturated fat that is fliped |
|
|
|
Phospholipids |
3 building blocks=1 glycerol 2 fatty acids A phosphate group Form micolleles or lipid bilayer(fatty acids clump to each other) |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
Is used to anilect monomers into polymer and hydrolysis breaks them down Dehydration synthesis-remove hydroxide and oxygen Central carbon atom surrounded by 1)amino group 2)carboxyl group Single hydrose |
|
|
|
Enzyme catalysis |
Stresses covalent bonds |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that start reaction/speed up a reaction |
|
|
|
Antigens(example of protein) |
Protein markers found in cells |
|
|
|
Antibodies(example of protein) |
Things attached to antigens that clump together |
|
|
|
Transport |
Cell membrane carriers |
|
|
|
Signaling |
Signals cells that there is insulin |
|
|
|
Motion Regulation Storage |
Muscle cell contraction Hormones Usually irons |
|
|
|
Protein |
Stores iron and carries oxygen-hemoglobin Protein and polymers are amino acids 12 amino acids are found in you body(8 are naturally made while the 4 are eaten Joined by dehydration synthesis Shape of protein determines what it does |
|
|
|
Variable R group |
Important part of protein R/radical=change/determines what protein is going to do |
|
|
|
Non-polar |
Hydrophobic-hide from water |
|
|
|
Polar |
Hydrophilic/loves water/spreads protein out |
|
|
|
Charged |
Contains acids or bases that ionize |
|
|
|
Primary structure |
Sequence of Amino acids/order |
|
|
|
Secondary stucture |
Interaction of groups in the peptides backbone Starts reacting differently based what they have |
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
=weak attractions towards something positively charged Break easily at 104 degrees |
|
|
|
Alpha helix and beta sheets |
Allow a lot of things to happen in the cell membrane |
|
|
|
Disilolphite bonds |
Very sturdy |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Nonpolar molecules |
|
|
|
Exclusions |
Fairly stable |
|
|
|
Tertiary |
3d -smaller and quartianary Segment of lines fold/folded shape of polypeptide chain |
Chapter of a book |
|
|
Quartenary structure |
Multiple kind of same fold lines(multiple polypeptide subunits) |
Whole book |
|
|
Denaturation |
Change in the shape of a protein/causes the loss if function Caused by 1)changes in the protein environment 2)ph (pickled foods) 3)temperature 4)salt concentration |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
Chemicals that aren't consumed in a reaction but speeds up a reaction |
|
|
|
Catalase(breaks down hydrogen peroxide) |
Enzyme that's found in chemical reaction Hydrogen peroxide is produced naturally |
|
|
|
Types of inhibition |
Competitive-chemical is blocking the active site Allosteric-changing the shape or giving another shape Every chemical reaction has a different enzyme |
|
|
|
Chemical tag |
Pull on the chemical to lower its activation energy so that they can break apart |
|
|
|
Activation |
Adding something to an enzyme to actually make it work Types of activators 1)cofactor-small chemicals that are inorganic(not made of carbons) 2)coenzymes-organic ex thiamine(Vitamin B1) |
|
|
|
Competitive inhibitor |
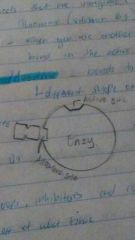
When you use another chemical to get that t bond in the active site(stops the substrate |
|
|
|
Thermodynamics |
The branch of chemistry concerned with energy changes |
|
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work Much of the work that living organism carry out involves transforming potential energy to kinetic energy Energy can take many forms 1)mechanical energy 2)heat. unit=kilocalories=1000calories 3)sound 4)electric current 5)light 6)radioactive radiation |
|
|
|
Kinetic energy |
Energy in motion |
|
|
|
Potential energy |
Stored energy |
|
|
|
Non competitive inhibitor/allosteric |

Bonds to the Allosteric site closes the active site |
|
|
|
Thermodynamic |
The branch of chemistry concerned with energy changes |
|
|
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work Much of the work that living organism carry out involves transforming potential energy to kinetic energy Energy can take many forms 1)mechanical 2)heat. Unit=kilocalories=1000calories 3) sound 4)electric current 5)light 6)radioactive radiation |
|
|
|
Oxidization |
An atom or molecule that loses an electron |
|
|
|
Reduction |
An atom or molecule that gains an electron The reduced form of a molecule has a high level of energy than the oxidized Oxidation and reduction always takes place together called oxidation_reduction |
|
|
|
Multi enzyme complex advantages |
Product of one reaction can directly be delivered to the next enzyme Function of enzyme can be affected by environment Molecules that trigger enzymes-vitamins/coenzymes-help shape protein to become enzymes |
|
|
|
Cell theory |
1) all organisms are compared of cells 2)cells are the smallest living things(viruses are not living things,they can be broken into small pieces and be put back together) 3)cells arise only from pre_existing cells |
|
|
|
Common structures of cells |
1)Genetic material-in a nucleoid or nucleus(DNA) 2)Cytoplasm-a semifluid matrix 3)Plasma |
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cells |
They lack a membrane bound nucleus Genetic material is present in the nucleoid Types of prokaryoted 1)archaea_bacteria in the cell line that resulted to us 2)bacteria-what we are scared of Prokaryotic cells posses 1)genetic material in the nucleoid 2)cytoplasm 3)plasma membrane 4)cell wall 5)ribosomes No membrane or bound organelles_little structures that have specific jobs |
|
|
|
Eukartotic cells |
Posses a membrane bound nucleus Are more complex that prokaryote Compartmentalize many cellular functions within organelles in the endomembrane system |
|
|
|
Endosymbiosis |
Proposal that Eukartotic organelles encolved through a symbiosis relationship/one benefits from the other) Inner membrane of mitochondria and chloroplast look like bacteria |
|
|
|
Synapse |
Space between 2 nerves |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement fro greater to lesser concentration 3 forms of molecular diffusion 1)passive transport_moves from high to low concentration 2)diffusion-molecules are slowly moving out/spread out 3)Semi permeable cell-only lets in a few molecules |
|
|
|
Function of a membrane |
Transporters protein that opens a door to transport Enzymes Cell surface receptors ex insulin receptor Cell surface identity marker El antigen Cell to cell adhesion protein(keeps you together) Attachment to the cytoskeleton |
|
|
|
Nerve |
Outside of the nerve is more positively charged than the inside of the nerve Its more positive because sodium/more positively charged than potassium(on the outside) and potassium/more potassium inside than outside(on the inside) are positively charged |
|
|
|
5 types of transportation in the cell |
Passive Facilitated Active Endosytosis Exosytosis |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water |
|
|
|
Selective permeable membrane |
Part of cell membrane that is impermeable |
|
|
|
Carrier protein |
Carries protein and moves them Can't be increased/no artificial increase/controlled by DNA |
|
|
|
Facilitate diffusion |
Going from high to low concentration ex peddling down a hill Uses carrier protein to get molecules across |
|
|
|
Tonic |
Stuff that's in the water/not water/doesn't move very fast) |
|
|
|
Hpertonic |
A lot of stuffing the water/water surrounding your cells |
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
Things left in your water/water surrounding your cells |
|
|
|
Phosphate |
Polar/negative charge |
|
|
|
Endosytosis |
Moving things into the cell |
|
|
|
Exosytosis |
Moving things/substance out of the cell |
|
|
|
Antigen presenting cells |
When one cell is sending a message to the other Sent the shape and then pass that off to make antibodies |
|
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
Send message from cell to cell |
|
|
|
Short distant cell |
Neuron connected to another neuron through a synapse Can send a neurotransmitter to make sure message gets across |
|
|
|
Long distant |
Growth hormone can send to multiple cells |
|
|
|
CD4 |
Protein of the surface of the antigen to its surface helper t cells |
|
|
|
Cues |
Transcript factors=protein or chemical that'll cause a Dna to make a transcript if itself/make messenger RNa |
|
|
|
Building block of protein |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
Building blocks of carbohydrates Glycogen comes from carbohydrates |
Monosacharides |
|
|
|
Building blocks of lypids |
Glycerol and fatty acids |
|
|
|
Building blocks of starch |
Monosacharides |
|
|
|
Protein |
Makes living tissue |
|
|
|
Microtubules |
Makes up the cytoskeleton |
|

