![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The smallest basic unit of matter |
atom |
|
|
substance made of only one type of Adam that cannot be broken down by chemical elements |
Element |
|
|
substance made of Adams of different elements that are bonded together in a particular ratio |
compound |
|
|
Adam that has gained or lost one or more electrons |
Ion |
|
|
Chemical bond formed for the electrical force between oppositely charged ions |
ionic bond |
|
|
Chemical bond formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons |
covalent bond |
|
|
two or more Adams held together by a covalent bond not necessarily a compound |
molecule |
|
|
attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen Atom and I slightly negative Atom |
hydrogen bond |
|
|
attraction between molecules of the same substance |
cohesion |
|
|
attraction between molecules of different substances |
adhesion |
|
|
mixture that is consistent throughout also called a homeogeneus mixture |
solution |
|
|
substance in which solutes dissolve and that is present and greatest concentration in a solution |
solvent |
|
|
substance that dissolves in a solvent and his present at a lower concentration then the solvent |
Solute |
|
|
compound that donates a proton(h+) when dissolved in a solvent |
acid |
|
|
compound that accepts a proton (h+)when dissolved insulation |
base |
|
|
measurement of acidity related to free hydrogen ion concentration in a solution |
pH |
|
|
A molecular subunit of a polymer |
monomer |
|
|
large carbon-based molecules formed by monomers |
polymer |
|
|
molecule composed of carbon hydrogen and oxygen includes sugars and starches |
carbohydrate |
|
|
Nonpolar molecule composed of carbon hydrogen and oxygen and includes fats and oils |
lipid |
|
|
fatty acid polymer composed of amino acids linked together by hippity bonds folds into our particular structure depending on bonds between amino acids |
protein |
|
|
molecule that makes up proteins composed of carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen and sometimes sulfur |
amino acid |
|
|
polymer of nucleotides ; the genetic material of organisms |
nucleic acid |
|
|
process by which substances changed into different substances through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds |
Chemical reaction |
|
|
substance that is changed by a chemical reaction |
reactant |
|
|
substance formed by a chemical reaction |
product |
|
|
amounts of energy needed to break a bond between two particular Atoms ; or the amount of energy released when a bond forms between two particular Atoms |
Bond energy |
|
|
condition in which reactants and products of a chemical reaction are formed at the same rate |
equilibrium |
|
|
Energy input necessary to initiate a chemical reaction |
activation energy |
|
|
Chemical reaction that yields a net release of energy in the form of heat |
exothermic |
|
|
Chemical reaction that requires a net input of energy |
endothermic |
|
|
substance that decreases activation energy and increase reaction rate in a chemical reaction |
catalyst |
|
|
protein that catalyzes chemical reactions for organisms |
enzyme |
|
|
reactants in the chemical reaction upon which it enzyme acts |
substrate |
|
|
A carbon Atom has how many electrons available for bonding in its outer energy level |
4 |
|
|
simplest type of carbohydrate; simple sugar or glucose |
monosaccharide( monomer) |
|
|
two monosaccharide molecules combined together; table sugar; sucrose |
disaccharide |
|
|
largest carbohydrate; composed of many monosaccharide subunits |
Polysaccharide |
|
|
subunit of polysaccharide; used as a energy storage by plant cells in the food reservoirs in seeds and bulbs |
starch |
|
|
subunit of polysaccharide ; memo store energy in the liver; broken down to glucose |
glycogen |
|
|
subunit of a polysaccharide; forms the cell walls of plants and supports plants |
cellulose |
|
|
fats oils and waxes and steroids |
lipids; polymer |
|
|
used for energy storage insulation and protective covering |
lipids |
|
|
insoluble in water |
lipids |
|
|
consist of three fatty acid's linked with one molecule of glycerol as the monomer |
lipid |
|
|
compounds that have The same chemical formula but different three-dimensional structures are |
Isomer |
|
|
A saturated fat lipid is from |
animals |
|
|
unsaturated and polyunsaturated lipids are from |
plants |
|
|
Chemical structure of proteins |
chons |
|
|
composed of carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen and sometimes sulfur |
protein |
|
|
has about 20 amino acids as the monomer |
proteins |
|
|
peptide bond bonds are covalent bonds formed between |
amino acids (protein) |
|
|
important in contracting of muscle tissue transporting oxygen in the bloodstream providing immunity regulating other proteins and carrying out chemical reactions |
proteins |
|
|
this polymer changes the rate of a chemical reaction |
protein |
|
|
this polymer speeds the reaction in the digestion of food |
proteins |
|
|
made of smaller subunits called neclutides |
nucleic acid |
|
|
carbon compounds that come from living organisms |
organic compounds(carbon) |
|
|
The monomer of nucleic acid |
nucleotides |
|
|
consists of carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen and phosphorus Atoms arranged in three groups |
neclutides |
|
|
blank is made of nitrogenous base a simple sugar and a phosphate group |
neclutides |
|
|
DNA and rna samples of |
nucleic acid |
|
|
large organic compounds are called |
biomolecules or a polymer |
|
|
many polymers are formed by chemical reaction known as |
condensation(made) |
|
|
polymers are broken apart by |
hydrolysis |
|
|
four biomolecules |
carbohydrate lipid protein nucleic acid(polymer) |
|
|
carbohydrates are what chemical structure |
cho |
|
|
carbohydrates are composed of |
carbon hydrogen and oxygen |
|
|
carbohydrates are used by cells to |
provide energy |
|
|
saturated fat has what kind of bond |
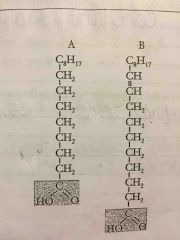
Single bond |
|
|
unsaturated fat has what kind of bond |
double bonds |

